Infantilization in relationships undermines autonomy by treating a partner as incapable, while micromanagement controls every detail, stifling independence and trust. Explore this article to understand how these behaviors affect partnership dynamics and ways to foster mutual respect.
Table of Comparison
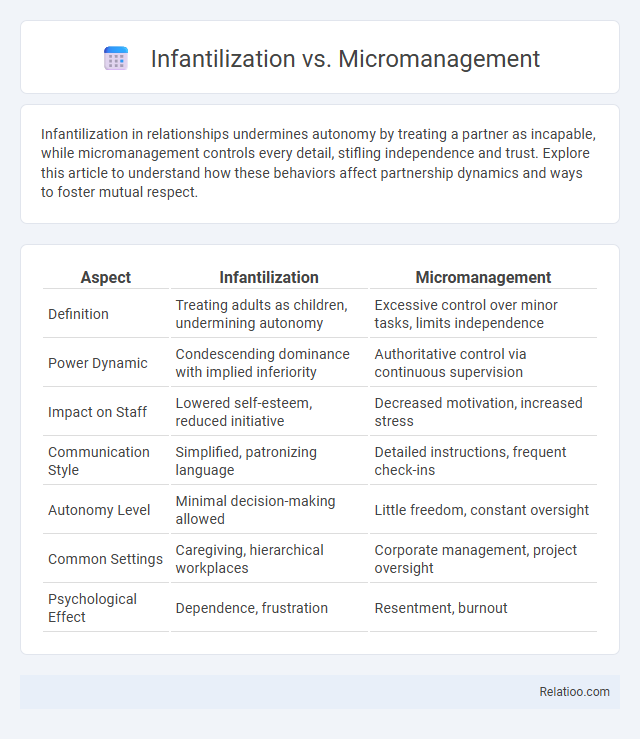
| Aspect | Infantilization | Micromanagement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Treating adults as children, undermining autonomy | Excessive control over minor tasks, limits independence |
| Power Dynamic | Condescending dominance with implied inferiority | Authoritative control via continuous supervision |
| Impact on Staff | Lowered self-esteem, reduced initiative | Decreased motivation, increased stress |
| Communication Style | Simplified, patronizing language | Detailed instructions, frequent check-ins |
| Autonomy Level | Minimal decision-making allowed | Little freedom, constant oversight |
| Common Settings | Caregiving, hierarchical workplaces | Corporate management, project oversight |
| Psychological Effect | Dependence, frustration | Resentment, burnout |
Understanding Infantilization in the Workplace
Understanding infantilization in the workplace involves recognizing behaviors that undermine an employee's autonomy by treating them as incapable or less competent than they are. Infantilization differs from micromanagement, which focuses on excessive control over tasks, whereas infantilization targets a person's overall sense of agency and decision-making capacity. Addressing infantilization requires fostering a culture of trust and respect to empower employees and promote professional growth.
Defining Micromanagement: Key Characteristics
Micromanagement involves excessive control and scrutiny over an employee's work, characterized by constant oversight, lack of delegation, and undermining autonomy. It differs from infantilization and infantalization, which relate more to treating adults as children beyond just workplace control. Key traits of micromanagement include detailed instructions, frequent check-ins, and reluctance to trust employees' judgment or competence.
Core Differences Between Infantilization and Micromanagement
Infantilization involves treating someone as if they are incapable of independent thought or decision-making, often undermining their autonomy and self-confidence, while micromanagement refers to excessively controlling or overseeing detailed aspects of tasks or projects, limiting an individual's freedom to execute work effectively. The core difference between infantilization and micromanagement lies in intent: infantilization diminishes a person's perceived competence, whereas micromanagement focuses on control over processes and outcomes. Your ability to recognize these distinctions can help foster healthier workplace dynamics and improve personal empowerment.
Psychological Impacts on Employees
Infantilization and infantalization involve treating employees as incapable or overly dependent, leading to reduced self-esteem and autonomy, which negatively affects motivation and job satisfaction. Micromanagement exacerbates stress and anxiety by limiting employees' control over their work and undermining trust, often resulting in decreased productivity and increased burnout. These behaviors collectively disrupt workplace dynamics, impairing psychological well-being and diminishing overall organizational performance.
Warning Signs of Infantilizing Leadership
Warning signs of infantilizing leadership include excessive control over minor decisions, persistent over-involvement in employees' tasks, and undermining their autonomy and confidence. Micromanagement often manifests through constant monitoring and detailed instructions, while infantilization shows in patronizing communication and treating adults as incapable or dependent. Recognizing these behaviors is crucial to fostering a healthy workplace that encourages trust, independence, and professional growth.
How Micromanagement Manifests in Teams
Micromanagement manifests in teams through excessive scrutiny of tasks, constant monitoring, and unwillingness to delegate authority, which undermines employees' autonomy and stifles creativity. Your team members may feel undervalued and demotivated when every minor decision requires approval, leading to decreased productivity and increased stress. Recognizing these behaviors helps distinguish micromanagement from infantilization and infantalization, ensuring healthier team dynamics and fostering trust.
The Consequences for Organizational Culture
Infantilization and micromanagement severely undermine organizational culture by eroding employee autonomy and trust, leading to decreased motivation and innovation. When leaders treat employees as incapable or overly control their work, it fosters resentment and stifles creativity, harming team collaboration. Your organization's culture thrives when empowerment replaces infantilization and micromanagement, promoting engagement and sustained performance.
Strategies to Prevent Infantilization
Preventing infantilization requires implementing strategies that promote autonomy, such as encouraging decision-making and respecting individual competence in both personal and professional contexts. Clear communication and setting appropriate boundaries help You avoid micromanagement tendencies that undermine confidence and growth. Empowerment through skill development and acknowledging achievements fosters a balanced relationship free from infantilization.
Approaches to Minimize Micromanagement
Micromanagement can be minimized by fostering a culture of trust and autonomy, where managers provide clear goals and resources but allow employees to execute tasks independently. Implementing regular, constructive feedback sessions helps identify challenges early without intrusive oversight, promoting empowerment rather than control. Emphasizing skill development and open communication channels reduces infantilization by encouraging responsibility and mature decision-making.
Fostering Autonomy and Employee Empowerment
Micromanagement and infantilization both undermine employee empowerment by limiting autonomy and restricting decision-making capabilities, often leading to decreased motivation and productivity. Infantilization, sometimes confused with infantalization, involves treating employees as if they lack competence, impeding their growth and self-confidence, whereas fostering autonomy encourages skill development, innovation, and accountability. By recognizing and avoiding these detrimental management styles, you can create a work environment that promotes trust, independence, and empowered team members.
Infographic: Infantilization vs Micromanagement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com