Infantilization in relationships undermines autonomy by treating partners as incapable, while empowerment fosters mutual respect and personal growth. Discover effective strategies to nurture empowerment and avoid infantilization in this article.
Table of Comparison
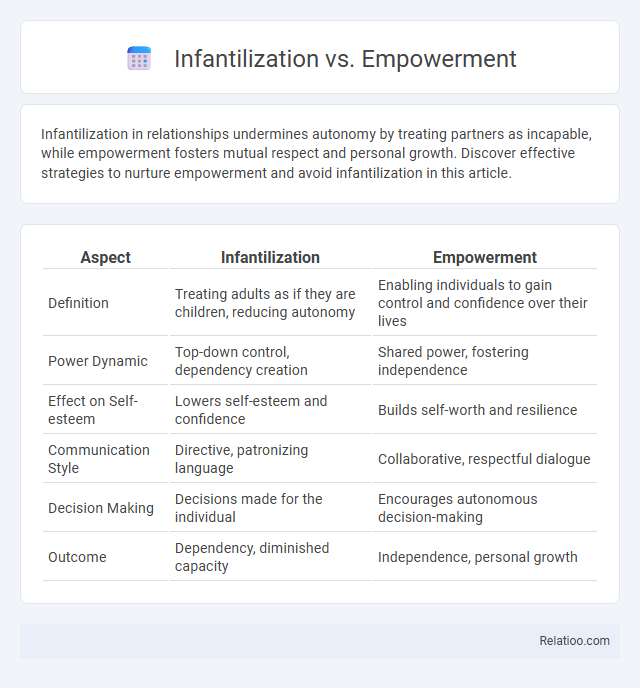
| Aspect | Infantilization | Empowerment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Treating adults as if they are children, reducing autonomy | Enabling individuals to gain control and confidence over their lives |
| Power Dynamic | Top-down control, dependency creation | Shared power, fostering independence |
| Effect on Self-esteem | Lowers self-esteem and confidence | Builds self-worth and resilience |
| Communication Style | Directive, patronizing language | Collaborative, respectful dialogue |
| Decision Making | Decisions made for the individual | Encourages autonomous decision-making |
| Outcome | Dependency, diminished capacity | Independence, personal growth |
Understanding Infantilization: Definition and Origins
Infantilization refers to the treatment of adults as if they are incapable or childlike, often undermining their autonomy and competence. Its origins lie in social and psychological contexts where power dynamics lead to belittling behaviors, frequently observed in caregiving, education, and workplace environments. Understanding infantilization helps you recognize and challenge behaviors that diminish individual empowerment and promote respect for adult agency.
Empowerment Explained: Key Concepts and Principles
Empowerment involves enabling Your personal growth by fostering autonomy, self-confidence, and decision-making capabilities. Key principles include promoting self-efficacy, encouraging active participation, and providing access to resources and opportunities. Unlike infantilization or infantalization, which diminish independence by treating individuals as incapable, empowerment supports Your ability to control and influence life outcomes.
Key Differences Between Infantilization and Empowerment
Infantilization involves treating adults as if they lack independence or competence, often resulting in reduced autonomy and self-confidence. Empowerment, in contrast, promotes self-efficacy by encouraging decision-making, access to resources, and the development of personal strengths. Your ability to recognize these key differences is crucial for fostering respectful, supportive interactions that enhance individual growth rather than limit it.
Psychological Effects of Infantilization
Infantilization involves treating adults as if they are children, which undermines autonomy and can lead to feelings of helplessness and low self-esteem. This psychological effect differs from empowerment, which fosters confidence and independence by recognizing an individual's capabilities. Your mental health may suffer if infantilization persists, causing increased stress, anxiety, and diminished motivation to engage in decision-making or personal growth.
How Empowerment Boosts Confidence and Autonomy
Empowerment enhances Your confidence by encouraging decision-making and fostering a sense of control over personal choices, contrasting sharply with infantilization, which undermines independence by treating adults as incapable. Unlike infantalization, which diminishes autonomy through overprotection and patronizing behavior, empowerment cultivates skills and self-efficacy that promote growth and self-reliance. This boost in autonomy through empowerment leads to improved mental well-being and the ability to navigate challenges effectively.
Infantilization in Society: Common Examples
Infantilization in society often appears through patronizing behaviors, such as speaking to adults as if they were children or making decisions on their behalf without consent. You may encounter this in workplace environments where employees are overly supervised or denied autonomy, and in caregiving contexts where independence is unnecessarily restricted. These common examples demonstrate how infantilization undermines personal empowerment and stifles growth.
Empowerment Strategies in Education and the Workplace
Empowerment strategies in education and the workplace center on fostering autonomy, critical thinking, and skill development to enable individuals to make informed decisions and take control of their own growth. Techniques such as participatory learning, collaborative problem-solving, and providing access to resources and mentorship contribute to building confidence and competence. These approaches counteract infantilization by promoting agency and valuing the individual's contributions, leading to increased motivation and productivity.
Recognizing Infantilizing Behaviors and Attitudes
Recognizing infantilizing behaviors involves identifying actions and attitudes that undermine an individual's autonomy by treating them as incapable or overly dependent, often seen in excessive control or dismissive communication. Empowerment fosters independence and self-efficacy, encouraging decision-making and validating personal strengths, which contrasts sharply with infantilization's tendency to diminish confidence and perpetuate dependency. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in settings such as healthcare, education, and caregiving, where promoting respect and autonomy directly impacts psychological well-being and development.
Overcoming Infantilization: Steps Toward Personal Empowerment
Overcoming infantilization involves recognizing and rejecting behaviors that diminish your autonomy and self-confidence. Empowerment grows through setting clear boundaries, cultivating self-awareness, and developing decision-making skills that affirm your independence. Consistent practice of these steps helps dismantle infantalization patterns, fostering a stronger sense of personal agency and resilience.
Building a Culture of Empowerment: Best Practices
Building a culture of empowerment involves fostering trust, encouraging autonomy, and providing opportunities for skill development, which contrasts sharply with infantilization or infantalization that undermine individual capabilities. Empowerment thrives in environments where leaders actively listen, delegate meaningful responsibilities, and recognize achievements, promoting confidence and growth among team members. Your leadership approach can shift organizational dynamics by prioritizing respect and support over control, ensuring that every person feels valued and capable.
Infographic: Infantilization vs Empowerment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com