Internal oversight involves monitoring and evaluating organizational processes from within, enhancing compliance and operational efficiency. External oversight provides independent assessment and accountability, ensuring transparency and trust; discover more about their distinct roles and impacts in this article.
Table of Comparison
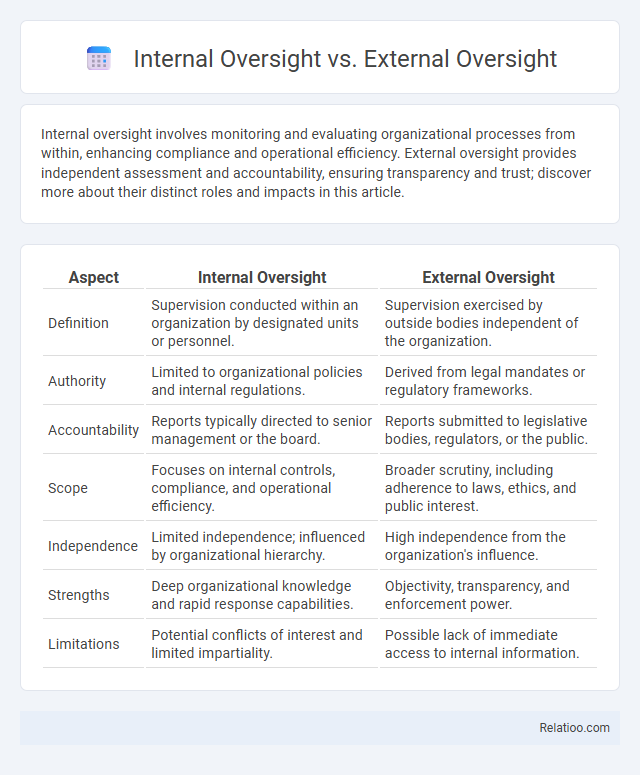
| Aspect | Internal Oversight | External Oversight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supervision conducted within an organization by designated units or personnel. | Supervision exercised by outside bodies independent of the organization. |
| Authority | Limited to organizational policies and internal regulations. | Derived from legal mandates or regulatory frameworks. |
| Accountability | Reports typically directed to senior management or the board. | Reports submitted to legislative bodies, regulators, or the public. |
| Scope | Focuses on internal controls, compliance, and operational efficiency. | Broader scrutiny, including adherence to laws, ethics, and public interest. |
| Independence | Limited independence; influenced by organizational hierarchy. | High independence from the organization's influence. |
| Strengths | Deep organizational knowledge and rapid response capabilities. | Objectivity, transparency, and enforcement power. |
| Limitations | Potential conflicts of interest and limited impartiality. | Possible lack of immediate access to internal information. |
Understanding Internal Oversight
Internal oversight involves systematic monitoring and evaluation conducted within an organization to ensure compliance, risk management, and operational efficiency. It empowers you to proactively identify process weaknesses and implement corrective actions without external intervention. Unlike external oversight, internal oversight is continuous, closely tied to organizational culture, and integral to governance frameworks.
Defining External Oversight
External oversight refers to the monitoring and evaluation conducted by independent bodies outside an organization to ensure compliance, accountability, and transparency. It contrasts with internal oversight, which is performed by internal teams focused on self-regulation and process improvement within the organization. Understanding external oversight helps you identify how third-party audits, regulatory agencies, and watchdog groups enforce standards and protect stakeholder interests.
Key Differences between Internal and External Oversight
Internal oversight involves monitoring and evaluation conducted within an organization, focusing on compliance, risk management, and process improvement using internal audits and reviews. External oversight is performed by independent entities or regulatory bodies to ensure accountability, transparency, and adherence to laws or standards, often involving external audits and investigations. You must understand these key differences to effectively balance internal controls with external accountability mechanisms.
Objectives and Functions of Internal Oversight
Internal oversight primarily aims to enhance organizational efficiency, ensure compliance with laws and policies, and safeguard assets by conducting regular audits, risk assessments, and performance evaluations. External oversight involves independent bodies or regulators assessing organizational accountability and transparency, often through external audits or investigations. Your internal oversight functions create early detection of irregularities and promote continual improvement within the organization, complementing the broader scope of external oversight mechanisms.
Roles and Responsibilities in External Oversight
External oversight holds the critical role of independently monitoring and evaluating an organization's adherence to laws, regulations, and standards, ensuring accountability beyond internal controls. Its responsibilities include conducting audits, investigations, and compliance reviews to protect public interest and promote transparency. Your organization benefits from this external scrutiny by gaining objective assessments that help mitigate risks and foster trust among stakeholders.
Advantages of Internal Oversight Mechanisms
Internal oversight mechanisms provide organizations with continuous monitoring and immediate corrective actions, enhancing operational efficiency and compliance. These mechanisms leverage insider knowledge, enabling proactive identification of risks and fostering a culture of accountability. By maintaining direct control over processes, internal oversight reduces dependency on external audits and minimizes response time to internal issues.
Benefits of External Oversight Bodies
External oversight bodies enhance transparency and accountability by providing unbiased evaluations independent from the organization's internal interests. These entities bring specialized expertise and enforce regulatory compliance, reducing risks of fraud, corruption, and mismanagement more effectively than internal oversight alone. Their objective assessments foster public trust and improve organizational performance through consistent monitoring and enforcement of standards.
Challenges Faced by Internal Oversight
Internal oversight faces challenges such as limited resources, potential bias due to proximity to the organization, and difficulties maintaining independence and objectivity during evaluations. External oversight provides a more unbiased perspective but may lack detailed organizational insight or timely access to information. Your organization benefits from balancing internal oversight's deep contextual knowledge with external oversight's impartiality to ensure comprehensive accountability.
Limitations of External Oversight
External oversight often faces limitations such as reduced access to sensitive internal information and delayed response times due to bureaucratic processes. Unlike internal oversight, which can conduct continuous, real-time monitoring and direct interventions, external bodies typically rely on periodic reviews and public reports, limiting their ability to enforce immediate corrective actions. These constraints can hinder the effectiveness of external oversight in ensuring comprehensive accountability and timely risk mitigation within organizations.
Best Practices for Integrating Oversight Approaches
Integrating internal oversight, external oversight, and general oversight requires establishing clear roles and communication channels to ensure comprehensive accountability and transparency within organizations. Best practices emphasize leveraging internal oversight for ongoing risk management and operational controls, while external oversight provides independent audits and compliance verification to enhance credibility. Coordinated oversight frameworks optimize resource use, minimize duplication, and promote continuous improvement by aligning internal audits, regulatory reviews, and stakeholder monitoring.
Infographic: Internal Oversight vs External Oversight
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com