Hard Power relies on military force and economic sanctions to influence other nations, while Soft Power leverages cultural appeal and diplomacy for persuasion. Discover in this article how combining these strategies shapes global relationships effectively.
Table of Comparison
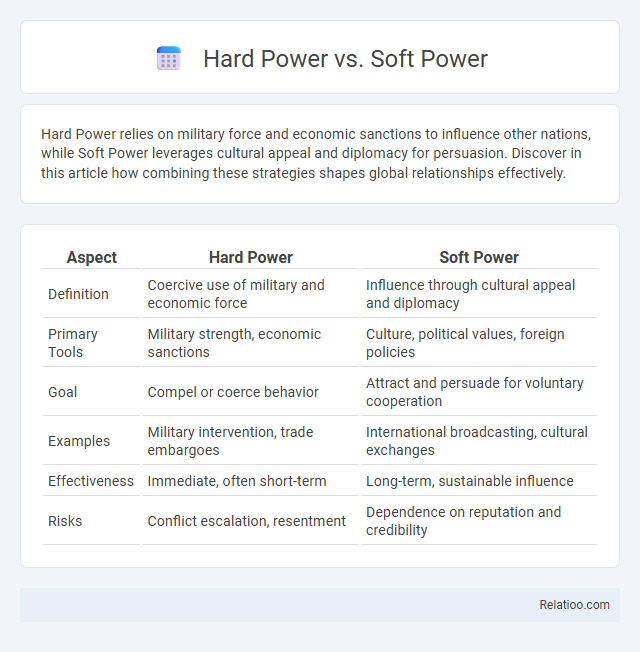
| Aspect | Hard Power | Soft Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coercive use of military and economic force | Influence through cultural appeal and diplomacy |
| Primary Tools | Military strength, economic sanctions | Culture, political values, foreign policies |
| Goal | Compel or coerce behavior | Attract and persuade for voluntary cooperation |
| Examples | Military intervention, trade embargoes | International broadcasting, cultural exchanges |
| Effectiveness | Immediate, often short-term | Long-term, sustainable influence |
| Risks | Conflict escalation, resentment | Dependence on reputation and credibility |
Understanding Hard Power and Soft Power
Hard power relies on military force and economic sanctions to influence other nations, while soft power uses cultural appeal, diplomacy, and ideological attraction to shape preferences. Understanding the distinction between hard power and soft power reveals how states balance coercion and persuasion to achieve strategic objectives. Competitive dynamics emerge as countries leverage both types of power, calibrating their strategies to gain geopolitical advantage and foster cooperation when beneficial.
Historical Origins of Hard and Soft Power
Hard power originates from traditional state-centric paradigms of military and economic coercion, rooted in the realist theories of international relations prominent during the Cold War. Soft power, conceptualized by Joseph Nye in the late 20th century, emerged as an essential complement emphasizing cultural influence, diplomacy, and institutional appeal without force or payment. The competitive dynamic between hard and soft power reflects the evolving strategies states use to assert influence, balancing coercion and attraction to achieve geopolitical objectives.
Key Differences Between Hard and Soft Power
Hard power relies on military force and economic sanctions to influence others, emphasizing coercion and tangible assets, whereas soft power uses cultural appeal, diplomacy, and ideological attraction to shape preferences and build alliances. You must understand that hard power is often fast-acting but can provoke resistance, while soft power works gradually by fostering goodwill and legitimacy. Competitive dynamics involve the strategic balance between these two approaches, where nations leverage both to maximize influence in global affairs.
Examples of Hard Power in International Relations
Hard power in international relations consists of military intervention, economic sanctions, and coercive diplomacy, as exemplified by the United States' military invasion of Iraq in 2003 and China's use of economic leverage over Taiwan through trade restrictions. Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014 illustrates the use of military force to alter territorial boundaries and influence geopolitical balance. These examples highlight how hard power directly imposes a nation's will through force or pressure, contrasting with the persuasion and attraction inherent in soft power strategies.
Instances of Soft Power in Global Affairs
Soft power in global affairs manifests through cultural diplomacy, international aid, and educational exchanges that shape global perceptions and foster cooperation without coercion. Countries like Japan utilize soft power by exporting culture and technology, while organizations such as the United Nations promote peace through dialogue and humanitarian efforts. Your understanding of these instances highlights how influence extends beyond military strength, relying on attraction and persuasion to achieve foreign policy goals.
The Role of Hard Power in Modern Diplomacy
Hard power remains a crucial element in modern diplomacy, utilizing military force, economic sanctions, and coercive measures to influence state behavior and secure national interests. Your understanding of this dynamic highlights how tangible assets and capabilities often establish leverage and deterrence in international relations. Despite the rise of soft power and competitive dynamics, hard power's role is indispensable for enforcing policies and maintaining geopolitical stability.
The Impact of Soft Power on Global Influence
Soft power, derived from cultural appeal, diplomacy, and value-based attraction, significantly shapes global influence by fostering cooperation and building long-term alliances. Unlike hard power, which relies on military or economic coercion, soft power enhances a nation's image and legitimacy on the international stage, leading to more sustainable diplomatic relationships. The competitive dynamic between nations increasingly favors soft power, as countries leverage cultural exports, education, and foreign aid to subtly shift global perceptions and achieve strategic objectives without armed conflict.
Balancing Hard Power and Soft Power Strategies
Balancing hard power and soft power strategies involves integrating military strength, economic influence, and diplomatic appeal to achieve national objectives effectively. Hard power relies on coercion through defense capabilities or economic sanctions, while soft power emphasizes cultural diplomacy and policy attractiveness to shape global perceptions. Successful competitive dynamics emerge when nations skillfully combine coercive tools with persuasive tactics, fostering resilience in international relations and sustainable strategic advantages.
Challenges in Implementing Hard and Soft Power
Implementing hard power faces challenges such as military overreach, high economic costs, and potential international backlash that can undermine long-term strategic goals. Soft power struggles with issues like cultural misunderstandings, inconsistent messaging, and the slow pace of influence-building in global diplomacy. The competitive dynamic between hard and soft power complicates statecraft, requiring careful balancing to avoid escalating conflicts or diminishing credibility on the world stage.
The Future of Power Dynamics in a Changing World
Hard power relies on military strength and economic sanctions to influence other nations, while soft power uses cultural influence, diplomacy, and values to achieve goals. Competitive dynamics shape the future of power by blending these strategies with technological innovation and information control, creating a more complex geopolitical landscape. Your understanding of emerging power dynamics must adapt to recognize hybrid approaches and the increasing importance of cyber capabilities.
Infographic: Hard Power vs Soft Power
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com