Power dynamics in relationships often create imbalance, where one partner controls decision-making and the other feels powerless, leading to emotional distress and diminished trust. Discover effective strategies to navigate and restore balance in power struggles within relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
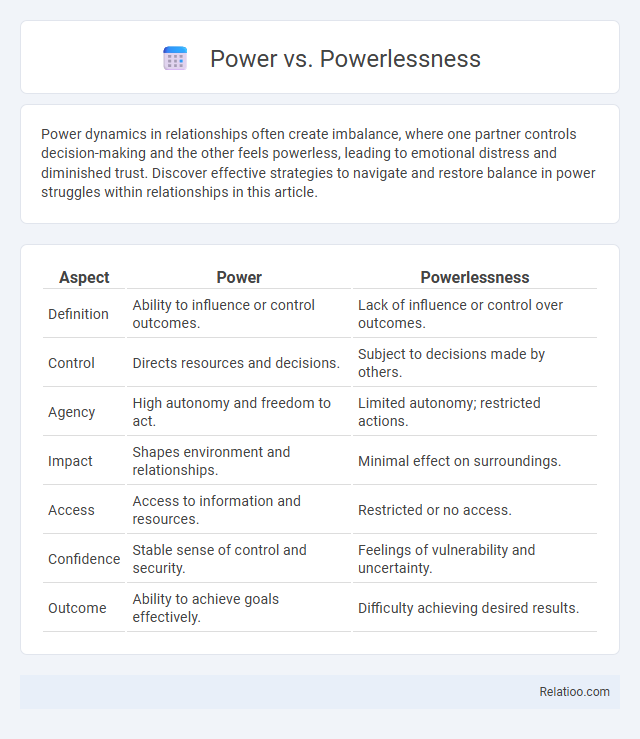
| Aspect | Power | Powerlessness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to influence or control outcomes. | Lack of influence or control over outcomes. |
| Control | Directs resources and decisions. | Subject to decisions made by others. |
| Agency | High autonomy and freedom to act. | Limited autonomy; restricted actions. |
| Impact | Shapes environment and relationships. | Minimal effect on surroundings. |
| Access | Access to information and resources. | Restricted or no access. |
| Confidence | Stable sense of control and security. | Feelings of vulnerability and uncertainty. |
| Outcome | Ability to achieve goals effectively. | Difficulty achieving desired results. |
Understanding the Dynamics of Power and Powerlessness
Understanding the dynamics of power and powerlessness involves recognizing how authority and control shape social relationships and individual experiences. Power manifests through social structures, access to resources, and decision-making capabilities, while powerlessness results from exclusion, marginalization, and lack of agency. Your awareness of these forces enables you to navigate systems of oppression and advocate for equity and justice effectively.
Historical Perspectives on Power Struggles
Historical perspectives on power struggles reveal how power dynamics shape societies through cycles of dominance and resistance. Epic battles for control, from feudal lords to colonial empires, illustrate the persistent tension between power and powerlessness that fuels social hierarchies and systemic oppression. Your understanding of history deepens by recognizing these patterns of struggle as foundational to the evolution of political and social orders.
Psychological Effects of Power and Powerlessness
Power significantly influences psychological well-being by enhancing individuals' sense of control, self-efficacy, and motivation, which can promote resilience and positive mental health outcomes. Conversely, powerlessness often leads to feelings of helplessness, decreased self-esteem, and increased stress, contributing to anxiety, depression, and learned helplessness. Your experience of oppression can exacerbate these psychological effects, embedding chronic stress and internalized negative beliefs that impair cognitive functioning and emotional regulation.
Social Structures and the Distribution of Power
Social structures shape the distribution of power by creating systems that either empower or marginalize individuals and groups within society. Power is often concentrated in institutions and social hierarchies, leading to oppression when certain populations are systematically excluded from resources, rights, and decision-making processes. Understanding how your position within these structures influences access to power is crucial for addressing inequalities and fostering social justice.
The Role of Authority in Shaping Power Relations
Authority serves as the structural foundation that defines and enforces power relations within societies, legitimizing certain actors' control while marginalizing others. Through institutional frameworks and social norms, authority shapes access to resources, decision-making, and freedom, thereby reinforcing power imbalances and facilitating systems of oppression. The interplay between authority and power underscores the mechanisms by which dominance is maintained and contested in political and social contexts.
Powerlessness: Roots, Manifestations, and Consequences
Powerlessness stems from systemic inequalities, lack of access to resources, and social exclusion, often rooted in historical marginalization and institutional discrimination. It manifests through limited autonomy, diminished voice in decision-making processes, and vulnerability to exploitation and abuse. Consequences of powerlessness include decreased mental and physical health, perpetuation of poverty cycles, and entrenched social disparities that hinder individual and community development.
Empowerment: Pathways from Powerlessness to Power
Empowerment transforms powerlessness by equipping individuals with resources, knowledge, and agency needed to challenge oppression and claim autonomy. Your active participation in community-building, education, and advocacy creates pathways to dismantle systemic barriers and foster social equity. By harnessing collective power, marginalized groups can redefine narratives and achieve sustainable change.
Power in Personal Relationships: Balance and Imbalance
Power in personal relationships is defined by the ability to influence or control decisions, behaviors, and emotional dynamics between partners, often manifesting through communication patterns, resource control, or emotional support. Imbalance in this power dynamic can lead to feelings of dominance, submission, and ultimately contribute to emotional distress or oppression within the relationship. Understanding your role in maintaining or challenging these power structures is essential for fostering mutual respect, equality, and healthy relational growth.
Power and Powerlessness in the Workplace
Power in the workplace governs decision-making authority, resource allocation, and influence over team dynamics, affecting employee motivation and productivity. Powerlessness often manifests through limited access to information, minimal control over tasks, and exclusion from critical conversations, leading to decreased job satisfaction and engagement. Recognizing these dynamics is essential for fostering equitable environments where all employees can contribute meaningfully and feel valued.
Strategies to Overcome Powerlessness and Build Resilience
You can overcome powerlessness by developing strong social networks and seeking supportive communities that share your goals and values. Building resilience involves cultivating self-efficacy through skill development and engaging in collective action to challenge oppressive structures. Empowerment strategies such as education, advocacy, and access to resources reinforce your ability to create meaningful change despite systemic barriers.
Infographic: Power vs Powerlessness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com