Legitimate power derives from formal authority granted by an organization, while referent power stems from personal charisma and the ability to inspire trust and admiration in others. Explore the distinctions and impacts of these power types on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
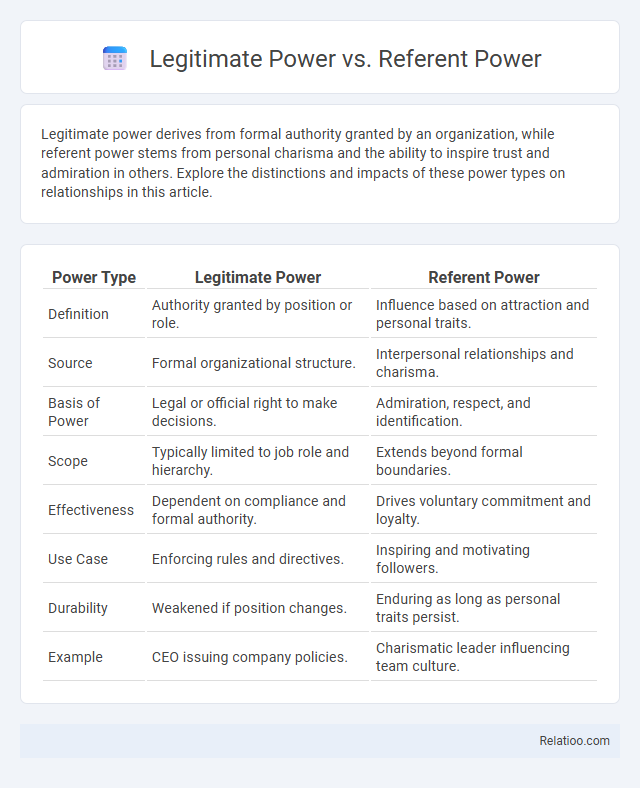
| Power Type | Legitimate Power | Referent Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authority granted by position or role. | Influence based on attraction and personal traits. |
| Source | Formal organizational structure. | Interpersonal relationships and charisma. |
| Basis of Power | Legal or official right to make decisions. | Admiration, respect, and identification. |
| Scope | Typically limited to job role and hierarchy. | Extends beyond formal boundaries. |
| Effectiveness | Dependent on compliance and formal authority. | Drives voluntary commitment and loyalty. |
| Use Case | Enforcing rules and directives. | Inspiring and motivating followers. |
| Durability | Weakened if position changes. | Enduring as long as personal traits persist. |
| Example | CEO issuing company policies. | Charismatic leader influencing team culture. |
Understanding Legitimate Power
Legitimate power is derived from an official position or role within an organization, granting authority that is recognized and accepted by others. Unlike referent power, which stems from personal charisma and relationships, legitimate power relies on formal structures and rules to influence behavior. Understanding your legitimate power helps you navigate organizational dynamics effectively, especially when competing for resources or leadership roles.
Defining Referent Power
Referent power arises from the personal qualities and charisma that inspire admiration and loyalty, allowing leaders to influence others through respect and emotional connection. Legitimate power, by contrast, is derived from formal authority and organizational roles, granting the ability to enforce rules and command compliance. Understanding referent power helps you navigate competitive dynamics by leveraging relationships and trust rather than relying solely on positional authority.
Key Differences Between Legitimate and Referent Power
Legitimate power stems from formal authority within an organization, granting individuals the right to make decisions and expect compliance, whereas referent power arises from personal traits and the respect and admiration others have for You. Legitimate power relies on established roles and rules, while referent power is rooted in influence and relationships. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in navigating competitive dynamics, as players with legitimate power command authority, but those with referent power inspire loyalty and voluntary cooperation.
Sources of Legitimate Power in Organizations
Sources of legitimate power in organizations stem from formal roles, hierarchical structures, and established authority documented in company policies and job descriptions. This power is derived from the position a person holds, granting them the right to make decisions, allocate resources, and enforce compliance within their scope of responsibility. Referent power relies on personal traits and relationships, while competitive dynamics influence how legitimate power is asserted and contested in organizational interactions.
Characteristics of Referent Power
Referent power is defined by the ability to influence others through personal traits, charisma, and the respect you inspire rather than formal authority. This power thrives on emotional connections and admiration, which makes followers more willing to align with your vision. Unlike legitimate power that relies on hierarchical position or competitive dynamics grounded in rivalry, referent power creates lasting influence through trust and identification.
Impact of Legitimate Power on Team Dynamics
Legitimate power, derived from formal authority and organizational hierarchy, shapes team dynamics by establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and decision-making structures, promoting order and accountability. This power fosters compliance and predictability within teams, enabling efficient coordination and goal alignment, but may also suppress creativity and reduce intrinsic motivation if overused. Compared to referent power, which relies on personal influence and respect, legitimate power primarily reinforces positional control, while competitive dynamics can either disrupt or reinforce power structures depending on how authority is exercised.
Influence of Referent Power on Employee Motivation
Referent power significantly influences employee motivation by fostering strong identification and admiration between leaders and employees, which enhances trust and loyalty within the organization. Unlike legitimate power that relies on formal authority, referent power leverages personal traits and relationships to inspire commitment and voluntary effort. Competitive dynamics may challenge referent power, but its ability to create intrinsic motivation and positive workplace culture often leads to sustained performance improvements.
Real-World Examples of Legitimate Power
Legitimate power derives from a formal position or role within an organization, granting the authority to make decisions and enforce rules, exemplified by a CEO's ability to direct company strategy and allocate resources. In real-world scenarios, government officials exercise legitimate power through statutory laws, while managers use it to delegate tasks and evaluate employee performance. Your understanding of these distinctions can clarify how legitimate power differs from referent power, which is based on personal influence, and from competitive dynamics driven by market forces and rivalry.
Building and Sustaining Referent Power
Building and sustaining referent power involves consistently demonstrating authenticity, empathy, and respect, which fosters trust and admiration from others. Unlike legitimate power derived from formal authority, referent power relies on your personal qualities and relationships to influence and inspire. In competitive dynamics, leveraging referent power can create loyalty and collaboration, making your influence more enduring and effective than authority alone.
Choosing the Right Power Type for Effective Leadership
Choosing the right power type for effective leadership depends on the context and goals of the organization. Legitimate power, derived from formal authority, is effective for enforcing rules and maintaining structure, while referent power, based on personal charisma and relationships, fosters trust and influence through admiration. Competitive dynamics often require a balance, leveraging legitimate power for clear decision-making and referent power to inspire collaboration and reduce resistance among team members.
Infographic: Legitimate Power vs Referent Power
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com