Bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior intended to intimidate or harm, often occurring among peers, while harassment includes unwelcome conduct based on protected characteristics like race, gender, or religion, creating a hostile environment. Discover key differences and legal implications of bullying versus harassment in this article.
Table of Comparison
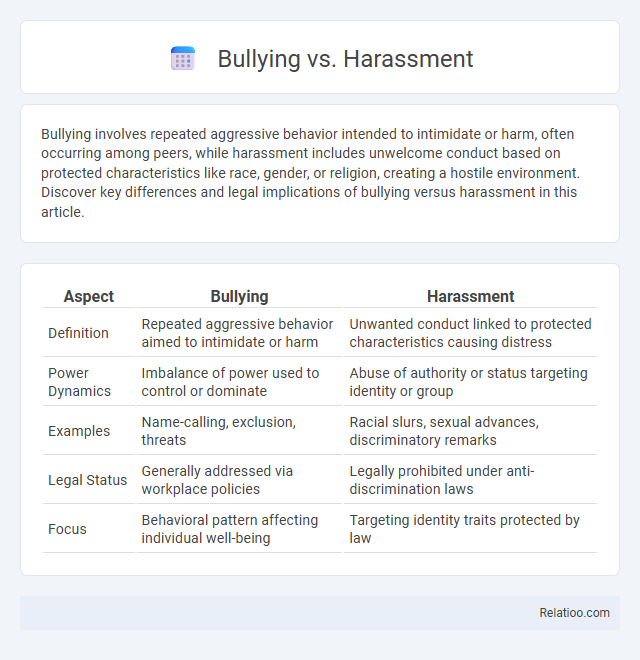
| Aspect | Bullying | Harassment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repeated aggressive behavior aimed to intimidate or harm | Unwanted conduct linked to protected characteristics causing distress |
| Power Dynamics | Imbalance of power used to control or dominate | Abuse of authority or status targeting identity or group |
| Examples | Name-calling, exclusion, threats | Racial slurs, sexual advances, discriminatory remarks |
| Legal Status | Generally addressed via workplace policies | Legally prohibited under anti-discrimination laws |
| Focus | Behavioral pattern affecting individual well-being | Targeting identity traits protected by law |
Understanding the Difference: Bullying vs Harassment
Bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior intended to hurt or intimidate someone physically or emotionally, often occurring in schools and workplaces. Harassment is unlawful conduct based on protected characteristics like race, gender, or disability, creating a hostile or offensive environment under legal frameworks such as Title VII or the ADA. Distinguishing bullying from harassment hinges on the presence of legally protected grounds and the intent to discriminate, making understanding these differences essential for effective prevention and intervention strategies.
Defining Bullying: Key Characteristics
Bullying involves repetitive aggressive behavior intended to harm, intimidate, or control another individual, characterized by a power imbalance between the bully and the victim. Unlike harassment, which is often defined by legally protected characteristics such as race, gender, or religion, bullying is behavior-driven and can occur in various contexts like schools or workplaces. Key features of bullying include intent to cause distress, repetition over time, and a consistent pattern of targeting the same individual or group.
What Constitutes Harassment?
Harassment constitutes unwelcome behavior based on protected characteristics such as race, gender, religion, or disability that creates a hostile or intimidating environment. Unlike general bullying, harassment is legally defined and can include verbal, physical, or written actions that interfere with your ability to work or participate in social settings. Recognizing harassment requires understanding its intent to discriminate and its impact on your well-being and rights under anti-discrimination laws.
Common Types of Bullying
Common types of bullying include physical aggression, verbal abuse, social exclusion, and cyberbullying, each targeting individuals through harm or intimidation. Harassment differs by being legally defined and often involves discrimination based on protected characteristics like race, gender, or disability. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize behaviors and seek appropriate support or intervention.
Recognizing Forms of Harassment
Recognizing forms of harassment involves understanding that harassment includes unwanted, repeated behaviors targeting an individual's protected characteristics such as race, gender, religion, or disability, which create a hostile or intimidating environment. Bullying typically refers to aggressive behavior causing physical or emotional harm but may not be linked to protected characteristics, whereas workplace bullying focuses on repeated mistreatment, intimidation, or humiliation affecting job performance. Your awareness of these distinctions helps identify and address harassment effectively to maintain a safe and respectful environment.
Legal Distinctions Between Bullying and Harassment
Bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior causing emotional or physical harm, often without legal consequences, while harassment specifically refers to unwelcome conduct based on protected characteristics such as race, gender, or disability, triggering legal protections under laws like Title VII or the ADA. Your understanding of these legal distinctions is crucial, as harassment claims require evidence of discrimination, whereas bullying is generally addressed through workplace policies rather than litigation. Recognizing these differences ensures appropriate actions for safeguarding rights and maintaining a respectful environment.
Psychological Impact on Victims
Bullying, harassment, and discrimination each inflict significant psychological harm, but their impacts manifest differently in victims. Bullying often leads to increased anxiety, depression, and lowered self-esteem due to repetitive aggressive behaviors, while harassment causes trauma related to targeted discriminatory acts, resulting in fear, stress, and emotional distress. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize and address the psychological consequences unique to each experience, fostering better mental health support for victims.
Responding to Bullying and Harassment
Responding to bullying and harassment requires recognizing the distinct nature of each: bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior causing physical or emotional harm, while harassment is discriminatory conduct based on protected characteristics such as race or gender. Your first step should be documenting incidents with detailed evidence, including dates, times, and witnesses, to support formal complaints. Engaging with human resources or relevant authorities ensures proper investigation and enforcement of anti-bullying and anti-harassment policies, protecting your rights in the workplace or educational environment.
Prevention Strategies and Policies
Effective prevention strategies and policies differentiate bullying, harassment, and discrimination by clearly defining behaviors and consequences, fostering a safe environment for all individuals. You should implement comprehensive training programs, establish confidential reporting systems, and enforce zero-tolerance policies to mitigate risks and promote respect. Regular evaluation of these policies ensures adaptability and reinforces commitment to preventing workplace or school misconduct.
Seeking Support and Resources
Seeking support for bullying, harassment, and discrimination is crucial for your mental health and safety. Resources such as counseling services, legal aid, and workplace human resources departments provide specialized help tailored to each issue. Connecting with support groups and advocacy organizations empowers you to navigate these challenges effectively and promotes your well-being.
Infographic: Bullying vs Harassment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com