Privilege creates unequal opportunities that reinforce systemic advantages for certain groups, while equality seeks to ensure fair treatment and access regardless of background. Discover how balancing privilege and equality shapes healthier relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
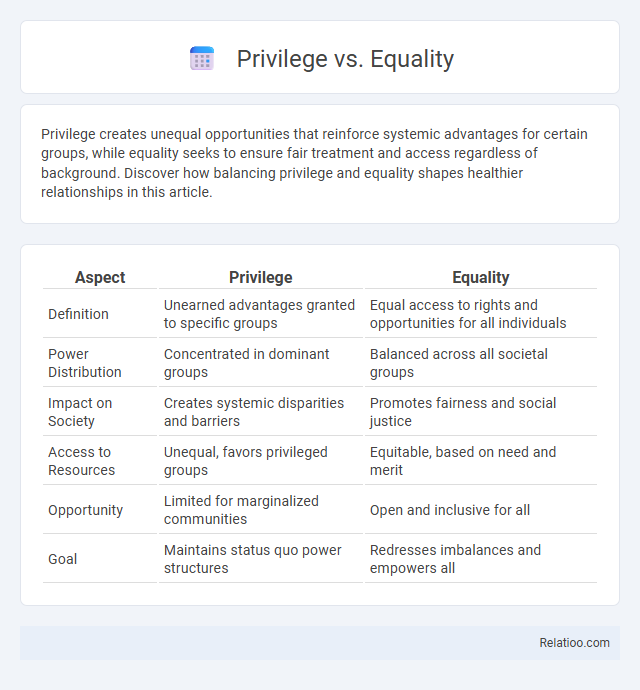
| Aspect | Privilege | Equality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unearned advantages granted to specific groups | Equal access to rights and opportunities for all individuals |
| Power Distribution | Concentrated in dominant groups | Balanced across all societal groups |
| Impact on Society | Creates systemic disparities and barriers | Promotes fairness and social justice |
| Access to Resources | Unequal, favors privileged groups | Equitable, based on need and merit |
| Opportunity | Limited for marginalized communities | Open and inclusive for all |
| Goal | Maintains status quo power structures | Redresses imbalances and empowers all |
Understanding Privilege: Definition and Types
Privilege refers to unearned advantages or rights granted to individuals or groups based on social categories such as race, gender, socioeconomic status, or ability. Types of privilege include racial privilege, gender privilege, socioeconomic privilege, and able-bodied privilege, each influencing access to resources, opportunities, and social mobility. Understanding privilege involves recognizing these systemic disparities and how they perpetuate inequalities in society.
Defining Equality: What Does It Really Mean?
Equality means providing everyone with the same opportunities and resources regardless of their background, ensuring fair treatment and access. It differs from privilege, which refers to unearned advantages granted to certain groups based on factors like race, gender, or socioeconomic status. Understanding equality requires recognizing systemic barriers and working towards dismantling them to create a truly level playing field for your community.
Historical Context: Roots of Privilege and Inequality
Historical context reveals that privilege often stems from systemic inequalities established through colonization, slavery, and discriminatory laws that favored certain groups over others. These entrenched advantages created disparities in access to resources, education, and power, shaping societal hierarchies that persist today. Understanding this background helps you recognize the deep-rooted origins of inequality and the ongoing impact of privilege in modern social structures.
Privilege in Modern Society: Recognizing the Signs
Privilege in modern society often manifests as unearned advantages linked to factors like race, gender, socioeconomic status, or education, creating systemic disparities in opportunities and outcomes. Recognizing the signs of privilege includes acknowledging implicit biases, unequal access to resources, and the normalization of certain groups' experiences over others. Addressing privilege requires conscious reflection on how societal structures perpetuate inequality and commitment to fostering equity through inclusive policies and practices.
Equality Movements: Past and Present Efforts
Equality movements have historically challenged systemic privilege to ensure fair access to rights and opportunities for marginalized groups. Efforts like the civil rights movement, women's suffrage, and LGBTQ+ advocacy highlight ongoing struggles to dismantle entrenched social hierarchies. Your awareness of these movements underscores the importance of continued activism to promote genuine equality in contemporary society.
Privilege in the Workplace: Barriers and Solutions
Privilege in the workplace creates barriers such as unequal access to opportunities, biased recruitment processes, and differential treatment based on social identities. Addressing these issues requires implementing inclusive hiring practices, promoting diversity training, and establishing clear policies against discrimination. Organizations that actively dismantle privilege barriers foster equitable environments where all employees can thrive and contribute fully.
The Role of Education in Shaping Privilege
Education plays a crucial role in shaping privilege by influencing access to resources, knowledge, and social networks that contribute to socioeconomic advantages. Unequal educational opportunities often reinforce existing social hierarchies, perpetuating disparities in privilege across different demographic groups. By promoting equitable access to quality education, societies can challenge entrenched privilege and advance greater equality.
Strategies for Promoting True Equality
Strategies for promoting true equality require recognizing and addressing systemic privilege that perpetuates disparities in opportunities and outcomes. You must implement policies that actively dismantle structural barriers while fostering inclusive environments where diverse voices are valued and empowered. Emphasizing equity over mere equality ensures that resources and support are distributed based on individual needs to achieve fair treatment and access for all.
The Social Impact of Privilege and Inequality
Privilege creates systemic advantages that influence access to resources, opportunities, and social power, resulting in entrenched inequalities within society. Inequality perpetuates disparities in wealth, education, and healthcare, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities and reinforcing social stratification. Recognizing your own position within these dynamics is crucial to advocating for equitable policies that address the root causes of social injustice.
Moving Forward: Building a More Equitable Future
Addressing privilege and inequality requires actively dismantling systemic barriers that perpetuate disparity across race, gender, and socioeconomic status. Implementing policies that promote equal access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities fosters a foundation for true equality. Empowering marginalized communities through representation and resource allocation drives sustainable progress toward an inclusive and just society.
Infographic: Privilege vs Equality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com