Understanding the dynamics of Passive versus Dominant roles in relationships helps clarify power balance and communication patterns. Explore this article to learn how these roles impact emotional intimacy and mutual respect.
Table of Comparison
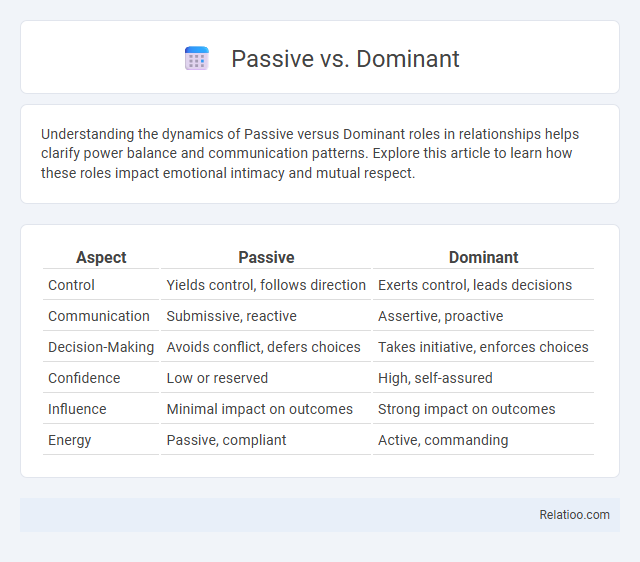
| Aspect | Passive | Dominant |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Yields control, follows direction | Exerts control, leads decisions |
| Communication | Submissive, reactive | Assertive, proactive |
| Decision-Making | Avoids conflict, defers choices | Takes initiative, enforces choices |
| Confidence | Low or reserved | High, self-assured |
| Influence | Minimal impact on outcomes | Strong impact on outcomes |
| Energy | Passive, compliant | Active, commanding |
Understanding Passive and Dominant Traits
Understanding passive and dominant traits helps you navigate interpersonal dynamics effectively by recognizing how individuals express control and submission. Passive traits often involve yielding, avoiding confrontation, and allowing others to make decisions, while dominant traits reflect assertiveness, decision-making, and influencing others' behavior. Identifying these characteristics enhances your ability to respond appropriately in social and professional settings.
Key Differences Between Passive and Dominant Personalities
Passive personalities tend to avoid confrontation and often comply with others' wishes, while dominant personalities assert control and influence in social or work environments. The key difference lies in decision-making: dominant individuals actively take charge, whereas passive individuals yield to others, sometimes leading to unresolved issues or suppressed emotions. Understanding these traits can help you navigate relationships and communication dynamics more effectively.
Psychological Foundations of Passivity and Dominance
Psychological foundations of passivity involve a tendency toward inhibition, low assertiveness, and reliance on external factors for decision-making, often linked to fear of conflict or low self-efficacy. Dominance is characterized by assertiveness, control, and influence, grounded in confidence, social power, and proactive behavior mechanisms. Passivity differs as a behavioral outcome, reflecting a lack of active engagement, often resulting from learned helplessness or avoidance coping strategies in response to stress or social dynamics.
Benefits of a Passive Approach
A passive approach emphasizes observation and receptivity, allowing individuals to conserve energy and reduce conflict by avoiding unnecessary engagement. This method benefits emotional well-being by promoting patience, mindfulness, and stress management through detachment from aggressive or dominant behaviors. In environments like negotiation or leadership, passive strategies often foster trust and open communication, encouraging collaboration without forcing control.
Advantages of a Dominant Personality
A dominant personality drives innovation and decision-making, allowing you to take control of situations and inspire confidence in others. This leadership style fosters clear communication, promotes accountability, and accelerates goal achievement within teams. Embracing dominance over passivity empowers you to influence outcomes effectively and create lasting impact.
Potential Challenges of Passive Behavior
Passive behavior often leads to unmet personal needs and suppressed self-expression, creating barriers in communication and decision-making. Dominant individuals may overshadow your contributions, causing feelings of frustration or invisibility in group settings. Recognizing passivity as a challenge allows you to develop assertiveness skills that enhance relationships and personal growth.
Risks Associated with Dominance
Dominant behavior often leads to increased risks such as strained relationships, reduced collaboration, and potential conflicts due to overpowering others. Your tendency toward dominance can hinder effective communication and limit diverse perspectives, which may negatively impact decision-making and team dynamics. Recognizing these risks is crucial to balancing assertiveness without crossing into harmful dominance or passivity.
Passive vs Dominant in Relationships
In relationships, being passive often means yielding to your partner's decisions and avoiding conflict, which can lead to unaddressed needs and imbalance, while dominant behavior involves taking control and influencing the direction of the relationship, sometimes overshadowing your partner's input. Your ability to recognize the difference between passivity and dominance helps in fostering mutual respect and healthy boundaries, promoting more equal and satisfying connections. Prioritizing assertiveness over passivity ensures your voice is heard without overpowering the relationship dynamic.
Workplace Impact: Passive vs Dominant Attitudes
Passive attitudes in the workplace often lead to missed opportunities and reduced team engagement, while dominant attitudes can create an environment of control but may stifle collaboration and innovation. Your ability to balance assertiveness without tipping into dominance fosters a culture of respect and productivity. Understanding the impact of passivity versus dominance helps optimize communication and enhances overall organizational efficiency.
Finding Balance: Integrating Passive and Dominant Traits
Finding balance between passive and dominant traits involves recognizing when to assert authority and when to adopt a receptive stance. Integrating passivity allows for flexibility and empathy, while dominance drives confidence and decisive action in leadership scenarios. Achieving harmony between these traits enhances interpersonal effectiveness and promotes adaptive communication strategies.
Infographic: Passive vs Dominant
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com