Parentification occurs when a child is forced to take on adult responsibilities, while infantilization involves treating an adult as if they were much younger or incapable. Explore the dynamics and effects of parentification and infantilization in relationships by reading this article.
Table of Comparison
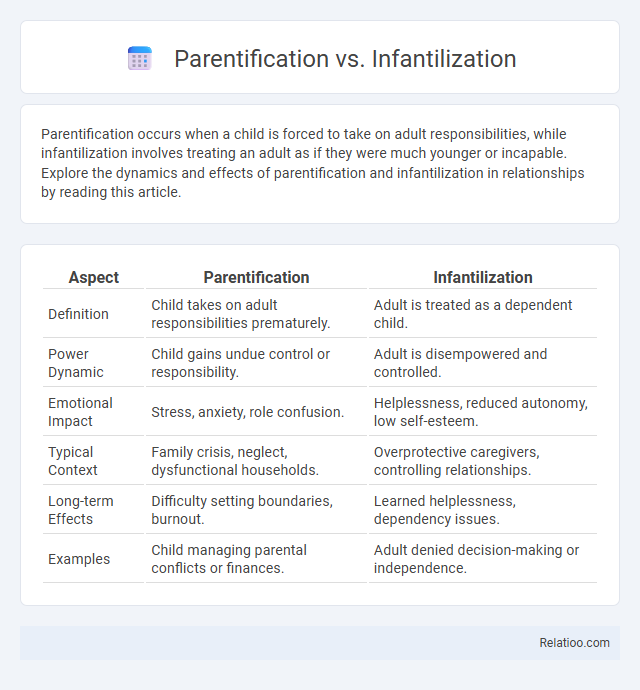
| Aspect | Parentification | Infantilization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child takes on adult responsibilities prematurely. | Adult is treated as a dependent child. |
| Power Dynamic | Child gains undue control or responsibility. | Adult is disempowered and controlled. |
| Emotional Impact | Stress, anxiety, role confusion. | Helplessness, reduced autonomy, low self-esteem. |
| Typical Context | Family crisis, neglect, dysfunctional households. | Overprotective caregivers, controlling relationships. |
| Long-term Effects | Difficulty setting boundaries, burnout. | Learned helplessness, dependency issues. |
| Examples | Child managing parental conflicts or finances. | Adult denied decision-making or independence. |
Understanding Parentification: Definition and Types
Parentification involves a child assuming adult responsibilities, often providing emotional or practical support beyond their developmental stage, leading to emotional strain. It manifests in two main types: instrumental parentification, where the child handles household tasks, and emotional parentification, where the child meets the emotional needs of caregivers. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for identifying impacts on a child's development and addressing potential psychological consequences.
What is Infantilization? Key Characteristics
Infantilization refers to treating an adult or older child as if they are much younger, undermining their autonomy and decision-making abilities. Key characteristics include excessive control, minimizing the person's capabilities, and using overly simplistic language or patronizing behavior. Understanding infantilization helps you recognize when someone's independence is being unfairly restricted, often leading to frustration and decreased self-esteem.
Psychological Impact of Parentification on Children
Parentification places adult responsibilities on children, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and impaired emotional development. Unlike infantilization, where children are overly sheltered or treated as younger than their age, parentification forces children into caregiving roles, often resulting in feelings of guilt and difficulty forming healthy relationships. Your child's psychological health may suffer long-term effects, including poor self-esteem and challenges with identity due to this role reversal.
Effects of Infantilization on Child Development
Infantilization often stunts your child's emotional growth by undermining their ability to develop independence and self-confidence, leading to increased dependency and low self-esteem. Unlike parentification, where a child assumes adult responsibilities prematurely, infantilization restricts a child's autonomy by treating them as younger than their actual age, which can cause delays in cognitive and social skill development. Long-term effects may include difficulties in decision-making, poor problem-solving abilities, and challenges in forming healthy adult relationships.
Parentification vs Infantilization: Key Differences
Parentification occurs when a child takes on adult responsibilities, often managing household duties or providing emotional support beyond their developmental stage, leading to role reversal within the family. Infantilization involves treating an individual, often an adult, as if they are much younger, undermining their autonomy and decision-making capabilities. Key differences between parentification and infantilization lie in role dynamics: parentification imposes adult roles on a child, whereas infantilization restricts an adult by denying their maturity.
Signs of Parentification in Family Dynamics
Signs of parentification in family dynamics include a child taking on adult responsibilities such as caregiving for siblings or managing household tasks beyond their age. You might notice emotional parentification when a child becomes the confidant or emotional support for a distressed parent, often sacrificing their own needs. These behaviors can result in role confusion, where the child loses the chance to experience a typical childhood.
Identifying Infantilization in Parenting Styles
Infantilization in parenting styles occurs when a parent consistently treats their child as younger or less capable than they actually are, limiting the child's autonomy and development of independence. This contrasts with parentification, where the child is burdened with adult responsibilities, often leading to role reversal within the family dynamic. Identify infantilization by recognizing behaviors that restrict your child's decision-making abilities and discourage self-sufficiency, which can hinder emotional growth and confidence.
Long-term Consequences: Adult Outcomes
Parentification leads to adults who often struggle with boundary issues, assuming excessive responsibility and experiencing chronic stress-related problems. Infantalization causes adults to exhibit dependency, low self-esteem, and difficulty making independent decisions, impairing their ability to function autonomously. Understanding these contrasting long-term consequences helps you recognize the impact of childhood dynamics on adult emotional health and relational patterns.
Healing and Support Strategies for Affected Individuals
Parentification involves children taking on adult responsibilities prematurely, while infantilization occurs when adults are treated as incapable, limiting their autonomy. Healing strategies for affected individuals include therapy focused on boundary-setting and emotional regulation, empowering you to regain control and develop healthy self-identity. Support systems like counseling, peer groups, and consistent validation play crucial roles in overcoming the impacts of these dynamics.
Preventing Harmful Family Roles: Healthy Parenting Approaches
Preventing harmful family roles such as parentification and infantilization requires establishing clear boundaries and promoting age-appropriate responsibilities. Healthy parenting approaches emphasize nurturing autonomy, emotional support, and balanced role distribution to foster child development and well-being. Recognizing early signs of these dysfunctional dynamics aids in intervention and supports a stable family environment.
Infographic: Parentification vs Infantalization
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com