Bullying involves repeated, intentional harm with a power imbalance, while teasing is usually playful and lacks malicious intent. Learn more about distinguishing these behaviors and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
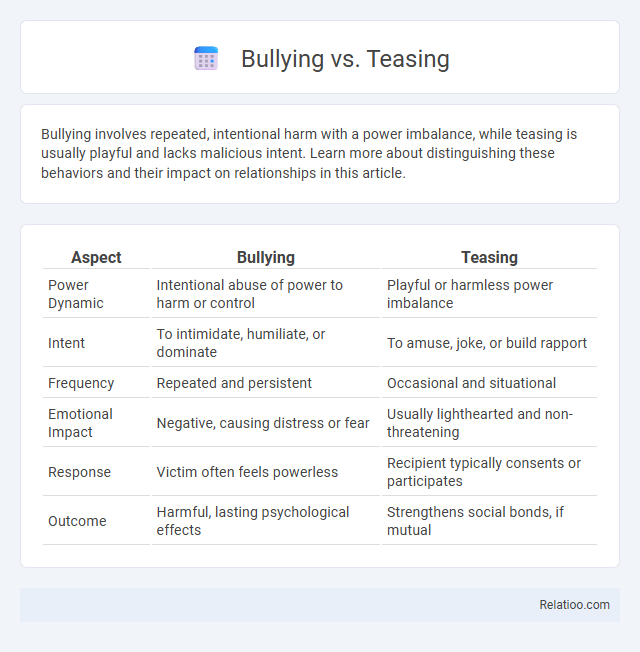
| Aspect | Bullying | Teasing |
|---|---|---|
| Power Dynamic | Intentional abuse of power to harm or control | Playful or harmless power imbalance |
| Intent | To intimidate, humiliate, or dominate | To amuse, joke, or build rapport |
| Frequency | Repeated and persistent | Occasional and situational |
| Emotional Impact | Negative, causing distress or fear | Usually lighthearted and non-threatening |
| Response | Victim often feels powerless | Recipient typically consents or participates |
| Outcome | Harmful, lasting psychological effects | Strengthens social bonds, if mutual |
Understanding the Difference: Bullying vs Teasing
Understanding the difference between bullying and teasing is crucial for creating a safe environment. Bullying involves intentional, repetitive aggression with the goal of harming or intimidating another person, while teasing is often playful, light-hearted, and consensual, though it can sometimes cross boundaries. Your awareness of these distinctions helps in identifying harmful behavior and fostering respectful interactions.
Defining Bullying: Key Characteristics
Bullying involves intentional, repetitive aggressive behavior aimed at causing harm or discomfort to another person, characterized by an imbalance of power where the bully exerts control over the victim. Unlike teasing, which can be playful or mutual without intent to harm, bullying includes physical, verbal, or psychological abuse designed to intimidate or degrade. Understanding these key characteristics helps you recognize and address bullying effectively, ensuring a safer environment for everyone.
What is Teasing? Types and Intentions
Teasing involves playful or light-hearted comments meant to provoke reactions without causing harm, often found in friendly social interactions. Types of teasing include affectionate teasing, which strengthens bonds, and hurtful teasing, which can lead to emotional distress depending on intention and context. Understanding the intention behind teasing helps you differentiate it from bullying, where repeated aggressive behavior aims to intimidate or harm others.
Motivations Behind Bullying and Teasing
Bullying is driven by a desire for power and control, often reflecting deeper issues such as insecurity or a need to dominate others, while teasing typically stems from playful intent or social bonding without the intent to harm. The motivations behind bullying involve aggression, intentional harm, and repeated behaviors targeting perceived vulnerabilities. Teasing lacks the persistent cruelty and malicious intent found in bullying, distinguishing it through its occasional, non-threatening nature linked to humor or camaraderie.
Emotional Impact on Victims
Bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior that causes significant emotional distress, often leading to long-term anxiety, depression, and lowered self-esteem in victims. Teasing, while sometimes playful or mild, can escalate to emotional harm when persistent, causing feelings of shame, embarrassment, or social isolation. Cyberbullying amplifies emotional impact through constant digital exposure, increasing victim vulnerability and psychological trauma.
When Teasing Crosses the Line to Bullying
Teasing becomes bullying when it is repeated, intentional, and meant to harm or intimidate someone, rather than being playful or consensual. Unlike teasing, bullying involves a power imbalance where the aggressor targets the victim to cause emotional distress or physical harm. Recognizing this shift requires attention to the frequency, intent, and impact of the behavior on the individual's well-being.
Signs and Red Flags to Watch For
Recognizing the signs and red flags of bullying versus teasing is essential for your child's safety and well-being. Bullying often involves repeated aggressive behavior with intent to harm, such as physical violence, verbal abuse, or social exclusion, while teasing is usually playful and mutual without malicious intent. Look for persistent signs like fearfulness, withdrawal, unexplained injuries, changes in mood, and avoidance of social situations to identify bullying early.
Role of Bystanders in Bullying and Teasing
Bystanders play a critical role in shaping the dynamics of bullying and teasing, with their reactions often determining whether harmful behaviors escalate or diminish. In bullying situations, active intervention or support for the victim by bystanders can disrupt the cycle of abuse and reduce the perpetrator's power, whereas passive or encouraging behavior may reinforce bullying. During teasing, bystander responses influence social norms by either validating playful interaction or highlighting disrespect, affecting how individuals perceive acceptable behavior within peer groups.
Effective Ways to Respond and Intervene
Effective ways to respond to bullying, teasing, and harassment involve understanding the distinct nature of each behavior and tailoring interventions accordingly. Responding to bullying requires firm, consistent actions such as setting clear boundaries, involving authority figures, and fostering a safe environment that discourages repeated aggression. Addressing teasing involves educating both parties about respectful communication, promoting empathy, and encouraging positive social interactions to prevent escalation into more harmful behaviors.
Prevention Strategies for Bullying and Harmful Teasing
Effective prevention of bullying and harmful teasing involves clear communication of zero-tolerance policies within schools and communities, fostering an environment where respect and empathy are prioritized. Your role includes teaching children emotional regulation and encouraging bystanders to intervene safely, which reduces the occurrence and impact of negative behaviors. Implementing regular training for staff and providing accessible support systems empower victims and create a proactive defense against bullying and teasing.
Infographic: Bullying vs Teasing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com