Dominance in relationships often involves the exercise of control and authority, while subversion seeks to undermine or resist such control to reshape power dynamics. Discover how these opposing forces influence relationship health and communication in this article.
Table of Comparison
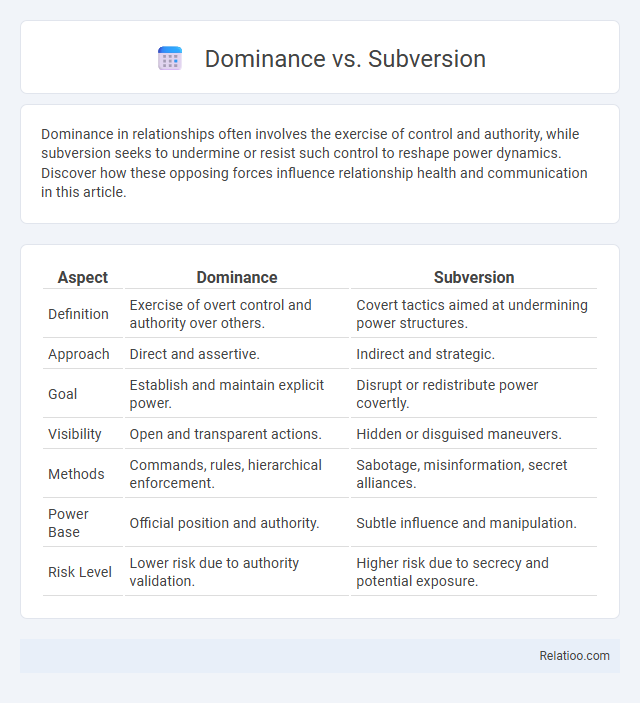
| Aspect | Dominance | Subversion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exercise of overt control and authority over others. | Covert tactics aimed at undermining power structures. |
| Approach | Direct and assertive. | Indirect and strategic. |
| Goal | Establish and maintain explicit power. | Disrupt or redistribute power covertly. |
| Visibility | Open and transparent actions. | Hidden or disguised maneuvers. |
| Methods | Commands, rules, hierarchical enforcement. | Sabotage, misinformation, secret alliances. |
| Power Base | Official position and authority. | Subtle influence and manipulation. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to authority validation. | Higher risk due to secrecy and potential exposure. |
Understanding Dominance: Definitions and Contexts
Dominance refers to the power or influence exerted by an individual or group over others within social, organizational, or political contexts, often characterized by control, authority, and hierarchy. Understanding dominance involves analyzing behaviors such as assertiveness, decision-making capacity, and resource control that establish and maintain this power dynamic. In psychological and sociological studies, dominance is examined through interactions, conformity pressures, and status negotiation processes that reinforce or challenge existing social structures.
The Roots of Subversion: Challenging Established Norms
Subversion targets the foundational structures of power by challenging established norms through covert actions and cultural disruption. Rooted in dissent against dominance, subversion destabilizes traditional authority by questioning accepted beliefs and promoting alternative ideologies. This process undermines societal control, paving the way for rebellion to emerge as a more overt resistance to the status quo.
Historical Perspectives: Dominance vs Subversion Through Time
Historical perspectives reveal dominance as a tool wielded by rulers to enforce power through hierarchy and control, while subversion emerged as covert resistance challenging established orders. Throughout history, marginalized groups used subversion to undermine dominant regimes, paving the way for rebellion when oppressed populations sought open revolt against systemic injustice. Your understanding of these dynamics highlights how power struggles shape societal change across time.
Power Dynamics: Systems of Control and Resistance
Power dynamics shape how dominance manifests through control over resources, decision-making, and social hierarchies, reinforcing systemic authority. Subversion operates by covertly undermining these structures, using tactics like sabotage, misinformation, or cultural disruption to challenge established power. Your ability to navigate and influence these systems depends on recognizing the subtle interplay between overt dominance and hidden resistance within social and political frameworks.
Cultural Manifestations: Dominance in Media and Art
Dominance in media and art often manifests through the portrayal of hegemonic narratives that reinforce prevailing power structures, emphasizing control and hierarchy within cultural contexts. This is evident in mainstream films, literature, and visual arts that prioritize dominant ideologies while marginalizing alternative perspectives, thus shaping societal norms and values. Subversion and rebellion challenge these narratives by introducing countercultural expressions and disruptive themes, but dominance maintains its influence by continuously co-opting and commodifying such resistance in popular culture.
Acts of Subversion: Strategies and Impacts
Acts of subversion employ covert strategies such as misinformation, sabotage, and psychological manipulation to undermine authority and destabilize established power structures. These tactics erode trust in dominant systems, creating environments ripe for change and challenging the legitimacy of regime control. Understanding how your actions or support can influence the success of subversive activities reveals the profound impact they have on social and political dynamics.
Psychology of Authority: Why We Seek to Dominate or Subvert
Psychology of authority reveals that individuals seek to dominate or subvert as a response to power dynamics and social hierarchy. Dominance often stems from an innate drive for control and status, enhancing feelings of security and self-worth, while subversion arises from perceived injustice or threats to autonomy, motivating covert resistance. Understanding these behaviors explains how humans navigate authority structures, balancing the pursuit of influence with the impulse to challenge or undermine power.
Case Studies: Dominance and Subversion in Society
Dominance and subversion shape social dynamics by influencing power structures and resistance tactics, as seen in historical case studies like the civil rights movement, where marginalized groups subverted dominant norms to challenge systemic racism. Your understanding of these interactions reveals how social hierarchies are maintained or disrupted through cultural expressions, strategic alliances, and acts of defiance. Analyzing such cases highlights the complex interplay between authority and resistance, offering insights into mechanisms of societal change.
The Balance of Power: Cooperation or Conflict?
The balance of power between dominance, subversion, and rebellion hinges on the interplay between cooperation and conflict within social or political systems. Dominance seeks control and hierarchical order, while subversion operates covertly to undermine authority, often leading to rebellion that openly challenges the status quo. Effective power dynamics depend on the capacity of dominant forces to integrate cooperation mechanisms, limiting conflict escalation and fostering stability.
Future Trends: Shifting Lines Between Dominance and Subversion
Emerging technologies and decentralized systems are blurring traditional boundaries between dominance and subversion, enabling marginalized groups to challenge established power structures more effectively. Artificial intelligence, blockchain, and social media platforms facilitate new forms of subversion that disrupt conventional dominance by redistributing control and influence. These trends signal a future where power dynamics become more fluid, emphasizing adaptability and networked resistance over centralized authority.
Infographic: Dominance vs Subversion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com