Privilege often grants unearned advantages based on social identity, while oppression imposes systemic disadvantages and barriers on marginalized groups. Explore how power dynamics shape these experiences and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
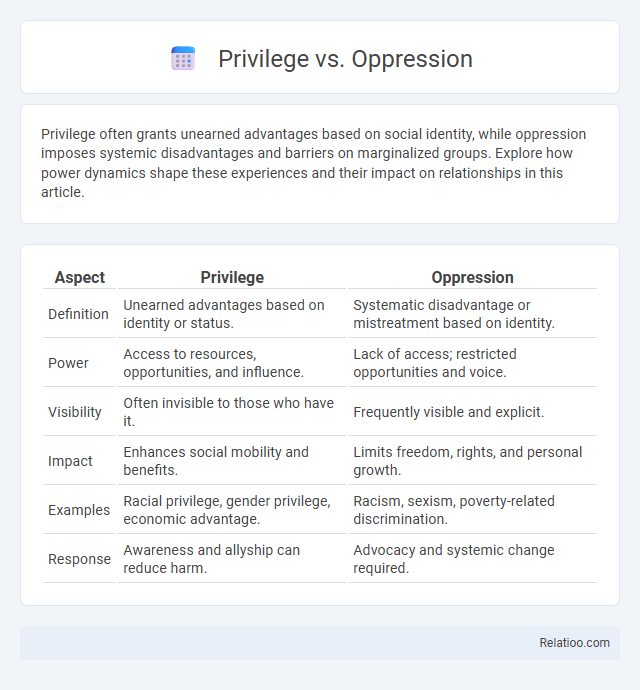
| Aspect | Privilege | Oppression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unearned advantages based on identity or status. | Systematic disadvantage or mistreatment based on identity. |
| Power | Access to resources, opportunities, and influence. | Lack of access; restricted opportunities and voice. |
| Visibility | Often invisible to those who have it. | Frequently visible and explicit. |
| Impact | Enhances social mobility and benefits. | Limits freedom, rights, and personal growth. |
| Examples | Racial privilege, gender privilege, economic advantage. | Racism, sexism, poverty-related discrimination. |
| Response | Awareness and allyship can reduce harm. | Advocacy and systemic change required. |
Understanding Privilege and Oppression
Privilege refers to unearned advantages granted to individuals based on aspects of their identity such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status, while oppression involves systemic and institutionalized discrimination that disadvantages specific groups. Understanding privilege requires recognizing these inherent benefits and how they perpetuate inequality, often invisibly to those who hold them. Oppression operates through social, political, and economic mechanisms, reinforcing disparities and limiting access to resources and opportunities for marginalized communities.
Historical Roots of Privilege
Historical roots of privilege stem from systemic power imbalances established through colonialism, slavery, and institutionalized discrimination, which have embedded advantages for dominant groups across generations. Privilege manifests in social, economic, and political spheres, reinforcing inequities experienced by marginalized communities deprived of agency and resources. Understanding these origins is crucial for addressing the interlinked dynamics of oppression and marginalization that perpetuate social hierarchies.
Different Forms of Oppression
Different forms of oppression include systemic racism, sexism, ableism, and homophobia, each reinforcing social inequalities and limiting opportunities for marginalized groups. Privilege refers to unearned advantages that individuals or groups experience based on characteristics such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status, often remaining invisible to those who hold it. Understanding how these dynamics intersect helps you recognize the complex layers of marginalization that impact people's daily lives and access to resources.
Intersectionality: Where Privilege and Oppression Meet
Intersectionality reveals how privilege and oppression overlap in complex social identities, affecting Your experience based on race, gender, class, and other factors. Individuals can simultaneously hold privilege in one context while facing marginalization in another, highlighting the multidimensional nature of inequality. Understanding these intersections is crucial for creating more inclusive policies and addressing systemic discrimination effectively.
Recognizing Unconscious Bias
Recognizing unconscious bias is essential for understanding how privilege, oppression, and marginalization operate within social structures. Your awareness of these implicit biases can reveal how certain groups benefit from systemic advantages (privilege) while others face disadvantages (oppression and marginalization). Addressing unconscious bias helps dismantle these inequities by promoting empathy and inclusive decision-making.
The Role of Power in Society
Power structures shape the dynamics of privilege, oppression, and marginalization by determining access to resources, opportunities, and social influence. Privilege arises when certain groups hold systemic advantages, while oppression enforces disadvantages through institutional control and cultural dominance. Marginalization occurs as power excludes or silences groups, limiting their participation and reinforcing societal inequalities.
Common Myths About Privilege
Common myths about privilege often include the misconception that having privilege means your life is entirely easy or free of struggle, which is inaccurate. Privilege refers to unearned advantages or rights granted to certain groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status, and it coexists with individual challenges. Understanding your privilege helps recognize systemic oppression and marginalization that affect others differently, fostering empathy and social awareness.
Impact of Oppression on Marginalized Groups
Oppression systematically limits opportunities and resources for marginalized groups, reinforcing social inequalities and restricting access to education, healthcare, and employment. Your ability to participate fully in society is hindered by barriers rooted in discrimination and power imbalances, which exacerbate economic and social disparities. The lasting impact of oppression perpetuates cycles of disadvantage, preventing marginalized communities from achieving equity and social justice.
Allyship and Addressing Privilege
Understanding privilege involves recognizing unearned advantages based on identity, while oppression systematically disadvantages certain groups, and marginalization excludes them from societal participation. Effective allyship requires you to actively address your own privilege by listening, amplifying marginalized voices, and challenging oppressive systems in everyday interactions. Commitment to continuous self-reflection and education strengthens your role in promoting equity and dismantling structural inequalities.
Steps Toward Equity and Inclusion
Addressing privilege, oppression, and marginalization requires intentional steps toward equity and inclusion, including recognizing systemic inequalities and amplifying marginalized voices. Implementing policies that promote fair access to resources and opportunities helps dismantle existing power imbalances. Creating inclusive environments involves continuous education, promoting diversity, and fostering a culture of empathy and accountability.
Infographic: Privilege vs Oppression
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com