Government surveillance monitors citizens primarily for national security and law enforcement purposes, while corporate surveillance collects user data to enhance marketing strategies and product development. Explore this article to understand the implications and differences between government and corporate surveillance.
Table of Comparison
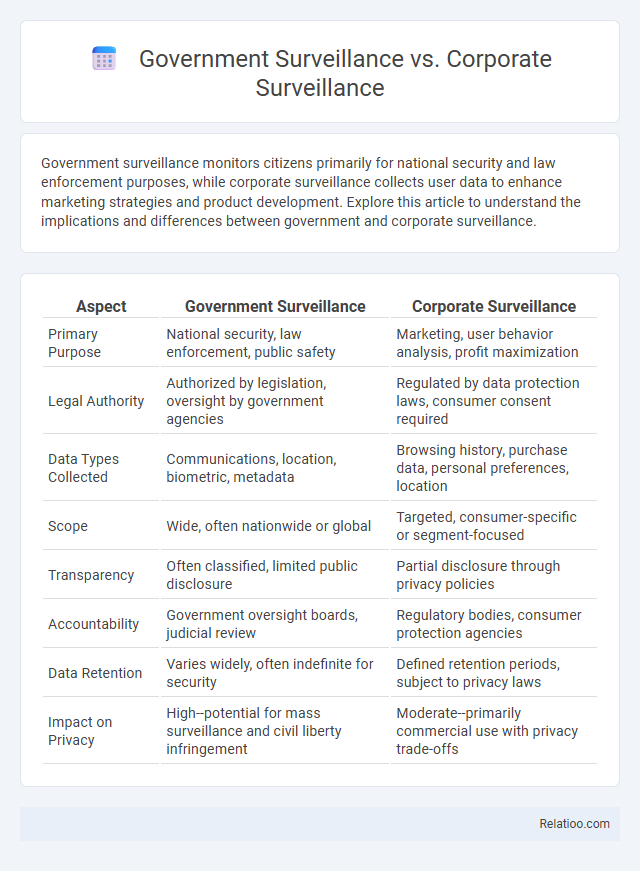
| Aspect | Government Surveillance | Corporate Surveillance |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | National security, law enforcement, public safety | Marketing, user behavior analysis, profit maximization |
| Legal Authority | Authorized by legislation, oversight by government agencies | Regulated by data protection laws, consumer consent required |
| Data Types Collected | Communications, location, biometric, metadata | Browsing history, purchase data, personal preferences, location |
| Scope | Wide, often nationwide or global | Targeted, consumer-specific or segment-focused |
| Transparency | Often classified, limited public disclosure | Partial disclosure through privacy policies |
| Accountability | Government oversight boards, judicial review | Regulatory bodies, consumer protection agencies |
| Data Retention | Varies widely, often indefinite for security | Defined retention periods, subject to privacy laws |
| Impact on Privacy | High--potential for mass surveillance and civil liberty infringement | Moderate--primarily commercial use with privacy trade-offs |
Introduction to Government and Corporate Surveillance
Government surveillance involves state agencies monitoring citizens' activities to ensure national security, enforce laws, and prevent crime, typically authorized by legal frameworks. Corporate surveillance focuses on businesses collecting and analyzing consumer data to enhance marketing strategies, improve products, and maximize profits, often through tracking online behavior and purchases. Understanding the differences in purpose, scope, and legal backing helps you navigate privacy concerns in both contexts.
Defining Government Surveillance
Government surveillance refers to the monitoring and collection of data on individuals or groups by state authorities, primarily for national security, law enforcement, and public safety purposes. This type of surveillance often encompasses mass data collection, license plate readers, phone tapping, and internet activity tracking through legal frameworks like the Patriot Act or GDPR exemptions. Your awareness of government surveillance is crucial as it directly impacts privacy rights and legal protections compared to corporate surveillance, which mainly targets consumer behavior and advertising strategies.
Understanding Corporate Surveillance
Corporate surveillance involves the collection and analysis of consumer data by businesses to monitor behavior, improve targeting, and enhance services, often raising concerns about privacy and consent. Unlike government surveillance, which primarily addresses national security and law enforcement, corporate surveillance focuses on economic gain through personalized advertising and customer profiling. You should carefully evaluate your digital footprint and data-sharing practices to better understand the implications of corporate surveillance on your privacy rights.
Key Differences Between Government and Corporate Surveillance
Government surveillance primarily aims at national security and law enforcement, leveraging extensive legal authority to monitor communications, track individuals, and gather intelligence with broad jurisdiction and often classified methods. Corporate surveillance focuses on consumer behavior, data collection for marketing optimization, and enhancing user experience, typically relying on data analytics, cookies, and tracking technologies within privacy regulations and user agreements. Key differences include the scope of authority, purpose, legal oversight, and transparency, with government surveillance emphasizing public safety and corporate surveillance prioritizing profit-driven data utilization.
Methods and Technologies Used in Surveillance
Government surveillance commonly employs advanced technologies such as mass data collection, facial recognition, and signal interception to monitor communications and track individuals on a wide scale. Corporate surveillance typically utilizes data mining, cookies, location tracking, and behavior analytics to gather user data for targeted advertising and consumer behavior insights. Both forms of surveillance leverage artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing to enhance data processing capabilities, but government methods prioritize national security while corporate methods emphasize marketing and user profiling.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Government surveillance operates under national security laws such as the USA PATRIOT Act and the UK's Investigatory Powers Act, which authorize extensive data collection with oversight mechanisms to balance public safety and privacy. Corporate surveillance is regulated primarily through data protection frameworks like the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California, mandating transparency, user consent, and data minimization to protect Your personal information. Surveillance practices, whether governmental or corporate, must adhere to evolving legal standards that emphasize accountability, user rights, and limits on data usage to prevent abuses and safeguard privacy.
Impact on Privacy and Civil Liberties
Government surveillance often involves extensive data collection authorized by law, impacting privacy by enabling mass monitoring and potential abuse of civil liberties through unchecked state power. Corporate surveillance primarily targets consumer behavior and personal data for profit, raising concerns about data exploitation, lack of transparency, and erosion of individual autonomy. Both forms of surveillance challenge privacy rights, but government surveillance poses greater risks to democratic freedoms, while corporate practices raise ethical questions about consent and data security.
Surveillance in the Digital Age
Surveillance in the digital age encompasses government surveillance, corporate surveillance, and increasingly pervasive data tracking methods. Government surveillance often targets national security and law enforcement objectives, utilizing tools like mass data collection and monitoring communications. Corporate surveillance focuses on consumer behavior and personal data harvesting, influencing advertising strategies and user experience, impacting Your online privacy and digital footprint.
Public Perception and Trust Issues
Government surveillance often triggers public concerns over privacy violations and potential abuses of power, leading to widespread distrust in state institutions. Corporate surveillance raises alarms about data exploitation and the commercialization of personal information, resulting in skepticism towards tech companies. Both forms of surveillance contribute to a pervasive mistrust among the public, with transparency and accountability being crucial factors influencing perception and trust levels.
Future Trends and Ethical Considerations
Emerging trends in government surveillance leverage advanced AI and biometric technologies to enhance national security but raise significant ethical concerns regarding privacy rights and mass data collection. Corporate surveillance increasingly utilizes machine learning algorithms and behavioral analytics to optimize consumer targeting, prompting debates over consent and data ownership in digital marketplaces. Future surveillance frameworks demand robust regulatory policies emphasizing transparency, accountability, and balancing security benefits with individual civil liberties to mitigate potential abuses across both public and private sectors.
Infographic: Government Surveillance vs Corporate Surveillance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com