Formal power in relationships stems from official roles and authority, while informal power arises from personal influence, charisma, and trust. Discover how balancing these power dynamics impacts relationship effectiveness and harmony in this article.
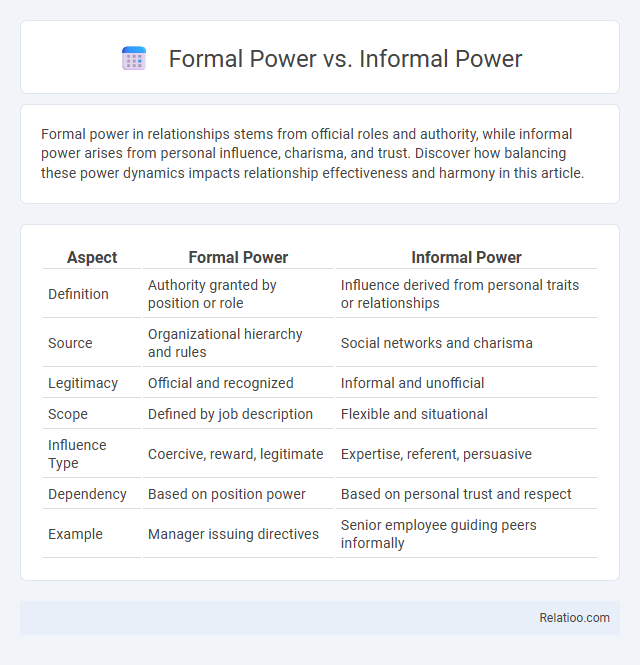
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formal Power | Informal Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authority granted by position or role | Influence derived from personal traits or relationships |
| Source | Organizational hierarchy and rules | Social networks and charisma |
| Legitimacy | Official and recognized | Informal and unofficial |
| Scope | Defined by job description | Flexible and situational |
| Influence Type | Coercive, reward, legitimate | Expertise, referent, persuasive |
| Dependency | Based on position power | Based on personal trust and respect |
| Example | Manager issuing directives | Senior employee guiding peers informally |
Introduction to Power Dynamics
Formal power stems from an individual's official position and authority within an organization, granting them explicit control over resources and decision-making. Informal power arises through personal influence, social networks, and expertise, often shaping outcomes without formal recognition. Competitive dynamics emerge as these power types interact, driving organizational behavior and shaping strategic decision processes.
Defining Formal Power
Formal power is authority granted through organizational structures, roles, and official positions within a company, enabling individuals to make decisions, allocate resources, and enforce compliance. Informal power, by contrast, arises from personal influence, relationships, expertise, or charisma, often shaping team dynamics and decision-making without official authority. Understanding the competitive dynamic between formal and informal power can help you navigate workplace politics and leverage both to achieve strategic objectives effectively.
Characteristics of Formal Power
Formal power is derived from an individual's official position or role within an organization, granting the authority to make decisions, assign tasks, and enforce rules. This power is often linked to hierarchical structures, clearly defined responsibilities, and organizational policies that legitimize control. Your ability to influence others through formal power depends on the recognition of your title and the institutional support backing your authority.
Understanding Informal Power
Informal power arises from interpersonal relationships, trust, and social networks within an organization, often enabling individuals to influence decisions without formal authority. Unlike formal power, which is granted through organizational hierarchy and defined roles, informal power depends on charisma, expertise, and communication skills. Understanding informal power is crucial in navigating competitive dynamics, as it shapes collaboration, conflict resolution, and the flow of information beyond official channels.
Key Traits of Informal Power
Informal power thrives on personal influence, trust, and relationships rather than official authority, enabling you to motivate and inspire others beyond hierarchical constraints. Key traits include strong communication skills, empathy, charisma, and the ability to build networks that foster collaboration and loyalty. Unlike formal power, which depends on position and rules, informal power leverages social connections and emotional intelligence to drive team dynamics and competitive advantage.
Sources of Formal and Informal Power
Formal power originates from an individual's official position within an organization, granting authority through roles such as managers or executives who control resources and decision-making processes. Informal power arises from personal attributes like expertise, charisma, or networks, enabling influence without official titles or authority. Competitive dynamics in organizations are shaped by the interplay between these power sources, where formal power establishes structure while informal power drives collaboration and innovation.
Impact of Formal vs Informal Power in Organizations
Formal power in organizations derives from hierarchical roles and explicit authority, ensuring compliance and structured decision-making, while informal power emerges from personal influence, relationships, and expertise, fostering collaboration and innovation. The interplay between formal and informal power impacts your organization's culture, employee motivation, and communication effectiveness, shaping overall performance and adaptability. Competitive dynamics intensify the need to balance these power forms to maintain organizational cohesion and drive sustainable success.
Balancing Formal and Informal Power
Balancing formal power, derived from official positions and authority, with informal power, based on personal influence and relationships, is crucial for effective leadership and organizational success. Your ability to navigate competitive dynamics relies on leveraging formal structures while fostering trust and collaboration through informal networks. Mastering this balance enhances decision-making, conflict resolution, and team cohesion in complex business environments.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Power Type
Formal power, derived from organizational hierarchy and official authority, enables clear decision-making and resource allocation but can lead to rigidity and reduced employee morale. Informal power, based on personal relationships and expertise, fosters collaboration and innovation yet may cause inconsistency and undermine formal structures. Competitive dynamics leverage both power types to drive performance and market positioning but risk creating conflict and short-term focus if not balanced effectively.
Conclusion: Navigating Power Structures
Navigating power structures requires understanding how formal power, derived from official authority and organizational roles, contrasts with informal power based on relationships, expertise, and personal influence. Recognizing the competitive dynamics between these forces enables you to strategically leverage both to achieve your goals while maintaining organizational harmony. Balancing formal authority with the subtlety of informal influence is essential for effective leadership in complex environments.
Infographic: Formal Power vs Informal Power
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com