Understanding the distinction between privileges and rights is essential for maintaining healthy relationships, as rights are inherent and universal, while privileges are conditional and granted based on behavior or trust. Explore how balancing these concepts strengthens trust and respect in relationships by reading more in this article.
Table of Comparison
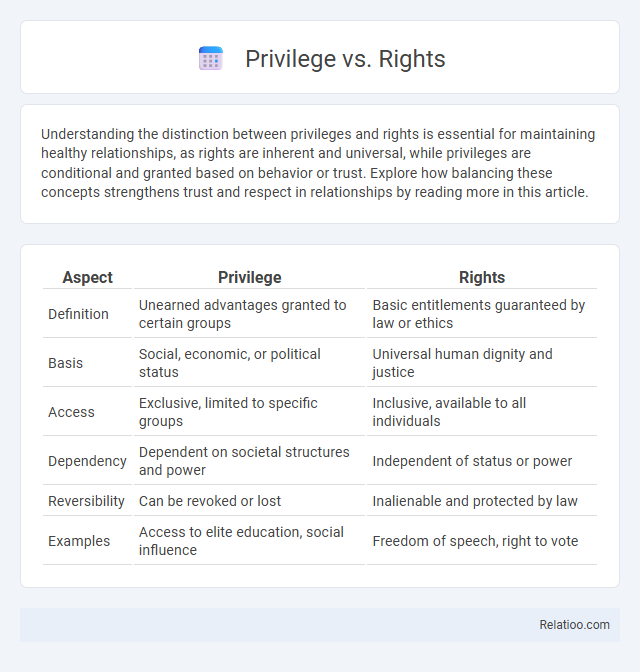
| Aspect | Privilege | Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unearned advantages granted to certain groups | Basic entitlements guaranteed by law or ethics |
| Basis | Social, economic, or political status | Universal human dignity and justice |
| Access | Exclusive, limited to specific groups | Inclusive, available to all individuals |
| Dependency | Dependent on societal structures and power | Independent of status or power |
| Reversibility | Can be revoked or lost | Inalienable and protected by law |
| Examples | Access to elite education, social influence | Freedom of speech, right to vote |
Understanding the Difference: Privilege vs Rights
Rights are inherent entitlements granted by law or nature, ensuring protection and freedom, while privileges are conditional benefits given by an authority that can be revoked. Your ability to exercise rights is universal and guaranteed, whereas privileges depend on circumstances, behavior, or status. Understanding the difference helps you advocate effectively for fairness and justice.
Defining Legal Rights and Social Privileges
Legal rights are enforceable entitlements granted by statutes or constitutions that protect individual freedoms and ensure justice within a society. Social privileges are advantages or benefits bestowed upon certain groups based on societal norms, often unearned and dependent on context rather than law. You should understand that while rights guarantee protections for everyone, privileges reflect unequal access to power or opportunities shaped by culture and social structures.
Historical Context of Rights and Privileges
Historically, rights originated as inherent entitlements tied to natural law or citizenship, ensuring protection and participation within a society, while privileges were granted selectively by monarchs or states, often contingent on status or service. The evolution of rights marked a shift towards universal claims recognized by legal systems, contrasting with privileges which remained conditional and revocable. This distinction underpins debates about equality and justice, influencing constitutional developments and human rights movements globally.
How Rights Are Protected by Law
Rights are guaranteed and safeguarded by constitutions, statutes, and judicial decisions, ensuring individuals receive legal protection against violations. Unlike privileges, which are conditional and granted by authorities, rights are inherent and cannot be arbitrarily revoked. Laws such as the Civil Rights Act and constitutional amendments establish frameworks that enforce and uphold these rights at both federal and state levels.
The Role of Privilege in Modern Society
Privilege in modern society functions as an unearned advantage granted to certain groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status, shaping access to resources and opportunities. Rights are fundamental entitlements guaranteed by law or ethical principles, ensuring equal treatment and protection for all individuals. The interplay between privilege and rights often influences social dynamics, where recognizing privilege is key to addressing systemic inequalities and promoting justice.
Examples of Common Privileges
Common privileges include driving a car, accessing restricted areas, or using company resources, which require meeting specific conditions unlike inherent rights such as freedom of speech or the right to vote. Rights are guaranteed by laws or constitutions and cannot be easily revoked, whereas privileges are conditional and can be taken away for non-compliance or misconduct. Understanding the distinction helps clarify why certain activities necessitate permits or licenses, emphasizing privileges are granted based on responsibility and behavior.
The Impact of Rights on Social Equality
Rights serve as fundamental guarantees that promote social equality by ensuring equal access to resources, opportunities, and protections under the law. Unlike privileges, which are conditional and often linked to status or power, rights are inalienable and designed to dismantle systemic barriers that perpetuate inequality. Understanding the impact of rights on social equality helps you advocate for policies that foster inclusivity and justice in society.
Recognizing Invisible Privilege
Invisible privilege refers to unearned advantages that individuals may not be consciously aware of, often tied to aspects like race, gender, or socioeconomic status. Recognizing these unseen benefits requires self-reflection and understanding systemic inequalities that contribute to disparities in opportunities and treatment. By acknowledging your own invisible privilege, you can better advocate for equity and support the dismantling of social barriers.
Challenges in Distinguishing Rights from Privileges
Distinguishing rights from privileges presents challenges due to their overlapping social and legal interpretations, where rights are inherently guaranteed and privileges are conditional benefits granted by authorities. Rights, such as freedom of speech or voting, are protected by law and considered inalienable, whereas privileges can be revoked or restricted based on behavior or compliance with regulations. This ambiguity complicates policy enforcement and public understanding, leading to debates about entitlement, social equity, and the scope of governmental power.
Promoting Awareness: Balancing Rights and Privileges
Balancing rights and privileges requires promoting awareness of their distinct roles in society, where rights guarantee fundamental freedoms, and privileges offer conditional benefits based on social or legal frameworks. Effective education campaigns highlight how respecting rights ensures equality while understanding privileges encourages responsible behavior and accountability. Fostering this awareness supports harmonious community development by preventing entitlement confusion and reinforcing legal and ethical standards.
Infographic: Privilege vs Rights
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com