Influence guides relationships through mutual respect and persuasion, while obedience relies on authority and compliance. Explore how these dynamics shape interactions in this article.
Table of Comparison
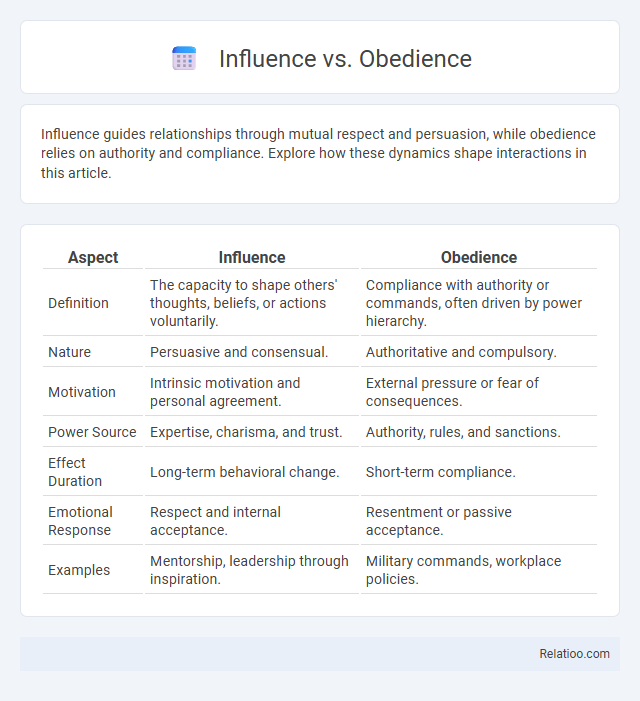
| Aspect | Influence | Obedience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The capacity to shape others' thoughts, beliefs, or actions voluntarily. | Compliance with authority or commands, often driven by power hierarchy. |
| Nature | Persuasive and consensual. | Authoritative and compulsory. |
| Motivation | Intrinsic motivation and personal agreement. | External pressure or fear of consequences. |
| Power Source | Expertise, charisma, and trust. | Authority, rules, and sanctions. |
| Effect Duration | Long-term behavioral change. | Short-term compliance. |
| Emotional Response | Respect and internal acceptance. | Resentment or passive acceptance. |
| Examples | Mentorship, leadership through inspiration. | Military commands, workplace policies. |
Defining Influence and Obedience
Influence refers to the capacity to affect the attitudes, behaviors, or beliefs of individuals or groups through persuasion, social pressure, or authority, often shaping decisions without explicit commands. Obedience involves compliance with direct orders or commands from an authority figure, typically driven by hierarchical power dynamics and the expectation of consequences for non-compliance. Understanding the distinction between influence as subtle behavioral shaping and obedience as overt rule-following is critical in psychology and social dynamics research.
Key Psychological Theories
Influence, obedience, and overshadowing are explained through key psychological theories such as social influence theory, Milgram's obedience study, and associative learning principles, respectively. Social influence theory underscores how individuals' behaviors are shaped by group dynamics and normative pressures, while Milgram's experiments reveal the power of authority in eliciting obedience even against personal morals. Overshadowing, rooted in classical conditioning, occurs when a more salient stimulus interferes with the associative learning of another, highlighting the impact of stimulus salience on memory encoding and response patterns.
Mechanisms of Influence
Mechanisms of influence rely on psychological processes such as social proof, authority, and reciprocity to guide behavior, contrasting obedience which depends on hierarchical commands, and overshadowing, where more salient stimuli dominate memory encoding. Your decision-making is shaped by subtle cues like conformity pressure or expert endorsement, which can override personal judgment without explicit coercion. Understanding these distinct mechanisms helps distinguish voluntary compliance from automatic obedience and attentional overshadowing in cognitive processing.
Mechanisms of Obedience
Mechanisms of obedience primarily involve hierarchical authority structures where individuals comply with commands to gain social approval or avoid punishment. Psychological factors such as normative social influence and the diffusion of responsibility increase obedience, often overshadowing personal morals and critical thinking. Studies like Milgram's experiment demonstrate how authoritative presence and situational pressure significantly amplify obedience behaviors.
Social Factors Affecting Influence
Social factors such as group size, unanimity, and status significantly impact influence, often increasing conformity and obedience within social contexts. Authority figures and cultural norms amplify obedience by establishing clear expectations and consequences. Overshadowing occurs when a dominant social cue or authority reduces the impact of other stimuli, highlighting the complex interplay between social environment and individual behavior.
Situational Factors Shaping Obedience
Situational factors such as authority presence, group pressure, and environmental context significantly shape obedience by influencing your likelihood to comply with commands. High-authority settings and unanimous group consensus enhance obedience levels, overshadowing personal beliefs or influence attempts. Understanding these factors clarifies why obedience can prevail despite conflicting individual values.
Influence in Everyday Life
Influence shapes your decisions and behaviors by subtly guiding thoughts and actions through social cues, authority, or peer pressure. Unlike obedience, which requires direct compliance with orders, influence operates through persuasion and emotional connection, often without explicit commands. In everyday life, understanding how influence works enables you to make conscious choices, recognize manipulation, and build healthier relationships based on mutual respect.
Obedience in Authority Structures
Obedience in authority structures plays a critical role in maintaining order, as individuals comply with directives from leaders perceived to hold legitimate power. Unlike influence, which often relies on persuasion and voluntary acceptance, obedience involves enforced compliance that can override personal judgment, especially in hierarchical institutions like the military or corporate environments. The psychological mechanisms behind obedience highlight how authority figures trigger automatic responses, sometimes leading to overshadowing of personal morals in favor of conformity to rules.
Ethical Implications and Consequences
Influence shapes your decisions through persuasion, while obedience compels action via authority, each presenting unique ethical challenges regarding autonomy and consent. Overshadowing occurs when dominant factors diminish alternative options, potentially leading to biased outcomes and ethical dilemmas in fairness. Understanding these dynamics helps navigate responsibility and respect in decision-making processes, ensuring informed and voluntary participation.
Balancing Influence and Obedience
Balancing influence and obedience requires understanding how each affects your leadership and decision-making dynamics. Influence shapes attitudes and behaviors through persuasion and motivation, while obedience ensures compliance and order through authority. Your ability to blend these elements effectively strengthens relationships, fosters trust, and drives sustainable outcomes without undermining autonomy or control.
Infographic: Influence vs Obedience
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com