Maternal involvement often emphasizes emotional support and caregiving, while paternal involvement frequently centers on play and discipline. Explore the distinct impacts of maternal and paternal roles on child development in this article.
Table of Comparison
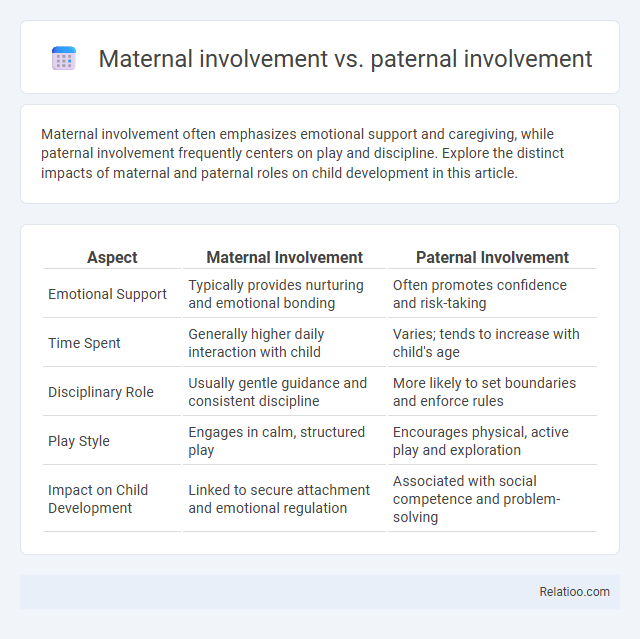
| Aspect | Maternal Involvement | Paternal Involvement |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Support | Typically provides nurturing and emotional bonding | Often promotes confidence and risk-taking |
| Time Spent | Generally higher daily interaction with child | Varies; tends to increase with child's age |
| Disciplinary Role | Usually gentle guidance and consistent discipline | More likely to set boundaries and enforce rules |
| Play Style | Engages in calm, structured play | Encourages physical, active play and exploration |
| Impact on Child Development | Linked to secure attachment and emotional regulation | Associated with social competence and problem-solving |
Understanding Maternal and Paternal Involvement
Maternal involvement typically centers on nurturing, emotional support, and daily caregiving tasks critical for early childhood development, while paternal involvement often emphasizes play, discipline, and fostering independence, contributing significantly to balanced child growth. Studies reveal that active parental involvement, combining both maternal and paternal roles, enhances cognitive, social, and emotional outcomes in children more effectively than singular parental engagement. Understanding these distinct yet complementary contributions of mothers and fathers is vital for optimizing family dynamics and promoting holistic child well-being.
Historical Perspectives on Parental Roles
Historical perspectives on parental roles reveal that maternal involvement traditionally centered on caregiving and nurturing, shaped by societal norms emphasizing motherhood. Paternal involvement historically focused on economic provision and authority within the family, reflecting patriarchal structures established over centuries. Modern research illustrates a shift toward more balanced parental involvement, recognizing the critical roles both mothers and fathers play in child development and family dynamics.
Key Differences Between Maternal and Paternal Engagement
Maternal involvement typically emphasizes nurturing behaviors, emotional support, and caregiving activities, whereas paternal involvement often centers on play, discipline, and providing resources. Parental involvement combines these distinct roles, fostering balanced child development by integrating maternal warmth and paternal structured engagement. Key differences include mothers generally spending more time in direct care, while fathers contribute through engagement in physical play and encouraging independence.
Psychological Impact on Child Development
Maternal involvement is often linked to enhanced emotional security and social competence in children, fostering resilience and attachment through nurturing behaviors. Paternal involvement contributes uniquely to cognitive development and risk-taking behaviors, promoting problem-solving skills and independence. Parental involvement, encompassing both maternal and paternal roles, synergistically supports balanced psychological development by combining emotional support and cognitive stimulation crucial for overall child well-being.
Time Commitment: Mothers vs. Fathers
Mothers generally dedicate more time to childcare activities, often spending an average of 2 to 3 hours daily on child-rearing compared to fathers, who typically commit around 1 to 1.5 hours. Studies reveal maternal involvement peaks in early childhood, emphasizing feeding, hygiene, and emotional support, whereas paternal involvement tends to increase as children grow, focusing more on play and education. Parental involvement, combining both maternal and paternal contributions, enhances child development outcomes by balancing nurturing care with active engagement.
Influence on Emotional and Social Skills
Maternal involvement plays a crucial role in shaping a child's emotional regulation and secure attachment, providing a foundation for strong social skills. Paternal involvement contributes significantly to developing a child's social competence and risk-taking abilities, fostering independence and confidence. Your child's emotional and social development benefits most from balanced parental involvement, combining nurturing maternal support with encouraging paternal engagement.
Cultural Factors Shaping Parental Involvement
Cultural factors significantly shape maternal, paternal, and overall parental involvement by influencing traditional gender roles and expectations within families. In many cultures, maternal involvement is emphasized through caregiving and emotional support, while paternal involvement often focuses on providing financial stability and discipline, affecting the dynamics of your child's development. Understanding these cultural nuances can help tailor strategies to enhance balanced parental engagement and foster better educational and social outcomes for children.
Barriers to Balanced Participation
Barriers to balanced parental involvement often stem from societal expectations, workplace demands, and unequal distribution of caregiving responsibilities. Maternal involvement tends to be higher due to traditional gender roles, while paternal involvement is frequently limited by lack of flexible work arrangements and social support. Understanding these obstacles can help you promote more equitable participation, enhancing child development and family dynamics.
Strategies for Enhancing Co-Parenting
Effective strategies for enhancing co-parenting emphasize consistent communication, shared decision-making, and mutual respect between maternal and paternal figures to ensure balanced parental involvement. Utilizing structured parenting plans and regular family meetings fosters collaborative efforts in child-rearing responsibilities, promoting stability and emotional support for the child. Implementing conflict resolution techniques and leveraging professional mediation services enhances co-parental coordination, benefiting overall family dynamics.
The Future of Parental Roles in Childcare
Maternal involvement historically dominates early childcare, contributing significantly to children's emotional and cognitive development, while paternal involvement is increasingly recognized for promoting social skills and resilience. Recent trends show a shift towards equitable parental involvement, where shared caregiving responsibilities enhance child outcomes by combining nurturing and disciplinary roles. The future of parental roles in childcare emphasizes flexible, co-parenting models supported by workplace policies and societal attitudes that value both maternal and paternal contributions equally.
Infographic: Maternal involvement vs Paternal involvement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com