Neglectful parenting is characterized by a lack of responsiveness and minimal involvement, often leading to poor social and emotional outcomes in children, whereas authoritative parenting balances high responsiveness with clear expectations, promoting healthy development and strong relationships. Explore this article to understand how these parenting styles impact child behavior and long-term well-being.
Table of Comparison
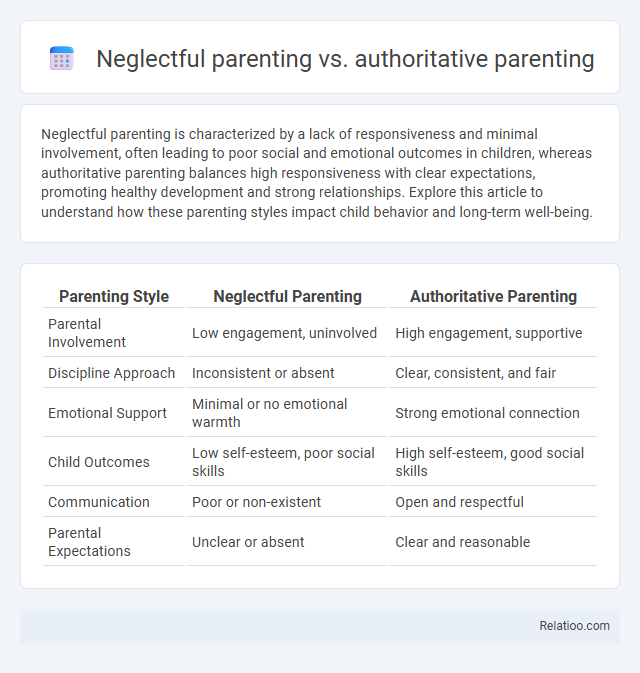
| Parenting Style | Neglectful Parenting | Authoritative Parenting |
|---|---|---|
| Parental Involvement | Low engagement, uninvolved | High engagement, supportive |
| Discipline Approach | Inconsistent or absent | Clear, consistent, and fair |
| Emotional Support | Minimal or no emotional warmth | Strong emotional connection |
| Child Outcomes | Low self-esteem, poor social skills | High self-esteem, good social skills |
| Communication | Poor or non-existent | Open and respectful |
| Parental Expectations | Unclear or absent | Clear and reasonable |
Introduction to Parenting Styles
Parenting styles significantly influence child development, with neglectful parenting characterized by low responsiveness and low demandingness, leading to potential emotional and social challenges. Authoritative parenting balances high responsiveness and high demandingness, promoting independence, self-regulation, and positive academic outcomes. Understanding the contrasts between neglectful and authoritative approaches is crucial for fostering effective parenting strategies that support healthy child development and well-being.
Defining Neglectful Parenting
Neglectful parenting is characterized by a lack of responsiveness and minimal involvement in a child's life, often resulting in emotional neglect and unmet basic needs. This style contrasts with authoritative parenting, which combines warmth, structure, and clear boundaries to foster healthy development. Neglectful parents fail to provide adequate guidance, supervision, or affection, leading to negative outcomes such as poor academic performance and social difficulties.
Understanding Authoritative Parenting
Authoritative parenting combines high responsiveness with high demands, fostering a supportive yet structured environment that promotes children's independence and self-regulation. Research shows that children raised with authoritative parenting often exhibit better social skills, higher academic performance, and enhanced emotional resilience compared to those with neglectful parents, who provide low responsiveness and low demands, leading to poor developmental outcomes. Understanding authoritative parenting's balance of warmth and discipline is crucial for promoting optimal child development and long-term well-being.
Key Differences Between Neglectful and Authoritative Parenting
Neglectful parenting is characterized by a lack of responsiveness and emotional involvement, leading to unmet basic needs and poor supervision, whereas authoritative parenting combines high responsiveness with appropriate demands and clear boundaries, fostering a supportive environment for healthy child development. Your child's behavioral outcomes differ significantly under these styles; authoritative parenting promotes self-regulation, social competence, and academic success, while neglectful parenting often results in attachment issues, low self-esteem, and increased risk of behavioral problems. Understanding these key differences helps you create an effective parenting approach that balances nurturing support and firm guidance.
Emotional Impact on Children
Neglectful parenting often leads to emotional detachment, low self-esteem, and difficulty forming healthy relationships in children due to a lack of parental responsiveness and support. Authoritative parenting fosters emotional resilience, self-regulation, and strong social skills by combining warmth with clear boundaries and consistent discipline. Understanding these differences can help you create a nurturing environment that supports your child's emotional well-being.
Behavioral Outcomes and Development
Neglectful parenting often leads to poor emotional regulation, low self-esteem, and increased risk of behavioral problems such as aggression and delinquency in children. In contrast, authoritative parenting, characterized by high responsiveness and consistent discipline, promotes positive behavioral outcomes including social competence, academic achievement, and emotional resilience. Research consistently shows that neglectful parenting is associated with developmental delays and attachment issues, whereas authoritative parenting supports healthy cognitive, emotional, and social development.
Academic Performance and Motivation
Authoritative parenting promotes higher academic performance and motivation by combining warmth, structure, and support, fostering Your confidence and self-regulation skills. In contrast, neglectful parenting often leads to lower academic achievement and diminished motivation due to lack of guidance, supervision, and emotional involvement. Children with authoritative parents generally exhibit better study habits, higher grades, and intrinsic motivation compared to those raised in neglectful environments.
Long-Term Effects into Adulthood
Neglectful parenting, characterized by a lack of responsiveness and support, often leads to long-term effects such as low self-esteem, poor emotional regulation, and higher risks of substance abuse in adulthood. Authoritative parenting, defined by high responsiveness and reasonable demands, promotes positive outcomes including strong social skills, academic success, and emotional resilience. Research consistently shows that individuals raised with neglectful parenting face more challenges in forming healthy relationships and maintaining stable employment compared to those raised in authoritative households.
Strategies for Transitioning to Authoritative Parenting
Transitioning from neglectful to authoritative parenting involves consistently setting clear expectations while providing emotional support and active involvement in the child's life. Implementing structured routines, practicing empathetic communication, and fostering positive reinforcement helps build trust and promote healthy development. Parents should gradually increase responsiveness and guidance, balancing authority with warmth to create a nurturing environment that encourages independence and self-discipline.
Conclusion: Fostering Positive Parent-Child Relationships
Fostering positive parent-child relationships requires embracing authoritative parenting, which combines warmth, structure, and clear communication to support your child's emotional and social development. Neglectful parenting often leads to emotional detachment and behavioral challenges, highlighting the critical need for active engagement and responsiveness. Prioritizing consistency, empathy, and involvement promotes a nurturing environment where children thrive and build lasting trust with their parents.
Infographic: Neglectful parenting vs Authoritative parenting
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com