Co-parenting involves shared responsibilities and decision-making between separated or divorced parents, promoting active cooperation for the child's well-being, while traditional parenting typically centers on a single household's authority and routine. Discover the benefits and challenges of each approach in this article.
Table of Comparison
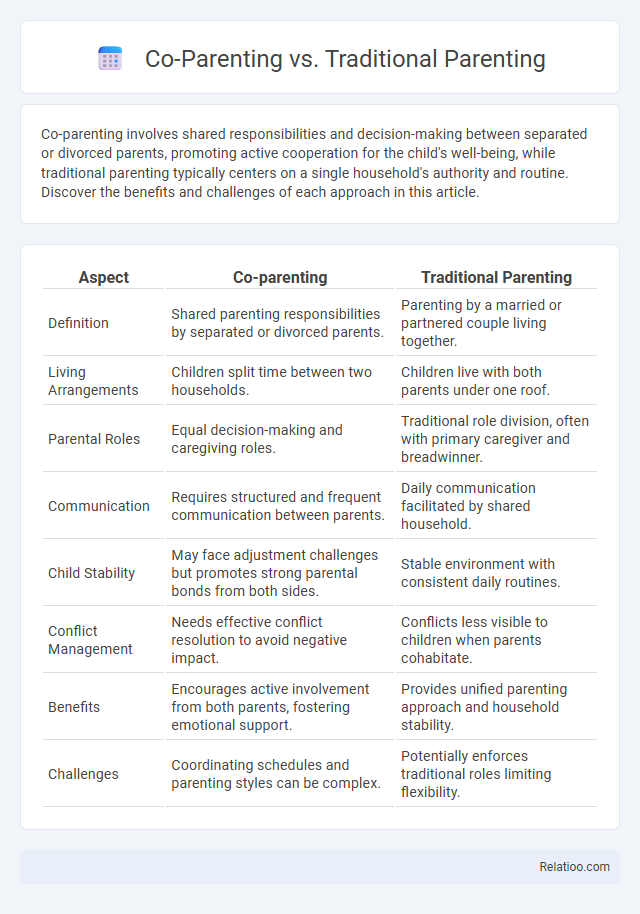
| Aspect | Co-parenting | Traditional Parenting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared parenting responsibilities by separated or divorced parents. | Parenting by a married or partnered couple living together. |
| Living Arrangements | Children split time between two households. | Children live with both parents under one roof. |
| Parental Roles | Equal decision-making and caregiving roles. | Traditional role division, often with primary caregiver and breadwinner. |
| Communication | Requires structured and frequent communication between parents. | Daily communication facilitated by shared household. |
| Child Stability | May face adjustment challenges but promotes strong parental bonds from both sides. | Stable environment with consistent daily routines. |
| Conflict Management | Needs effective conflict resolution to avoid negative impact. | Conflicts less visible to children when parents cohabitate. |
| Benefits | Encourages active involvement from both parents, fostering emotional support. | Provides unified parenting approach and household stability. |
| Challenges | Coordinating schedules and parenting styles can be complex. | Potentially enforces traditional roles limiting flexibility. |
Understanding Co-parenting and Traditional Parenting
Understanding co-parenting involves shared responsibilities and communication between separated or divorced parents, ensuring the child's well-being through cooperation and mutual support. Traditional parenting typically refers to a single or two-parent household where one or both parents handle child-rearing duties without necessarily coordinating separately. Your choice between co-parenting and traditional parenting impacts family dynamics, requiring clear roles and consistency to foster a stable environment for your child.
Key Differences Between Co-parenting and Traditional Parenting
Co-parenting involves shared responsibilities and decision-making between two or more adults who may live separately, emphasizing collaboration for the child's welfare. Traditional parenting typically features one primary caregiver responsible for daily child-rearing tasks and decisions, often within a single household. Key differences include the level of parental involvement, communication dynamics, and living arrangements, with co-parenting requiring structured cooperation despite physical separation.
Pros and Cons of Co-parenting
Co-parenting offers the advantage of shared responsibilities, allowing both parents to actively participate in their child's upbringing, which can lead to improved emotional support and balanced decision-making. However, co-parenting requires effective communication and cooperation, and conflicts or inconsistent parenting styles may negatively impact the child's stability. Traditional parenting, while providing a unified household environment, often places the majority of caregiving duties on one parent, which can lead to increased stress and limited parental engagement.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Traditional Parenting
Traditional parenting offers a structured family environment with clear roles, often providing children stability and consistent discipline. However, this approach can sometimes limit parental flexibility and communication, potentially leading to increased stress and less shared responsibility between parents. While traditional parenting emphasizes hierarchy, it may lack the collaborative decision-making found in co-parenting models, which can affect emotional support and adaptability.
Communication Strategies in Co-parenting
Effective communication strategies in co-parenting involve clear, consistent, and respectful dialogue focused on the child's best interests, which differs significantly from traditional parenting where one primary caregiver typically makes decisions. Co-parenting requires active listening, regular updates, and conflict resolution techniques to manage shared responsibilities and prevent misunderstandings. Utilizing tools such as parenting apps, scheduled meetings, and written agreements enhances transparency and cooperation between co-parents.
Parental Roles and Responsibilities Compared
Co-parenting involves shared parental roles and responsibilities where both parents actively participate in decision-making, child-rearing, and emotional support regardless of their living arrangements. Traditional parenting typically assigns distinct and often gender-based roles, with one parent primarily responsible for financial support and the other for daily caregiving tasks. Co-parenting emphasizes collaboration and flexibility, ensuring balanced involvement in education, healthcare, and discipline, while traditional parenting may centralize these duties within a single household dynamic.
Impact on Child’s Emotional Development
Co-parenting fosters collaborative decision-making, which enhances a child's emotional security by providing consistent support from both parents. Traditional parenting may offer stability, but can limit the child's exposure to diverse emotional guidance compared to co-parenting arrangements. Your child's emotional development thrives when both parents actively engage, balancing warmth and discipline to nurture resilience and self-esteem.
Legal and Financial Considerations
Co-parenting involves shared legal responsibilities and financial obligations between separated or unmarried parents, often requiring formal agreements to ensure clarity in child support, custody, and decision-making rights. Traditional parenting typically places legal and financial duties on one custodial parent, who manages child support and sole decision-making authority, with the non-custodial parent providing financial support through court-ordered arrangements. Your choice between these parenting approaches significantly impacts legal processes and financial planning, influencing stability and resource allocation for the child's upbringing.
Navigating Conflicts Between Parenting Styles
Navigating conflicts between co-parenting and traditional parenting styles requires clear communication and a commitment to prioritizing the child's well-being. You can reduce tension by establishing consistent routines that respect both parents' approaches while fostering mutual respect and flexibility. Implementing conflict resolution strategies tailored to your co-parenting arrangement helps maintain harmony and support your child's emotional stability.
Choosing the Best Approach for Your Family
Choosing the best approach for your family involves evaluating the unique dynamics of co-parenting, traditional parenting, and blended co-parenting models to ensure the child's well-being remains the priority. Co-parenting emphasizes shared responsibilities and communication between separated or divorced parents, fostering a supportive environment, while traditional parenting typically centers on a single primary caregiver managing the majority of child-rearing duties. Families benefit from assessing factors such as parental availability, conflict levels, and the child's needs to determine the most effective parenting structure that promotes emotional stability and healthy development.
Infographic: Co-parenting vs Traditional Parenting
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com