Co-regulation in relationships involves mutual emotional support that fosters secure attachment, which forms the foundation for trust and emotional safety. Discover how co-regulation strengthens attachment bonds and enhances relationship stability in this article.
Table of Comparison
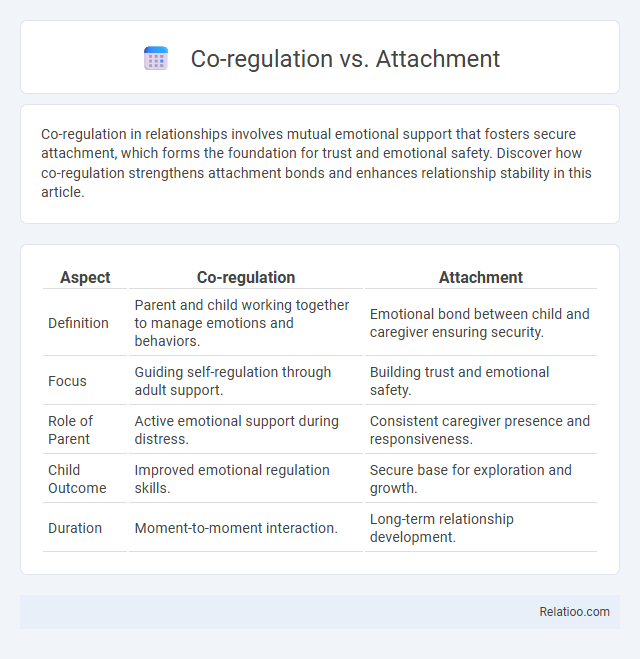
| Aspect | Co-regulation | Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Parent and child working together to manage emotions and behaviors. | Emotional bond between child and caregiver ensuring security. |
| Focus | Guiding self-regulation through adult support. | Building trust and emotional safety. |
| Role of Parent | Active emotional support during distress. | Consistent caregiver presence and responsiveness. |
| Child Outcome | Improved emotional regulation skills. | Secure base for exploration and growth. |
| Duration | Moment-to-moment interaction. | Long-term relationship development. |
Understanding Co-regulation: Definition and Principles
Co-regulation refers to the dynamic, reciprocal process where caregivers and children share emotional and physiological states to manage stress and regulate behavior, forming a foundation for healthy attachment. It involves responsive interactions that help children develop self-regulation skills by providing external support during moments of distress. Understanding co-regulation emphasizes principles such as caregiver sensitivity, consistency, and emotional attunement, which contribute to secure attachment and optimal child development.
The Fundamentals of Attachment Theory
Attachment theory centers on the emotional bond between a child and caregiver, which shapes the child's sense of security and influences future relationships. Co-regulation refers to the caregiver's role in helping the child manage emotions through responsive interactions, fostering emotional development and resilience. Your understanding of these fundamentals clarifies how secure attachment forms through consistent, supportive co-regulation that nurtures healthy emotional growth.
Key Differences Between Co-regulation and Attachment
Co-regulation involves the dynamic process where a caregiver supports and helps manage a child's emotional state, while attachment refers to the deep, enduring emotional bond that forms between a child and caregiver, providing security and trust. Key differences include co-regulation being an ongoing, moment-to-moment interaction influencing emotional regulation, whereas attachment is a lasting relationship that shapes a child's overall social and emotional development. Understanding these distinctions helps you better support your child's growth by recognizing when to actively assist their emotional regulation versus fostering long-term secure connections.
The Science Behind Emotional Regulation in Children
Attachment forms the foundation of a child's emotional regulation by establishing secure bonds that promote trust and safety, essential for healthy brain development. Co-regulation involves caregivers responding to a child's emotional cues, helping You guide Your child through stress by modeling calm and supportive behaviors. Understanding these mechanisms reveals how consistent co-regulation within the context of secure attachment enhances a child's ability to manage emotions independently over time.
Attachment Styles and Their Lifelong Impact
Attachment styles, including secure, anxious, avoidant, and disorganized, significantly shape an individual's emotional regulation and interpersonal relationships throughout life. Secure attachment fosters healthy co-regulation processes, enabling effective stress management and emotional support seeking, while insecure attachment styles often result in maladaptive co-regulation patterns that can lead to difficulties in trust, intimacy, and emotional resilience. Understanding the lifelong impact of attachment styles is crucial for addressing mental health challenges and improving relational dynamics across the lifespan.
How Co-regulation Influences Child Development
Co-regulation plays a crucial role in child development by providing a supportive emotional environment where a caregiver helps a child manage their physiological and emotional states, fostering self-regulation skills over time. This process strengthens neural connections in the prefrontal cortex, enhancing executive function, emotional control, and social competence. Unlike attachment, which forms the emotional bond ensuring safety and security, co-regulation directly facilitates the development of a child's ability to cope with stress and build resilience through responsive interactions.
Practical Strategies for Promoting Co-regulation
Practical strategies for promoting co-regulation involve creating a supportive environment where your child feels safe and understood, using calm and consistent responses to help them manage emotions effectively. Techniques such as mirroring your child's feelings, practicing deep breathing together, and establishing predictable routines enhance emotional connection and self-regulation skills. Prioritizing empathetic communication and modeling adaptive coping mechanisms strengthens the foundation for secure attachment and emotional resilience.
The Role of Secure Attachment in Emotional Health
Secure attachment provides a foundation for healthy emotional regulation by fostering trust and safety in relationships, which enhances Your ability to manage stress and emotional challenges. Co-regulation, involving mutual regulation between caregiver and child, supports emotional development and strengthens secure attachment bonds. Together, secure attachment and effective co-regulation contribute to improved emotional health and resilience throughout life.
Integrating Co-regulation and Attachment in Parenting
Integrating co-regulation and attachment in parenting enhances your child's emotional development by fostering a secure bond while guiding their self-regulation skills. Co-regulation involves parents responding sensitively to a child's emotional cues, supporting the gradual development of independent emotion management. Attachment theory emphasizes the importance of a strong, trusting relationship that provides a safe base for your child to explore and learn, making the combination essential for healthy psychological growth.
Common Misconceptions About Co-regulation vs Attachment
Co-regulation and attachment are often confused, but they represent distinct processes: co-regulation involves caregiver support in managing a child's emotional states, while attachment refers to the deep emotional bond formed over time. A common misconception is that co-regulation automatically ensures secure attachment, but secure attachment requires consistent, sensitive caregiving beyond moment-to-moment emotional regulation. Understanding these differences helps you foster healthier developmental relationships by addressing both emotional support and long-term bonding needs.
Infographic: Co-regulation vs Attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com