Redirection in relationships helps shift focus away from conflict toward constructive solutions, while time-outs provide necessary space to cool down emotions and prevent escalation. Discover how to effectively use redirection and time-outs to improve communication and strengthen your relationship in this article.
Table of Comparison
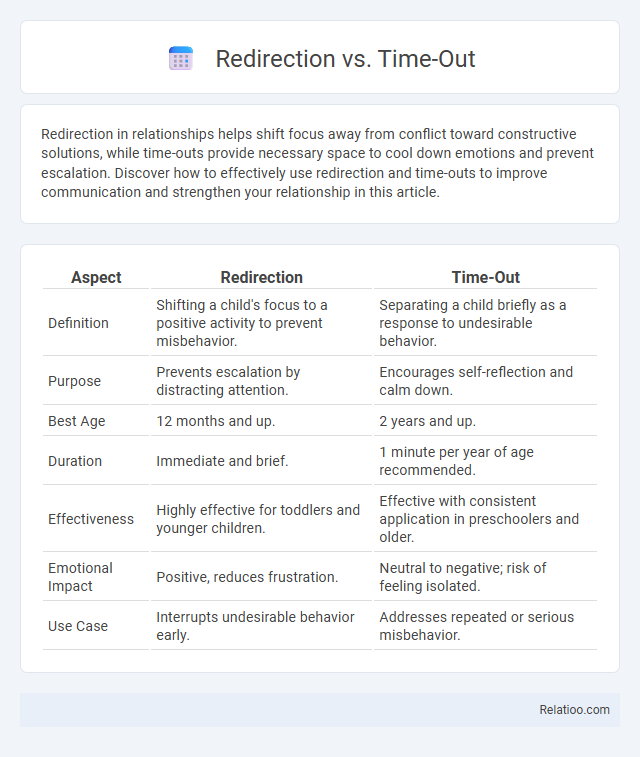
| Aspect | Redirection | Time-Out |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shifting a child's focus to a positive activity to prevent misbehavior. | Separating a child briefly as a response to undesirable behavior. |
| Purpose | Prevents escalation by distracting attention. | Encourages self-reflection and calm down. |
| Best Age | 12 months and up. | 2 years and up. |
| Duration | Immediate and brief. | 1 minute per year of age recommended. |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective for toddlers and younger children. | Effective with consistent application in preschoolers and older. |
| Emotional Impact | Positive, reduces frustration. | Neutral to negative; risk of feeling isolated. |
| Use Case | Interrupts undesirable behavior early. | Addresses repeated or serious misbehavior. |
Understanding Redirection and Time-Out
Redirection and time-out are behavioral management strategies primarily used to guide children's actions by addressing undesirable behavior in real time. Redirection involves shifting a child's attention from inappropriate behavior to a more acceptable activity, promoting positive engagement without punishment. Time-out temporarily removes the child from a stimulating environment, providing a calm space to reflect, which helps reduce aggression or defiance by decreasing the exposure to triggers.
Key Differences Between Redirection and Time-Out
Redirection involves guiding Your child's behavior by offering alternative actions or positive reinforcement, promoting learning and self-control, whereas Time-Out is a disciplinary method that temporarily isolates the child to discourage undesirable behavior. Redirection emphasizes engagement and proactive behavior change, while Time-Out focuses on providing a quiet space for reflection and calming down. The key difference lies in redirection's constructive approach compared to the punitive nature of Time-Out.
Psychological Principles Behind Each Technique
Redirection leverages cognitive refocusing by guiding attention away from distressing stimuli to more positive or neutral activities, reducing anxiety and agitation through environmental control. Time-Out employs behavior modification grounded in operant conditioning by removing access to reinforcement, thereby decreasing undesired behaviors through negative punishment. Combining Redirection and Time-Out utilizes both distraction and consequence-based learning, addressing immediate emotional regulation and long-term behavior change in therapeutic settings.
When to Use Redirection
Redirection should be used when the content or URL has permanently or temporarily changed, guiding users and search engines to the correct page to preserve SEO value and user experience. Time-outs are appropriate for temporary server unavailability or delays, indicating the server is temporarily unable to fulfill the request without changing the URL. Unlike time-outs, redirections ensure seamless navigation and prevent broken links by automatically forwarding users to the new destination.
Situations Ideal for Time-Out
Time-Out is ideal for situations requiring immediate behavioral correction without redirecting focus, such as calming a child after emotional outbursts or noncompliance in structured environments. It effectively separates the individual from stimuli that reinforce negative behavior, promoting self-regulation and reflection. Redirection suits scenarios needing gentle behavioral guidance by shifting attention, while traditional redirection involves guiding actions toward positive alternatives rather than isolation.
Pros and Cons of Redirection
Redirection offers the advantage of guiding behavior without confrontation, making it effective for preventing escalation and promoting positive actions. However, it requires patience and consistency, as repeated attempts may be needed before achieving desired outcomes. Your success with redirection depends on understanding individual triggers and providing clear alternatives to undesirable behaviors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Time-Out
Time-Out offers the advantage of providing a clear, consistent consequence for undesirable behavior, helping children learn self-regulation by removing them from reinforcing stimuli temporarily. However, its disadvantages include the potential for emotional distress or feelings of isolation if not implemented with empathy, and it may be less effective for children who do not respond to removal of attention. Unlike redirection, which guides behavior towards positive actions, Time-Out focuses on behavior cessation but requires careful timing and consistency to avoid reinforcing negative behaviors.
Impact on Child Behavior and Development
Redirection effectively improves child behavior by guiding attention away from negative actions toward positive alternatives, fostering self-regulation and problem-solving skills. Time-outs provide children with a pause to calm down, but excessive use can lead to feelings of isolation and impact emotional development negatively. When combined appropriately, redirection and time-outs balance immediate behavior management with long-term social and emotional growth.
Common Misconceptions About Both Methods
Redirection and time-out are often confused, yet they serve distinct purposes in behavior management; redirection guides Your child towards an appropriate activity, while time-out removes them momentarily to calm down. A common misconception is that time-out is purely punitive, but it is actually intended to help the child regain self-control. Many also believe redirection works immediately for all children, though its effectiveness depends on timing and understanding individual needs.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Child
Choosing between redirection, time-out, and ignoring behaviors depends on your child's temperament and the situation's severity. Redirection is effective for younger children or minor misbehaviors by shifting focus to a positive activity, while time-outs help older children understand consequences in a calm, structured environment. Ignoring intentional attention-seeking actions can reduce their frequency by removing reinforcement, but using this method requires consistent application and clear boundaries to ensure your child's behavioral development stays on track.
Infographic: Redirection vs Time-Out
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com