Bar Mitzvah marks a Jewish boy's religious coming of age at 13, while Confirmation celebrates a Christian youth's affirmation of faith typically in their early teens. Learn more about these distinct traditions and their significance in this article.
Table of Comparison
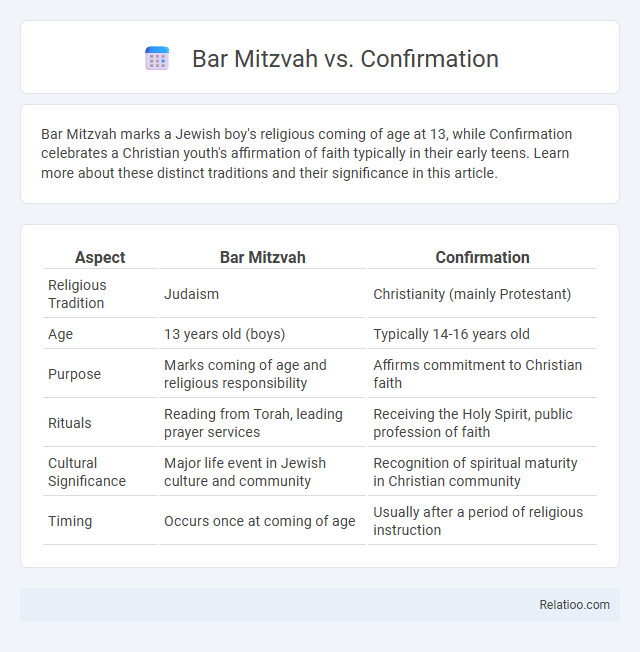
| Aspect | Bar Mitzvah | Confirmation |
|---|---|---|
| Religious Tradition | Judaism | Christianity (mainly Protestant) |
| Age | 13 years old (boys) | Typically 14-16 years old |
| Purpose | Marks coming of age and religious responsibility | Affirms commitment to Christian faith |
| Rituals | Reading from Torah, leading prayer services | Receiving the Holy Spirit, public profession of faith |
| Cultural Significance | Major life event in Jewish culture and community | Recognition of spiritual maturity in Christian community |
| Timing | Occurs once at coming of age | Usually after a period of religious instruction |
Introduction to Bar Mitzvah and Confirmation
Bar Mitzvah and Confirmation are significant rites of passage in Jewish and Christian traditions, marking a young person's transition into religious adulthood. Bar Mitzvah, celebrated at age 13 in Judaism, signifies the boy's obligation to observe commandments and participate fully in community life. Confirmation follows catechism instruction in Christianity, typically in adolescence, affirming the individual's commitment to faith and church membership.
Historical Origins of Bar Mitzvah and Confirmation
The Bar Mitzvah originated in Jewish tradition around the 13th century as a ceremony marking a boy's coming of age and religious responsibilities at age 13. Confirmation, rooted in Christian practice, especially within Protestant denominations, emerged during the Reformation in the 16th century to affirm a baptized person's faith. Your understanding of these rites of passage highlights distinct historical origins, reflecting cultural and religious milestones in adolescence.
Religious Significance in Judaism and Christianity
Bar Mitzvah in Judaism marks a boy's transition to religious adulthood at age 13, granting him full participation in Jewish rituals and obligations. Confirmation in Christianity, particularly in Protestant traditions, affirms a baptized individual's commitment to the faith, usually occurring in early adolescence and symbolizing spiritual maturity. Your understanding of these rites highlights their role as significant religious milestones, with the Bar Mitzvah emphasizing Jewish law and community responsibility, while Confirmation focuses on personal faith affirmation within Christian doctrine.
Age of Ceremony: Bar Mitzvah vs Confirmation
The age of ceremony distinguishes a Bar Mitzvah from Confirmation, with Bar Mitzvahs typically held at 13 years old for Jewish boys, marking their religious adulthood, while Confirmations usually occur around 14 to 16 years old in Christian traditions, symbolizing affirmation of faith. This age difference reflects cultural and religious milestones important in guiding your child's spiritual development. Understanding these age-specific rites of passage helps you appreciate their unique roles in fostering religious identity.
Rituals and Traditions Compared
Bar Mitzvah is a Jewish ritual marking a boy's coming of age at 13, characterized by reading from the Torah and leading prayers during synagogue services. Confirmation, common in Christian denominations, usually occurs around age 14-16 and involves a formal affirmation of faith, often celebrated with a church ceremony and the laying on of hands by clergy. Rite of passage rituals vary widely across cultures, encompassing ceremonies such as ceremonies involving symbolic objects, storytelling, and communal feasting to signify transition into adulthood or social roles.
Role of Family and Community
Bar Mitzvah, Confirmation, and Rite of Passage ceremonies each emphasize the integral role of family and community in marking a young person's transition into adulthood. Your involvement in these events strengthens communal bonds, as family members and community elders gather to offer support, guidance, and celebration. The shared rituals foster a sense of belonging and cultural continuity, underscoring the collective investment in the individual's spiritual and social growth.
Preparation and Education Requirements
Bar Mitzvah preparation involves extensive study of Hebrew, Jewish laws, and Torah portions, requiring months of tutoring to ensure the young person can read and understand religious texts confidently. Confirmation classes typically emphasize Christian teachings, Bible study, and moral education, often lasting several months to a year, to prepare youth for their public affirmation of faith. Your participation in either ceremony demands commitment to religious education, reflection, and practice, highlighting the transformative nature of these rites of passage.
Symbolic Meaning and Spiritual Impact
Bar Mitzvah signifies a Jewish boy's transition to religious adulthood, symbolizing responsibility for mitzvot and spiritual maturity within the community; its deep-rooted ritual fosters a lifelong connection to Jewish tradition and identity. Confirmation, primarily in Christian contexts, represents affirming faith and commitment following baptism, emphasizing personal acceptance of religious beliefs and active participation in the spiritual life of the church. Rite of passage broadly encompasses cultural ceremonies marking significant life transitions, serving as crucial symbols of transformation, social recognition, and spiritual growth across diverse societies.
Regional and Denominational Variations
Bar Mitzvah is primarily observed in Jewish communities, marking a boy's religious coming of age at 13, with variations between Orthodox, Conservative, and Reform denominations in ceremony style and religious emphasis. Confirmation is predominantly a Christian rite, especially within Lutheran, Methodist, and Anglican traditions, typically conducted in adolescence to affirm faith, with regional practices differing in age and ritual components. Rite of passage encompasses diverse cultural ceremonies worldwide, from Indigenous initiation rituals to secular milestone celebrations, reflecting significant regional and denominational distinctions that highlight specific social or spiritual transitions.
Modern Interpretations and Social Relevance
Bar Mitzvah, Confirmation, and Rite of Passage serve as pivotal ceremonies marking spiritual maturity across different religious and cultural traditions, with modern interpretations emphasizing personal identity and community belonging. Bar Mitzvah, rooted in Judaism, has evolved to include diverse educational and social components reflecting contemporary values of inclusivity and personal choice. Confirmation, common in Christian denominations, is increasingly viewed as a reaffirmation of faith tailored to individual spiritual journeys, while Rites of Passage in various cultures adapt to societal changes by integrating rites that promote social responsibility and cultural heritage preservation.
Infographic: Bar Mitzvah vs Confirmation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com