The sensitive period refers to a specific developmental phase when individuals are highly receptive to forming relationships, while the sensitive window denotes a broader timeframe allowing for flexibility in relational growth. Explore this article to understand how these concepts impact relationship development.
Table of Comparison
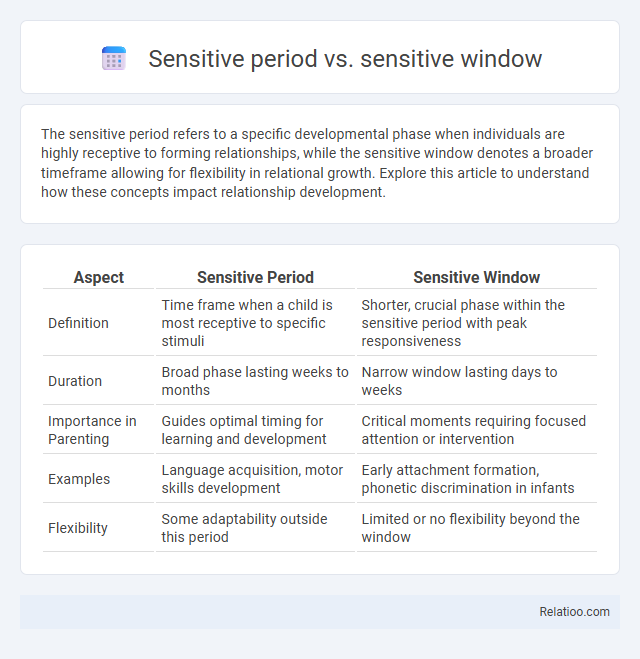
| Aspect | Sensitive Period | Sensitive Window |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Time frame when a child is most receptive to specific stimuli | Shorter, crucial phase within the sensitive period with peak responsiveness |
| Duration | Broad phase lasting weeks to months | Narrow window lasting days to weeks |
| Importance in Parenting | Guides optimal timing for learning and development | Critical moments requiring focused attention or intervention |
| Examples | Language acquisition, motor skills development | Early attachment formation, phonetic discrimination in infants |
| Flexibility | Some adaptability outside this period | Limited or no flexibility beyond the window |
Introduction to Sensitive Period and Sensitive Window
The sensitive period refers to a specific timeframe during development when Your brain is particularly receptive to acquiring certain skills or knowledge, such as language or emotional bonding. A sensitive window is a narrower interval within this period where environmental stimuli have the most pronounced impact on neural plasticity and developmental outcomes. Understanding these concepts is crucial for optimizing learning and intervention strategies during early childhood.
Defining Sensitive Period in Development
A sensitive period in development refers to a specific timeframe when the brain is particularly receptive to certain environmental stimuli, allowing for optimal learning and skill acquisition. Unlike a sensitive window, which implies a narrower and more rigid timeframe, a sensitive period offers some flexibility but still represents a peak in neural plasticity. Defining sensitive periods involves identifying phases during childhood or early life when experiences have a maximum impact on cognitive, emotional, or motor development.
Understanding the Concept of Sensitive Window
Sensitive period refers to a developmental phase when the brain is particularly receptive to certain environmental stimuli, enabling optimal learning and skill acquisition. Sensitive window is a more precise term emphasizing a narrower timeframe within the sensitive period during which specific neural circuits exhibit heightened plasticity and responsiveness. Understanding the concept of the sensitive window is crucial for effectively targeting interventions and educational strategies that capitalize on peak neural adaptability for language acquisition, emotional regulation, and sensory development.
Key Differences Between Sensitive Period and Sensitive Window
Sensitive periods refer to broad phases in development when the brain is particularly receptive to specific types of learning or environmental stimuli, whereas sensitive windows are narrower timeframes within these periods marked by peak neural plasticity. The key difference lies in the scope and intensity: sensitive periods encompass general developmental readiness, while sensitive windows denote heightened sensitivity crucial for optimal acquisition of particular skills. Understanding these distinctions helps you tailor interventions or educational approaches to maximize developmental outcomes during these critical times.
Biological Basis of Sensitive Periods
Sensitive periods refer to specific phases in development when the brain exhibits heightened plasticity, allowing optimal learning and adaptation to environmental stimuli. Sensitive windows are narrower time frames within these periods characterized by even more intense neural receptivity essential for acquiring particular skills or functions, such as language or sensory integration. Your understanding of the biological basis of sensitive periods highlights the role of synaptic pruning, neurochemical changes, and critical gene expression patterns that drive the brain's ability to adapt during these key developmental intervals.
Neural Mechanisms Underlying Sensitive Windows
Sensitive periods refer to developmental phases when the brain exhibits heightened plasticity, allowing for profound neural changes in response to environmental stimuli. Sensitive windows, a subset of sensitive periods, denote precise timeframes during which specific neural circuits or functions are optimally shaped by experience, mediated by mechanisms like synaptic pruning and critical gene expression. Neural mechanisms underlying sensitive windows involve molecular pathways such as NMDA receptor modulation, inhibitory interneuron maturation, and epigenetic modifications that regulate synaptic plasticity and ensure experience-dependent neural remodeling.
Examples of Sensitive Periods in Human Development
Sensitive periods in human development are specific times when the brain is particularly receptive to acquiring certain skills or knowledge, such as language acquisition in early childhood or emotional bonding during infancy. Sensitive windows refer to optimal but not exclusive timeframes for development, whereas sensitive periods denote more critical phases requiring specific stimuli for typical growth. Your awareness of examples like imprinting in infancy, vision development in early years, and motor skill acquisition during toddlerhood can enhance understanding of these crucial developmental stages.
Implications of Missing Sensitive Windows
Missing sensitive windows during early development can result in irreversible deficits in language acquisition, social bonding, and sensory processing. Sensitive periods represent optimal times for brain plasticity where environmental input crucially shapes neural circuits, while sensitive windows denote narrower intervals within those periods when specific skills must be reinforced. Failure to provide appropriate stimuli during these windows often leads to long-term cognitive and behavioral impairments, highlighting the importance of timely intervention in education and therapy.
Educational and Clinical Significance
Sensitive periods refer to developmental stages when the brain is particularly receptive to specific types of learning or environmental stimuli, crucial for acquiring language, motor skills, or social behaviors. Sensitive windows denote narrower timeframes within these periods where interventions yield maximal educational and clinical benefits, such as early speech therapy in children with delayed language development. Your timely recognition of these phases ensures targeted, effective education and therapy, optimizing developmental outcomes and minimizing long-term deficits.
Conclusion: Sensitive Period vs Sensitive Window
The sensitive period refers to a specific developmental timeframe during which an organism is particularly receptive to certain environmental stimuli, crucial for acquiring skills such as language or sensory abilities. A sensitive window, while similar, is often considered a more flexible or extended phase within the sensitive period where plasticity allows for learning or adaptation but with diminishing returns over time. In conclusion, sensitive periods denote rigid, critical phases essential for typical development, whereas sensitive windows offer broader intervals allowing for gradual input and potential recovery in developmental processes.
Infographic: Sensitive period vs Sensitive window
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com