Redirection involves guiding behavior away from negative actions to more appropriate ones, while positive reinforcement strengthens desirable behavior through rewards and praise. Explore this article to understand how mastering both techniques can improve your relationships.
Table of Comparison
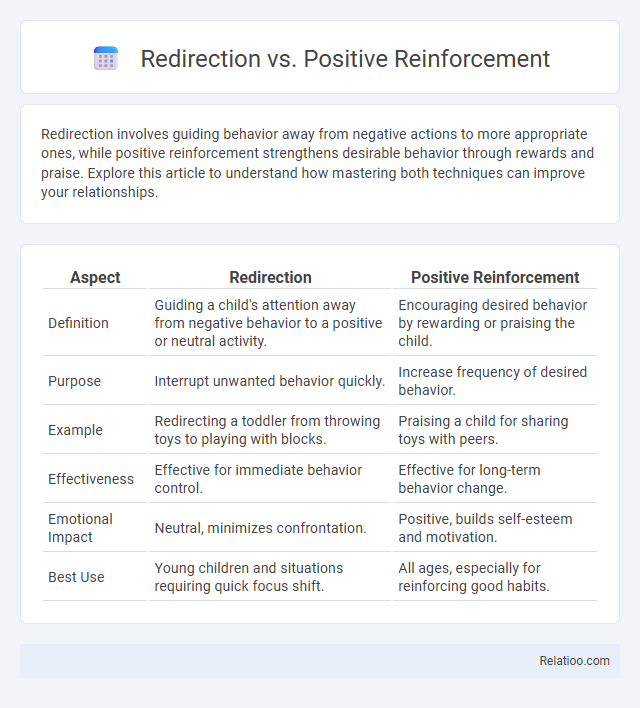
| Aspect | Redirection | Positive Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guiding a child's attention away from negative behavior to a positive or neutral activity. | Encouraging desired behavior by rewarding or praising the child. |
| Purpose | Interrupt unwanted behavior quickly. | Increase frequency of desired behavior. |
| Example | Redirecting a toddler from throwing toys to playing with blocks. | Praising a child for sharing toys with peers. |
| Effectiveness | Effective for immediate behavior control. | Effective for long-term behavior change. |
| Emotional Impact | Neutral, minimizes confrontation. | Positive, builds self-esteem and motivation. |
| Best Use | Young children and situations requiring quick focus shift. | All ages, especially for reinforcing good habits. |
Introduction to Redirection and Positive Reinforcement
Redirection guides Your behavior by diverting attention from undesirable actions to appropriate alternatives, promoting positive changes without punishment. Positive reinforcement strengthens desired behaviors by rewarding them, increasing the likelihood they will be repeated over time. Both strategies emphasize encouraging good habits through non-confrontational methods that support learning and growth.
Defining Redirection in Behavior Management
Redirection in behavior management involves guiding Your child's attention from undesirable behaviors to more appropriate activities, effectively preventing negative actions before they occur. Unlike positive reinforcement, which rewards desired behaviors to encourage repetition, redirection proactively shifts focus to promote positive alternatives. Clear redirection strategies create a foundation for consistent behavior modification and support long-term behavioral success.
Understanding Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement involves rewarding desired behavior to increase its occurrence, making it an effective tool in shaping Your pet's actions by providing clear positive outcomes. Redirection, by contrast, shifts unwanted behavior to a more acceptable activity without necessarily adding a reward, while punishment aims to decrease behavior through negative consequences. Understanding positive reinforcement helps create lasting behavioral changes by encouraging repetition of good habits through consistent rewards.
Key Differences Between Redirection and Positive Reinforcement
Redirection involves guiding your child or pet away from undesirable behavior toward a more acceptable alternative, while positive reinforcement rewards desired behavior to encourage its repetition. Redirection focuses on preventing negative actions by shifting attention, whereas positive reinforcement strengthens good behavior through praise or rewards. Understanding these distinctions helps you effectively shape behavior by combining immediate behavioral correction with long-term motivation strategies.
Psychological Principles Behind Each Approach
Redirection involves guiding Your child's attention away from undesirable behavior toward a more appropriate activity, leveraging distraction and refocusing techniques grounded in cognitive behavior theory. Positive reinforcement strengthens desirable behaviors by offering rewards or praise, employing principles from operant conditioning that increase the likelihood of behavior repetition. Punishment, contrasting with these methods, aims to decrease unwanted behaviors through negative consequences but may lead to adverse psychological effects if misapplied, highlighting the importance of understanding their underlying psychological impacts.
Benefits of Using Redirection
Redirection effectively guides behavior by diverting attention from undesired actions to appropriate alternatives, reducing conflicts and promoting positive outcomes. Unlike positive reinforcement, which rewards desired behavior, redirection proactively prevents escalation by modifying the environment or focus before issues arise. Employing redirection enhances emotional regulation while fostering cooperative interactions, making it a valuable strategy in educational and caregiving settings.
Advantages of Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Positive reinforcement techniques increase desired behaviors by rewarding positive actions, leading to longer-lasting behavioral changes compared to redirection alone. These methods strengthen neural pathways associated with good behavior, enhancing motivation and self-esteem in both children and adults. Unlike simple redirection, positive reinforcement creates a proactive environment that encourages consistent, repeatable positive behaviors through incentives such as praise, treats, or privileges.
When to Use Redirection vs Positive Reinforcement
Use redirection when Your pet or child is engaged in an unwanted or potentially harmful behavior that needs immediate interruption to prevent negative outcomes. Positive reinforcement is most effective when encouraging desirable behaviors by rewarding and reinforcing them to increase their frequency over time. Redirection is ideal for managing behaviors in the moment, while positive reinforcement builds long-term habits through consistent rewards.
Common Misconceptions about Both Methods
Redirection often gets confused with positive reinforcement, but redirection involves guiding behavior away from undesirable actions, while positive reinforcement strengthens desired behaviors through rewards. A common misconception is that redirection alone changes behavior long-term, whereas it mainly prevents immediate issues without encouraging repetition of good behavior like positive reinforcement does. Your best approach combines both methods to effectively shape and maintain positive behavioral patterns.
Best Practices for Effective Behavior Guidance
Effective behavior guidance involves choosing between redirection, positive reinforcement, and redirection again to manage and encourage desired actions in children or individuals. You should apply redirection by gently guiding attention away from negative behavior toward a productive alternative, while positive reinforcement strengthens desired behaviors through rewards or praise. Best practices emphasize consistency, timely responses, and understanding individual needs to create a supportive environment that promotes lasting behavioral improvements.
Infographic: Redirection vs Positive Reinforcement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com