Parental burnout results from chronic, overwhelming exhaustion and emotional detachment due to prolonged parenting demands, while stress refers to temporary challenges that parents can often manage effectively. Explore in this article how to identify, differentiate, and address parental burnout versus stress for healthier family dynamics.
Table of Comparison
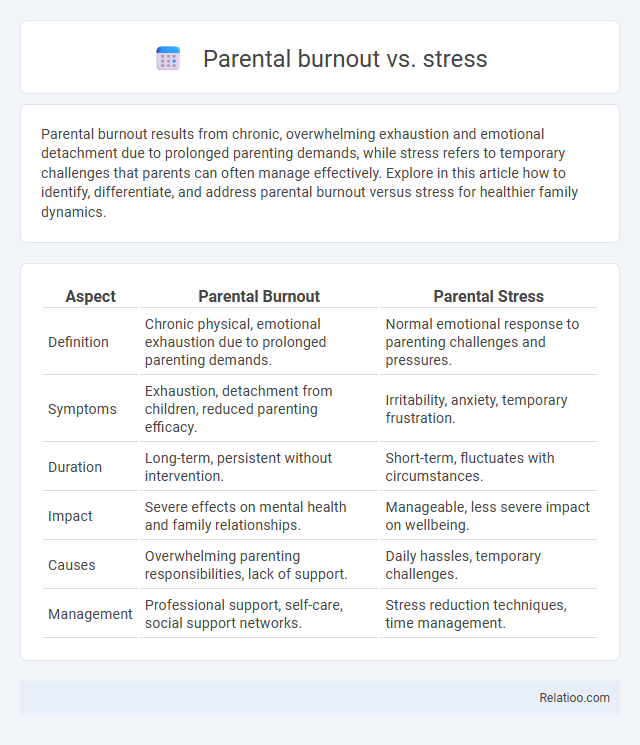
| Aspect | Parental Burnout | Parental Stress |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic physical, emotional exhaustion due to prolonged parenting demands. | Normal emotional response to parenting challenges and pressures. |
| Symptoms | Exhaustion, detachment from children, reduced parenting efficacy. | Irritability, anxiety, temporary frustration. |
| Duration | Long-term, persistent without intervention. | Short-term, fluctuates with circumstances. |
| Impact | Severe effects on mental health and family relationships. | Manageable, less severe impact on wellbeing. |
| Causes | Overwhelming parenting responsibilities, lack of support. | Daily hassles, temporary challenges. |
| Management | Professional support, self-care, social support networks. | Stress reduction techniques, time management. |
Understanding Parental Burnout: Definition and Signs
Parental burnout is a state of physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion caused by the chronic stress of parenting, distinct from general parental stress which is temporary and situational. Understanding parental burnout involves recognizing key signs such as overwhelming fatigue, emotional detachment from your children, and a sense of ineffectiveness in parenting duties. Identifying these symptoms early can help you seek appropriate support and prevent long-term consequences on family well-being.
What Differentiates Parental Burnout from Everyday Stress?
Parental burnout is characterized by overwhelming exhaustion, emotional distancing from your child, and a sense of inefficacy, distinct from everyday stress which is often temporary and manageable. Unlike typical stress that fluctuates with daily challenges, parental burnout results from prolonged exposure to chronic parenting demands without adequate support or recovery. Recognizing these differences helps identify when professional intervention may be necessary to restore your well-being and improve family dynamics.
Causes of Parental Burnout: Risk Factors to Know
Parental burnout stems from chronic overwhelming stress caused by prolonged emotional exhaustion, feelings of ineffectiveness, and emotional distancing from your children. Key risk factors include high parental demands, lack of social support, perfectionism, and insufficient recovery time, all contributing to the mental strain parents endure. Recognizing these causes helps differentiate parental burnout from general stress, highlighting the need for targeted strategies to manage and prevent this debilitating condition.
Common Triggers of Parental Stress
Parental burnout and stress both stem from prolonged caregiving demands, but burnout involves emotional exhaustion, cynicism, and a sense of inefficacy, while stress is typically more acute and manageable. Common triggers of parental stress include lack of support, unrealistic expectations, financial pressures, and children's challenging behaviors, which may intensify and escalate into burnout if unaddressed. Understanding these triggers helps you develop effective coping strategies to prevent chronic exhaustion and maintain your well-being.
Emotional and Physical Symptoms: Burnout vs. Stress
Parental burnout manifests through chronic emotional exhaustion, feelings of detachment from your children, and a pervasive sense of inefficacy, while stress typically triggers temporary anxiety, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Physically, burnout can cause severe fatigue, sleep disturbances, and somatic complaints such as headaches or muscle pain, whereas stress often results in increased heart rate, muscle tension, and short-term disruptions in sleep. Recognizing these distinct emotional and physical symptoms can help you address parental burnout more effectively compared to managing everyday stress.
The Impact of Burnout on Family Dynamics
Parental burnout significantly disrupts family dynamics by reducing emotional availability and increasing detachment from children, unlike general parental stress which tends to be situational and temporary. The chronic exhaustion and overwhelming feelings associated with burnout lead to impaired communication, decreased patience, and strained parent-child relationships. This persistent state of burnout may result in long-term negative effects on children's emotional well-being and overall family cohesion.
Coping Mechanisms for Managing Parental Stress
Parental burnout results from chronic, unmanaged stress and differs from everyday parental stress, which is typically temporary and situational. Effective coping mechanisms for managing parental stress include practicing mindfulness, seeking social support, prioritizing self-care, and setting realistic expectations to prevent burnout. You can reduce the risk of parental burnout by consistently applying these strategies to maintain emotional balance and resilience.
Prevention Strategies for Avoiding Parental Burnout
Parental burnout, distinct from general parenting stress, results from prolonged emotional exhaustion, detachment, and reduced parental efficacy. Stress typically stems from temporary challenges, whereas burnout involves chronic overwhelm demanding targeted prevention strategies such as establishing consistent self-care routines, seeking social support, and setting realistic expectations. Your commitment to these proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of parental burnout and promote long-term well-being.
When to Seek Professional Help: Warning Signs
Parental burnout manifests through chronic exhaustion, emotional distancing from children, and a reduced sense of accomplishment, signaling when professional help is necessary. Stress may cause temporary irritability and fatigue, but persistent symptoms such as overwhelming feelings of hopelessness or inability to care for children indicate burnout requiring intervention. Early recognition of warning signs, like sleep disturbances and withdrawal, enables timely support from mental health professionals to prevent long-term psychological harm.
Building Resilience: Supporting Parental Well-Being
Parental burnout differs from typical stress as it involves emotional exhaustion, detachment, and a sense of inefficacy directly related to parenting demands, often requiring targeted resilience-building strategies to mitigate long-term negative effects. Stress in parenting is usually temporary and situational, whereas parental burnout signifies a chronic state that undermines well-being, necessitating support systems focusing on emotional regulation, self-care, and social connection. Building resilience through mindfulness, realistic goal-setting, and seeking community resources enhances parental well-being by reducing burnout risks and fostering sustainable parenting practices.
Infographic: Parental burnout vs stress
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com