Parental authority defines the rights and responsibilities parents have to guide and discipline their children, while parental autonomy emphasizes a child's right to make independent choices and develop self-governance. Explore the balance and implications of these concepts in family dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
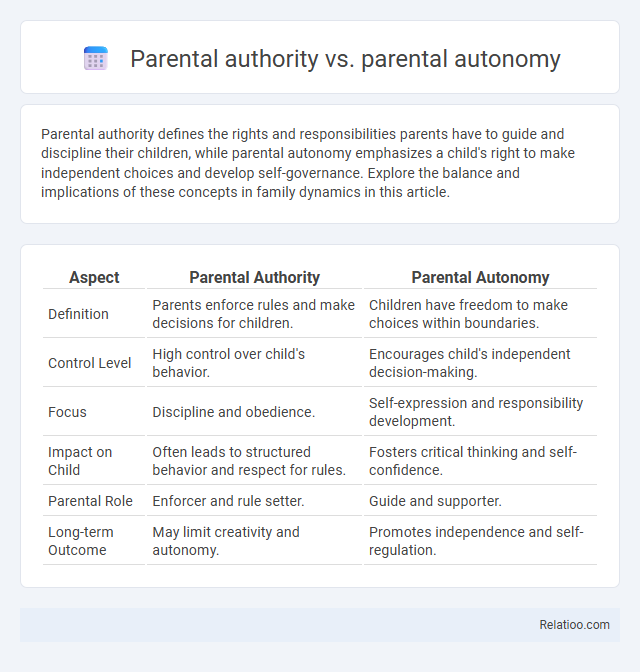
| Aspect | Parental Authority | Parental Autonomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Parents enforce rules and make decisions for children. | Children have freedom to make choices within boundaries. |
| Control Level | High control over child's behavior. | Encourages child's independent decision-making. |
| Focus | Discipline and obedience. | Self-expression and responsibility development. |
| Impact on Child | Often leads to structured behavior and respect for rules. | Fosters critical thinking and self-confidence. |
| Parental Role | Enforcer and rule setter. | Guide and supporter. |
| Long-term Outcome | May limit creativity and autonomy. | Promotes independence and self-regulation. |
Defining Parental Authority and Parental Autonomy
Parental authority refers to the legal and societal rights granted to parents to make decisions for their child's welfare, including education, health, and discipline. Parental autonomy emphasizes your personal choice and freedom in raising and guiding your child according to your values and beliefs without undue external interference. Understanding the balance between parental authority and parental autonomy is essential for fostering effective parenting that respects both legal responsibilities and individual family dynamics.
Historical Perspectives on Parental Roles
Historical perspectives on parental roles reveal a dynamic interplay between parental authority, autonomy, and control shaped by cultural, legal, and social norms. In traditional societies, parental authority was predominantly unquestioned, with parents exercising extensive control over children's lives, reflecting embedded patriarchal or communal structures. Over time, shifts toward recognizing parental autonomy emphasized children's rights and individual development, leading to modern legal frameworks balancing parental authority with children's welfare and independence.
Legal Frameworks Shaping Parental Decision-Making
Parental authority, parental autonomy, and parental rights are distinct concepts within legal frameworks that shape parental decision-making. Parental authority refers to the legal rights and responsibilities granted to parents by the state, allowing them to make key decisions about their child's welfare, education, and health. Your ability to exercise parental autonomy depends on these legal boundaries, which vary by jurisdiction and aim to balance parental control with the child's best interests and protection under family law.
Societal Influences on Parenting Styles
Parental authority defines the rules and discipline parents impose, while parental autonomy emphasizes a child's independence in decision-making. Societal influences on parenting styles shape how parents balance these concepts, impacting children's development and family dynamics. Understanding how cultural norms and social expectations affect your approach can help foster a more adaptive and supportive parenting style.
The Balance Between Control and Freedom in Parenting
Parental authority establishes the legal and moral right to make decisions for a child, while parental autonomy refers to the parents' freedom to choose their parenting style without undue interference. Balancing these concepts requires maintaining sufficient control to ensure a child's safety and development, while granting enough freedom to foster independence and self-expression. Achieving this equilibrium promotes healthy family dynamics and supports a child's emotional and psychological growth.
Impacts on Child Development and Wellbeing
Parental authority establishes clear guidelines and boundaries essential for a child's emotional security and social development, fostering self-discipline and respect for rules. Parental autonomy emphasizes the child's individuality and decision-making abilities, promoting self-confidence and independence that contribute to healthy psychological growth. Balancing parental authority with autonomy supports Your child's overall wellbeing by nurturing both structure and personal freedom, critical for optimal cognitive and emotional development.
Cultural Differences in Parental Authority and Autonomy
Cultural differences significantly influence parental authority and autonomy, with collectivist societies often emphasizing hierarchical parental authority and obedience, while individualistic cultures prioritize child autonomy and self-expression. In East Asian cultures, parental authority is reinforced through Confucian values promoting respect and filial piety, contrasting with Western norms that encourage open dialogue and independence. These cultural frameworks shape legal perspectives and family dynamics, influencing how parental rights and children's autonomy are negotiated globally.
Navigating Conflicts: When Authority Clashes with Autonomy
Parental authority represents the legal rights and responsibilities parents have to make decisions for their children, while parental autonomy reflects the freedom parents need to raise their children according to their values and beliefs. Navigating conflicts arises when parental authority clashes with autonomy, especially in situations involving medical care, education choices, or discipline methods. Understanding your legal rights and the child's best interests can help balance control with respect for your family's individual preferences.
Educational Choices: Who Decides for the Child?
Parental authority grants parents the legal right to make educational decisions for their child, but parental autonomy emphasizes the family's freedom to choose educational paths aligned with their values without undue government interference. You must balance parental authority with your child's needs and best interests by considering state laws and educational regulations. Disputes often arise when parental rights conflict with school policies or child welfare concerns, requiring careful negotiation or legal intervention.
Evolving Trends: The Future of Parental Rights and Independence
Evolving trends in parental rights emphasize a delicate balance between parental authority and autonomy, highlighting increased recognition of children's rights alongside parental responsibilities. Legal frameworks are progressively adapting to promote parental independence in decision-making while ensuring child welfare and protection. Future developments are expected to integrate technological advancements and cultural shifts, fostering more collaborative and flexible approaches to parenting rights.
Infographic: Parental authority vs Parental autonomy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com