Redirecting behavior in relationships encourages positive communication and problem-solving, while ignoring issues can lead to misunderstandings and emotional distance. Learn how mastering redirection over ignoring can strengthen your connection in this article.
Table of Comparison
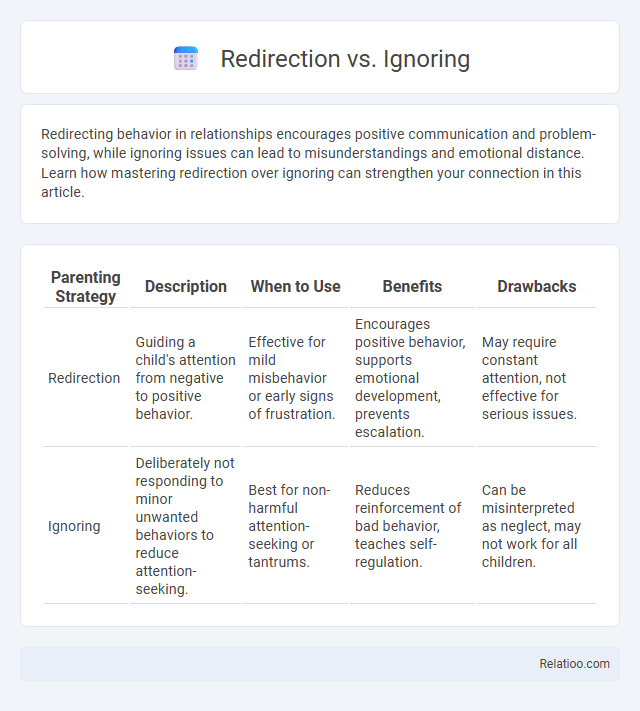
| Parenting Strategy | Description | When to Use | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redirection | Guiding a child's attention from negative to positive behavior. | Effective for mild misbehavior or early signs of frustration. | Encourages positive behavior, supports emotional development, prevents escalation. | May require constant attention, not effective for serious issues. |
| Ignoring | Deliberately not responding to minor unwanted behaviors to reduce attention-seeking. | Best for non-harmful attention-seeking or tantrums. | Reduces reinforcement of bad behavior, teaches self-regulation. | Can be misinterpreted as neglect, may not work for all children. |
Introduction to Redirection and Ignoring
Redirection involves guiding behavior towards a positive or intended outcome by offering alternative actions, often used in behavioral management to replace undesirable habits. Ignoring entails deliberately withholding attention from specific behaviors to reduce or eliminate them, leveraging the absence of reinforcement as a key strategy. Both techniques are essential in shaping actions, with redirection promoting engagement and ignoring focusing on diminishing unwanted responses.
Defining Redirection: What Does It Mean?
Redirection involves guiding an individual's attention or behavior away from an undesired action toward a more appropriate or positive alternative, often used in behavioral management techniques. It serves as a proactive strategy to prevent escalation by addressing the root cause of disruptive behavior and promoting constructive engagement. Unlike ignoring, which involves withholding attention to reduce reinforcement of negative behavior, redirection actively engages and refocuses responses to shape desired outcomes.
Understanding Ignoring: A Quick Overview
Ignoring involves consciously choosing not to respond to certain stimuli or behaviors to avoid reinforcement or escalation, often used in behavior management for children or conflict resolution. This technique helps diminish unwanted actions by withholding attention, encouraging individuals to self-regulate and modify their conduct without external intervention. Effective ignoring requires consistency and clarity, making it distinct from redirection, which actively guides attention to an alternative behavior or focus.
Key Differences Between Redirection and Ignoring
Redirection involves guiding Your child's attention from negative behavior to a positive alternative, promoting learning and self-control, whereas ignoring intentionally withholds attention to decrease undesirable behaviors by not reinforcing them. The key difference lies in engagement; redirection actively substitutes behaviors while ignoring eliminates reinforcement by absence of response. Choosing between redirection and ignoring depends on the behavior's cause, Your goals, and the child's developmental needs to foster effective behavior management.
When to Use Redirection in Behavior Management
Redirection in behavior management is most effective when a child exhibits mild disruptive behaviors, such as minor tantrums or off-task actions, that can be gently guided towards positive alternatives. Ignoring is appropriate for attention-seeking behaviors that do not pose safety risks and when the goal is to reduce reinforcement of negative actions. Use redirection to proactively steer behaviors toward desired outcomes before escalation, ensuring a supportive environment that fosters learning and self-regulation.
Appropriate Scenarios for Ignoring
Ignoring is appropriate in scenarios involving minor user errors or when feedback is unnecessary to prevent cognitive overload, such as small typos or brief input lapses. It helps maintain user flow by avoiding unnecessary interruptions, especially in low-stakes interactions where prompting or redirection might cause frustration. Ignoring is effective in automated systems designed for rapid, seamless user experiences where non-critical deviations do not impact overall task completion.
Benefits of Redirection
Redirection offers significant benefits by guiding Your child's attention from undesirable behavior to positive alternatives, fostering better emotional regulation and improved focus. This approach encourages skill development and helps prevent conflicts without punishment, promoting a supportive and nurturing environment. Redirection enhances communication and builds stronger relationships by addressing underlying needs instead of ignoring or suppressing behaviors.
Potential Drawbacks of Ignoring
Ignoring problematic behaviors in child development can lead to reinforcement of negative actions, as children may perceive a lack of response as tacit approval, potentially escalating the undesired behavior. Unlike redirection, which actively guides the child towards acceptable alternatives, ignoring risks missed opportunities for teaching appropriate responses and may foster frustration or confusion. Research in behavioral psychology highlights that consistent ignoring without combined positive reinforcement strategies often diminishes long-term effectiveness, underscoring the importance of balanced intervention methods.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right strategy between redirection, ignoring, and reinforcement depends primarily on your child's age, temperament, and the specific behavior you want to address. Redirection works best for younger children by shifting their focus to acceptable activities, while ignoring is effective for minimizing attention-seeking behaviors without reinforcing them. Reinforcement strengthens positive behavior and should be used consistently to encourage desired actions, making your choice critical to effective behavior management.
Conclusion: Redirection vs Ignoring – Making Informed Choices
Choosing between redirection and ignoring depends on the behavior's context and the desired outcome; redirection effectively guides attention toward positive actions, while ignoring minimizes reinforcement of minor negative behaviors. Redirection is preferable for teaching appropriate responses and fostering learning, whereas ignoring suits behaviors driven by attention-seeking that are non-harmful. Informed decisions rely on understanding the behavior's function, consistency in application, and individual temperament to optimize behavioral management strategies.
Infographic: Redirection vs Ignoring
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com