Foster care provides temporary care for children in need, while adoption offers a permanent, legal parent-child relationship. Explore key differences and impacts on family dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
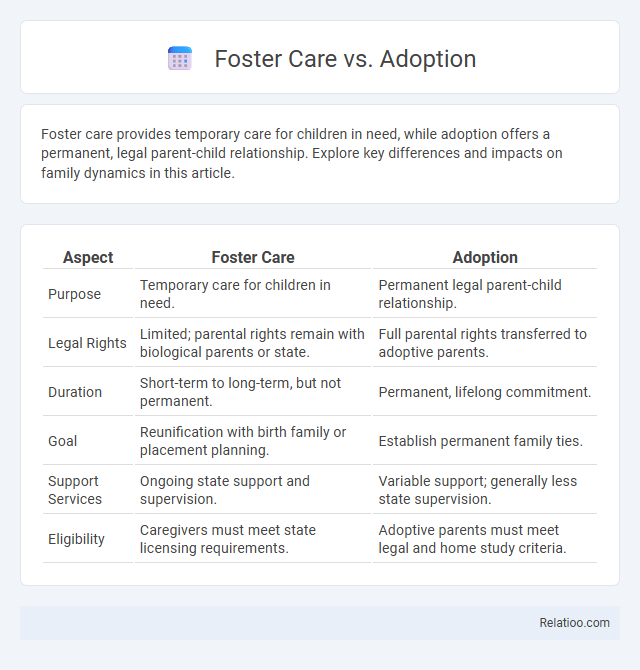
| Aspect | Foster Care | Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Temporary care for children in need. | Permanent legal parent-child relationship. |
| Legal Rights | Limited; parental rights remain with biological parents or state. | Full parental rights transferred to adoptive parents. |
| Duration | Short-term to long-term, but not permanent. | Permanent, lifelong commitment. |
| Goal | Reunification with birth family or placement planning. | Establish permanent family ties. |
| Support Services | Ongoing state support and supervision. | Variable support; generally less state supervision. |
| Eligibility | Caregivers must meet state licensing requirements. | Adoptive parents must meet legal and home study criteria. |
Understanding Foster Care and Adoption
Foster care provides temporary placement for children who cannot live with their biological families due to safety or welfare concerns, while adoption establishes a permanent legal parent-child relationship, transferring all parental rights. Foster parenting involves caring for foster children during their stay, ensuring stability and support without permanent legal ties. Understanding the differences between foster care and adoption is essential for recognizing the varied roles, responsibilities, and long-term outcomes for children and caregivers in these systems.
Key Differences Between Foster Care and Adoption
Foster care provides temporary care for children who cannot live with their birth families, while adoption is a permanent legal process transferring parental rights to the adoptive parents. Foster parenting involves supporting children for limited periods, allowing them to reunite with their biological families when possible, whereas adoption offers lifelong stability and legal responsibility. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the best option for providing care and support to vulnerable children.
Legal Rights and Responsibilities
Foster care grants temporary legal custody to foster parents, while adoption transfers permanent parental rights and responsibilities to adoptive parents. Your legal responsibilities as a foster parent include providing care under state supervision, but you do not have the same authority as an adoptive parent, who assumes full legal rights and decision-making power. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating your rights and obligations within the child welfare system.
The Process: Foster Care vs Adoption
The process of foster care primarily involves temporary placement, where you care for children in need while their biological families work towards reunification, requiring background checks, training, and home studies. Adoption is a permanent legal process that transfers parental rights, involving a more extensive legal procedure, home evaluations, and final court approval to establish enduring family bonds. Foster parenting bridges the two, demanding commitment to both the child's immediate safety and long-term stability, often requiring ongoing education and compliance with state regulations.
Emotional Impact on Children and Families
Foster care often brings emotional challenges for children due to temporary placements and uncertainty, impacting attachment and stability in families. Adoption provides permanent family integration, fostering long-term emotional security but may involve complex identity and loss issues for children. Foster parenting requires emotional resilience as caregivers navigate the fluctuating needs and trauma histories of foster children while supporting biological family reunification efforts.
Financial Considerations and Support
Foster care often provides financial support through monthly stipends to cover the child's basic needs, while adoption typically involves one-time or limited financial assistance but grants permanent parental rights. Foster parenting requires ongoing commitment and may include reimbursement for expenses, training stipends, and access to state resources, but you may need to manage variable costs not always covered by agencies. Understanding these financial considerations helps ensure your ability to provide stable, nurturing care while navigating the different support systems available.
Long-Term Outcomes for Children
Long-term outcomes for children in foster care often show higher risks of instability, emotional challenges, and lower educational attainment compared to those in adoption or foster parenting arrangements. Adoption provides children with permanent legal and emotional security, leading to better mental health, higher academic achievement, and increased chances of stable adult relationships. Foster parenting, while offering a supportive temporary environment, may lack the permanency necessary for optimal long-term developmental and psychological outcomes.
Who Can Become a Foster or Adoptive Parent?
Individuals or couples who meet state-specific requirements, including age, background checks, and financial stability, can become foster or adoptive parents. Prospective foster parents often undergo training and licensing processes to provide temporary care for children, while adoptive parents complete home studies and legal procedures for permanent custody. Both pathways welcome diverse applicants, including singles, married couples, and LGBTQ+ individuals committed to providing a safe and nurturing environment for children.
Challenges and Rewards of Each Path
Foster care presents challenges like temporary placements and emotional instability but rewards you with the opportunity to provide critical support during a child's vulnerable periods. Adoption involves a permanent legal commitment, which may include complex paperwork and emotional adjustments, yet it offers the lifelong reward of forming a lasting family bond. Foster parenting requires balancing the needs of multiple children while navigating the foster system, delivering the rewarding experience of impacting children's lives through stability and nurturing care.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Family
Choosing the right option for your family depends on your long-term goals, commitment level, and emotional readiness. Foster care offers temporary support for children in crisis, while adoption provides a permanent legal relationship and lifelong stability. Foster parenting requires flexibility and dedication to nurture children through transitional phases, ensuring your family's needs align with the child's best interest.
Infographic: Foster Care vs Adoption
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com