Instant gratification in relationships often leads to short-term happiness but can undermine long-term trust and emotional growth. Understanding the balance between immediate pleasure and delayed rewards is crucial for building lasting connections; discover more insights in this article.
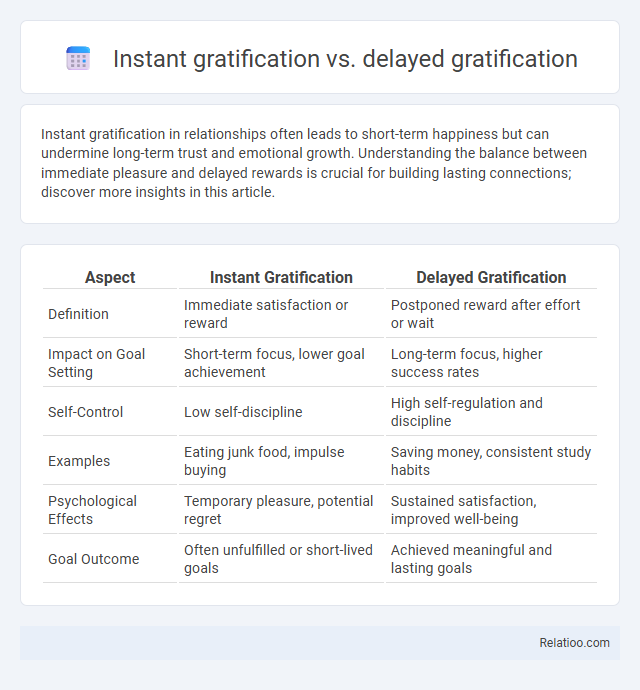
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Instant Gratification | Delayed Gratification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate satisfaction or reward | Postponed reward after effort or wait |
| Impact on Goal Setting | Short-term focus, lower goal achievement | Long-term focus, higher success rates |
| Self-Control | Low self-discipline | High self-regulation and discipline |
| Examples | Eating junk food, impulse buying | Saving money, consistent study habits |
| Psychological Effects | Temporary pleasure, potential regret | Sustained satisfaction, improved well-being |
| Goal Outcome | Often unfulfilled or short-lived goals | Achieved meaningful and lasting goals |
Understanding Instant Gratification
Instant gratification involves the immediate fulfillment of desires, often driven by impulsive behavior and seeking quick rewards. Understanding instant gratification is crucial, as it contrasts with delayed gratification, which emphasizes patience and long-term benefits, while sacrifices require forgoing immediate pleasures for future gains. Recognizing the psychological and emotional triggers behind instant gratification helps in managing impulses and making balanced decisions that benefit overall well-being and goal achievement.
The Psychology Behind Delayed Gratification
The psychology behind delayed gratification reveals that it strengthens your self-control and enhances long-term rewards by resisting immediate temptations. Research indicates that individuals who practice delayed gratification experience greater academic success, better emotional regulation, and higher life satisfaction. Comparing this to instant gratification, which offers fleeting pleasure, and sacrifices, which demand giving up something valuable, delayed gratification uniquely balances patience with meaningful outcomes.
Instant Gratification: Benefits and Drawbacks
Instant gratification provides immediate pleasure and satisfaction, enhancing motivation and reducing stress by fulfilling desires quickly. However, reliance on instant rewards can impair long-term goal achievement, leading to impulsive behaviors and potential negative consequences such as financial strain or health issues. Balancing instant gratification with delayed gratification and thoughtful sacrifices is essential for sustainable success and well-being.
Delayed Gratification: Why Patience Pays Off
Delayed gratification strengthens self-control and enhances long-term success by enabling individuals to resist immediate temptations in favor of future rewards. Studies in psychology highlight that people practicing delayed gratification often experience better academic performance, career advancement, and financial stability. Sacrificing short-term pleasures for sustained goals aligns with brain functions in the prefrontal cortex, which governs decision-making and impulse control, ultimately proving that patience pays off through improved life outcomes.
The Impact of Technology on Gratification Choices
The rapid advancement of technology has significantly influenced your gratification choices by amplifying instant gratification through easy access to entertainment, social media, and online shopping. This accessibility often reduces patience and shifts focus away from delayed gratification, despite its long-term benefits such as improved self-control and goal achievement. Navigating these digital temptations demands intentional sacrifices, such as limiting screen time, to balance immediate desires with future rewards.
Brain Chemistry: How Rewards Influence Behavior
Instant gratification triggers dopamine release in your brain's reward system, providing immediate pleasure but often leading to impulsive decisions. Delayed gratification involves sustained dopamine regulation, strengthening neural pathways associated with self-control and long-term goal achievement. Sacrifices alter brain chemistry by balancing stress hormones like cortisol, enhancing resilience while maintaining motivation toward meaningful rewards.
Real-Life Examples: Success Stories of Delayed Gratification
Successful entrepreneurs like Jeff Bezos and Oprah Winfrey exemplify the power of delayed gratification by reinvesting early profits and enduring years of hard work before achieving massive success. Delayed gratification allows you to build sustainable wealth and long-term career growth, unlike the fleeting satisfaction of instant rewards. Sacrificing immediate pleasures in favor of future gains often leads to breakthrough achievements and personal fulfillment.
Strategies to Strengthen Self-Control
Strengthening self-control involves strategies such as setting clear goals, practicing mindfulness, and employing delay techniques to resist instant gratification. Using visualization methods helps individuals anticipate rewards tied to delayed gratification, thereby increasing motivation. Creating structured routines and self-monitoring tools supports managing sacrifices and sustaining long-term discipline essential for success.
Balancing Instant and Delayed Gratification in Daily Life
Balancing instant and delayed gratification involves making conscious choices that prioritize long-term rewards without completely foregoing immediate pleasures. Effective strategies include setting clear goals, practicing self-control, and scheduling short breaks or small rewards to maintain motivation. Recognizing when sacrifices are necessary helps individuals optimize productivity while sustaining mental well-being and life satisfaction.
Long-Term Consequences: Making Healthier Choices
Choosing delayed gratification over instant gratification leads to more sustainable health benefits, such as improved cardiovascular health and weight management. Sacrifices like avoiding sugary snacks and prioritizing regular exercise contribute to lower risks of chronic diseases and enhanced overall well-being. Emphasizing long-term consequences fosters disciplined habits that promote lifelong physical and mental health.
Infographic: Instant gratification vs Delayed gratification
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com