Proactive relationships prioritize open communication and early conflict resolution, fostering trust and long-term stability, while reactive relationships often address issues only after problems escalate, leading to increased misunderstandings. Discover effective strategies to cultivate proactive relationship dynamics in this article.
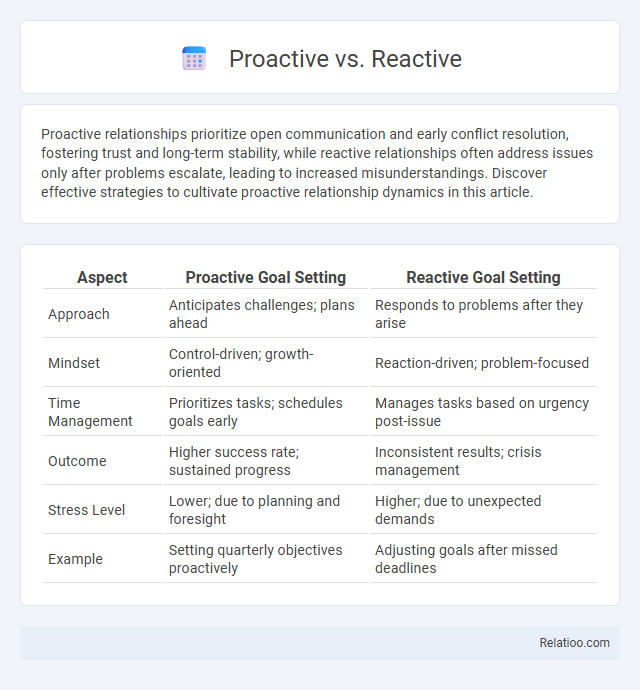
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Proactive Goal Setting | Reactive Goal Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Anticipates challenges; plans ahead | Responds to problems after they arise |
| Mindset | Control-driven; growth-oriented | Reaction-driven; problem-focused |
| Time Management | Prioritizes tasks; schedules goals early | Manages tasks based on urgency post-issue |
| Outcome | Higher success rate; sustained progress | Inconsistent results; crisis management |
| Stress Level | Lower; due to planning and foresight | Higher; due to unexpected demands |
| Example | Setting quarterly objectives proactively | Adjusting goals after missed deadlines |
Understanding Proactive and Reactive Approaches
Understanding proactive and reactive approaches helps you optimize decision-making and problem-solving strategies. Proactive approaches involve anticipating challenges and implementing solutions in advance, while reactive approaches focus on responding to issues after they arise. Mastering the balance between these methods enhances efficiency and resilience in personal and professional contexts.
Key Differences Between Proactive and Reactive Strategies
Proactive strategies involve anticipating future challenges and taking early action to prevent problems, whereas reactive strategies focus on responding to issues only after they arise. Key differences include timing, with proactive approaches emphasizing foresight and planning, while reactive methods rely on quick responses to immediate threats. Proactivity enhances long-term success by minimizing risks, whereas reactivity often increases vulnerability due to delayed intervention.
Benefits of a Proactive Mindset
A proactive mindset empowers individuals to anticipate challenges and implement solutions before problems arise, significantly reducing risks and enhancing productivity. Embracing proactivity fosters better decision-making, increased resilience, and a stronger ability to adapt to changing environments. Organizations that prioritize proactivity benefit from improved innovation, higher employee engagement, and sustained competitive advantage.
Drawbacks of Reactivity in Problem Solving
Reactivity in problem solving often leads to delayed responses and increased stress, causing inefficiencies and missed opportunities for prevention. Your team may face recurring issues due to a lack of foresight and strategic planning, resulting in higher costs and reduced overall performance. Emphasizing proactivity enables continuous improvement by anticipating challenges before they escalate, fostering more sustainable solutions.
Real-life Examples of Proactive vs Reactive Actions
Proactive actions involve anticipating potential challenges and implementing solutions ahead of time, such as regularly maintaining a vehicle to prevent breakdowns. Reactive actions occur after an issue arises, like repairing the car only once it stalls on the road. Proactivity enhances efficiency and minimizes risk by addressing problems before they escalate, illustrated by businesses conducting market research to adjust strategies before competitors do.
When to Use Proactive vs Reactive Approaches
Choosing between proactive and reactive approaches depends on the nature of the situation and desired outcomes. You should employ a proactive strategy when anticipating potential challenges to prevent issues before they arise, ensuring long-term success and efficiency. Reactive methods are suitable for immediate problem-solving when unforeseen events occur, requiring quick adjustments and responses to minimize negative impacts.
Impact of Proactive vs Reactive Behaviors in the Workplace
Proactive behaviors in the workplace enhance productivity by anticipating challenges and implementing solutions before issues escalate, reducing downtime and improving team morale. Reactive behaviors often lead to crisis management, increased stress, and inefficiencies as employees respond only after problems arise. Emphasizing proactivity fosters a culture of continuous improvement, innovation, and resilience, driving long-term organizational success.
Building a Proactive Culture in Organizations
Building a proactive culture in organizations enhances employee engagement by encouraging anticipation of challenges and opportunities before they arise. Proactivity fosters continuous improvement, empowering your team to take initiative, innovate, and prevent problems rather than just reacting to crises. Emphasizing proactive behaviors shifts decision-making from reactive troubleshooting to strategic planning, driving long-term organizational success.
Common Challenges in Shifting from Reactive to Proactive
Shifting from reactive to proactive strategies often encounters challenges such as entrenched organizational culture resistant to change, inadequate data analytics capabilities, and lack of clear predictive frameworks. Organizations struggle with inconsistent communication and limited employee empowerment, which hinder early identification and mitigation of potential issues. Developing a robust proactive approach requires investing in advanced technologies, fostering continuous training, and promoting a forward-thinking mindset across all levels of management.
Tips to Cultivate Proactivity in Daily Life
Cultivating proactivity in daily life requires intentional habits such as setting clear goals, prioritizing tasks, and anticipating challenges before they arise. You can enhance your proactive mindset by regularly reflecting on your actions and planning ahead to create solutions rather than reacting to problems. Consistently practicing time management and embracing responsibility empowers you to take control of your circumstances and drive meaningful outcomes.
Infographic: Proactive vs Reactive
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com