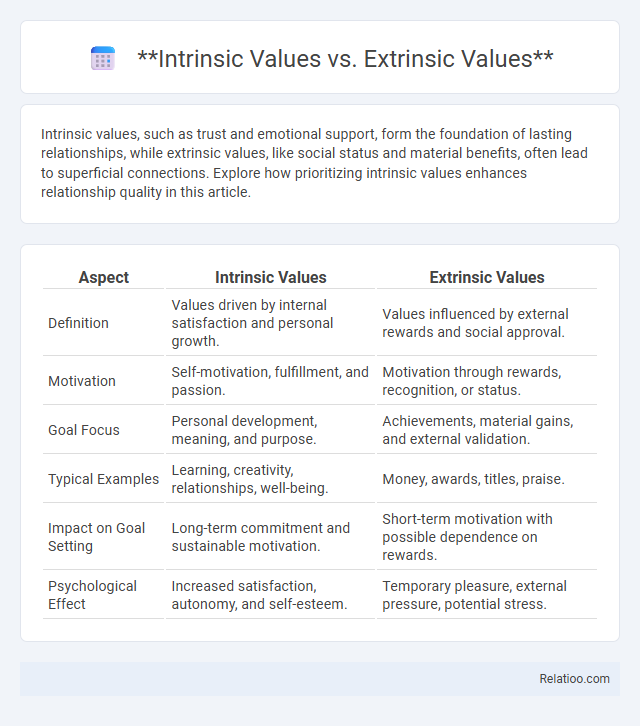
Intrinsic values, such as trust and emotional support, form the foundation of lasting relationships, while extrinsic values, like social status and material benefits, often lead to superficial connections. Explore how prioritizing intrinsic values enhances relationship quality in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Intrinsic Values | Extrinsic Values |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Values driven by internal satisfaction and personal growth. | Values influenced by external rewards and social approval. |
| Motivation | Self-motivation, fulfillment, and passion. | Motivation through rewards, recognition, or status. |
| Goal Focus | Personal development, meaning, and purpose. | Achievements, material gains, and external validation. |
| Typical Examples | Learning, creativity, relationships, well-being. | Money, awards, titles, praise. |
| Impact on Goal Setting | Long-term commitment and sustainable motivation. | Short-term motivation with possible dependence on rewards. |
| Psychological Effect | Increased satisfaction, autonomy, and self-esteem. | Temporary pleasure, external pressure, potential stress. |
Introduction to Intrinsic and Extrinsic Values
Intrinsic values refer to the inherent worth of something appreciated for its own sake, such as happiness, love, or knowledge. Extrinsic values depend on external rewards or outcomes, like money, status, or praise, which serve as means to achieve other ends. Understanding the distinction between these values is essential for your value clarification process and helps prioritize what truly matters in decision-making.
Defining Intrinsic Values
Intrinsic values refer to qualities or principles considered valuable in and of themselves, independent of any external rewards or outcomes. These values, such as honesty, compassion, and authenticity, guide behavior by reflecting what individuals inherently deem important for personal fulfillment and ethical living. Distinguishing intrinsic values from extrinsic values, which depend on external validation or material gain, is essential during value clarification processes that help individuals identify and prioritize their core beliefs.
Understanding Extrinsic Values
Extrinsic values are external motivators driven by tangible rewards such as money, status, or approval from others, contrasting with intrinsic values rooted in internal satisfaction and personal growth. Understanding extrinsic values involves recognizing how external incentives influence behavior and decision-making, often shaping actions through social expectations or material gains. This awareness enables individuals to balance extrinsic motivations with intrinsic values during value clarification, fostering a more authentic alignment of goals and priorities.
Key Differences Between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Values
Intrinsic values are those valued for their own sake, such as happiness or virtue, representing what is inherently worthwhile. Extrinsic values depend on external outcomes or rewards, like money or status, valued for the benefits they bring. Value clarification is a process helping individuals identify and prioritize their intrinsic and extrinsic values to make aligned decisions.
Examples of Intrinsic Values
Intrinsic values are those inherently rewarding and valuable for their own sake, such as happiness, honesty, and personal growth, which contribute deeply to an individual's sense of fulfillment. Examples of intrinsic values include compassion, creativity, and autonomy, each fostering internal satisfaction rather than external rewards like money or status. Value clarification helps individuals identify these intrinsic values by distinguishing them from extrinsic values, facilitating more authentic decision-making aligned with personal beliefs.
Examples of Extrinsic Values
Extrinsic values are external rewards or outcomes valued for their consequences rather than inherent qualities, such as money, fame, or social status. For example, a person may work overtime to earn a bonus (extrinsic value) rather than for personal satisfaction or passion for the job (intrinsic value). Value clarification involves recognizing these distinctions to better understand motivations and make conscious decisions aligning actions with either intrinsic or extrinsic values.
The Role of Values in Personal Decision-Making
Intrinsic values, such as honesty and compassion, drive personal decision-making by reflecting core beliefs that motivate behavior from within. Extrinsic values, including wealth and status, influence choices based on external rewards or social approval. Value clarification helps individuals identify and prioritize these values, leading to more authentic and consistent decision-making aligned with their true self.
Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Values in the Workplace
Intrinsic values in the workplace refer to internal motivations such as personal growth, job satisfaction, and alignment with one's core beliefs, while extrinsic values focus on external rewards like salary, bonuses, and promotions. Understanding the balance between these values helps you prioritize meaningful engagement over superficial incentives, fostering long-term motivation and fulfillment. Value clarification assists individuals and organizations in identifying which intrinsic and extrinsic values align most closely with their mission and employees' well-being.
Balancing Intrinsic and Extrinsic Values for Well-being
Balancing intrinsic values, such as personal growth and meaningful relationships, with extrinsic values like wealth and social status is essential for your overall well-being. Intrinsic values foster long-term happiness and psychological fulfillment, while extrinsic values can provide motivation and external rewards but may lead to stress if prioritized excessively. Value clarification helps identify which values align most closely with your authentic self, enabling a harmonious integration that supports mental health and life satisfaction.
Conclusion: Choosing and Cultivating Your Values
Choosing and cultivating your values involves distinguishing intrinsic values, which provide deep personal fulfillment, from extrinsic values, which often relate to external rewards or recognition. Value clarification helps you identify what truly matters by aligning your actions with your core beliefs, fostering authentic decision-making. By consciously embracing intrinsic values, you create a meaningful foundation that guides your growth and life satisfaction.
Infographic: Intrinsic Values vs Extrinsic Values
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com