Self-efficacy, the belief in one's ability to succeed, directly influences motivation by enhancing persistence and goal-setting in relationships. Discover how strengthening self-efficacy can transform motivation and improve relationship dynamics in this article.
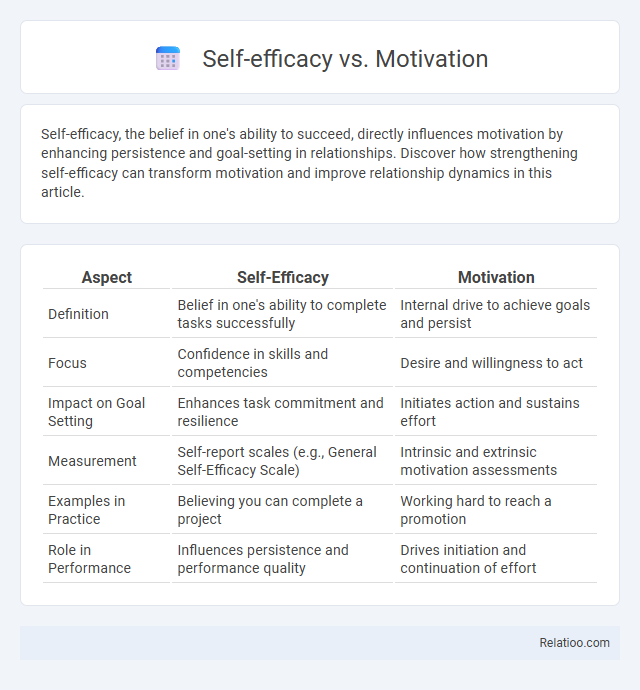
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Self-Efficacy | Motivation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in one's ability to complete tasks successfully | Internal drive to achieve goals and persist |
| Focus | Confidence in skills and competencies | Desire and willingness to act |
| Impact on Goal Setting | Enhances task commitment and resilience | Initiates action and sustains effort |
| Measurement | Self-report scales (e.g., General Self-Efficacy Scale) | Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation assessments |
| Examples in Practice | Believing you can complete a project | Working hard to reach a promotion |
| Role in Performance | Influences persistence and performance quality | Drives initiation and continuation of effort |
Understanding Self-Efficacy
Understanding self-efficacy involves recognizing your belief in your ability to succeed in specific tasks, which directly influences motivation by shaping the goals you set and the effort you invest. Unlike motivation, which drives the desire to act, self-efficacy determines your confidence in overcoming challenges during the process. Enhancing your self-efficacy boosts perseverance and resilience, leading to improved performance and goal achievement.
Defining Motivation
Motivation refers to the internal drive that initiates, guides, and sustains goal-oriented behavior, playing a crucial role in influencing your actions and persistence. Unlike self-efficacy, which is the belief in your ability to execute specific tasks, motivation centers on the reasons behind those efforts and the intensity of your desire to achieve them. Understanding motivation helps in harnessing your personal incentives and emotional energy to maintain consistent progress toward desired outcomes.
Key Differences Between Self-Efficacy and Motivation
Self-efficacy refers to Your belief in your ability to succeed in specific tasks, while motivation drives the desire or willingness to take action. Key differences include that self-efficacy influences the confidence to initiate and persist in activities, whereas motivation determines the intensity and direction of effort. Understanding these distinctions helps in tailoring strategies to boost performance and achieve goals effectively.
How Self-Efficacy Influences Behavior
Self-efficacy profoundly influences behavior by shaping an individual's confidence in their ability to execute specific tasks successfully, thereby directly impacting goal-setting and perseverance. High self-efficacy enhances motivation by promoting resilience in the face of challenges, leading to increased effort and persistence in activities. Unlike general motivation, which reflects a desire to achieve, self-efficacy specifically governs the belief in personal capability, making it a critical determinant of behavioral outcomes.
The Role of Motivation in Achievement
Motivation plays a crucial role in achievement by driving individuals to set goals, persist through challenges, and maintain effort over time. While self-efficacy refers to the belief in one's ability to succeed, motivation fuels the desire and commitment necessary to translate that confidence into action. Research shows that high motivation amplifies self-efficacy's impact, enhancing performance and leading to greater accomplishment in academic, professional, and personal domains.
Interplay Between Self-Efficacy and Motivation
The interplay between self-efficacy and motivation significantly influences your ability to achieve goals, as self-efficacy shapes your belief in your capacity to succeed while motivation drives the effort and persistence toward those goals. High self-efficacy enhances intrinsic motivation by increasing confidence, which in turn boosts willingness to tackle challenges and sustain long-term engagement. Understanding how self-efficacy reinforces motivation helps optimize performance and personal development in various contexts.
Factors Affecting Self-Efficacy
Factors affecting self-efficacy include mastery experiences, social modeling, social persuasion, and physiological states, all of which shape your confidence in completing tasks. Unlike motivation, which drives the direction and intensity of behavior, self-efficacy specifically influences your belief in your capabilities to achieve specific outcomes. Understanding these factors can enhance your ability to build resilience and improve performance across various domains.
Types of Motivation: Intrinsic vs Extrinsic
Self-efficacy influences motivation by shaping beliefs in one's abilities to achieve goals, thereby impacting performance and persistence. Types of motivation include intrinsic motivation, driven by internal satisfaction and personal growth, and extrinsic motivation, fueled by external rewards or social recognition. Understanding the interplay between self-efficacy and these motivation types is crucial for enhancing learning outcomes and goal attainment.
Strategies to Enhance Self-Efficacy and Motivation
Strategies to enhance self-efficacy include setting achievable goals, providing positive feedback, and modeling successful behaviors to build confidence. Motivation can be boosted by aligning tasks with personal interests, offering rewards, and fostering a growth mindset that emphasizes effort over innate ability. Combining techniques such as mastery experiences, verbal encouragement, and intrinsic motivation creates a synergistic effect that strengthens both self-efficacy and motivation for sustained performance improvement.
Self-Efficacy and Motivation: Real-Life Examples
Self-efficacy influences motivation by shaping individuals' belief in their ability to succeed, which directly affects their goal-setting and persistence in tasks like completing a challenging project or learning a new skill. For example, a student with high self-efficacy is more motivated to study harder, believing their efforts will improve exam performance, whereas low self-efficacy can diminish motivation and increase avoidance behaviors. In workplace settings, employees confident in their problem-solving skills show greater motivation to take initiative and contribute to team goals, illustrating the dynamic relationship between self-efficacy and motivation in real-life scenarios.
Infographic: Self-efficacy vs Motivation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com