In-state tuition offers significantly lower rates for residents compared to higher fees for out-of-state students, impacting college affordability and enrollment decisions. Explore this article to understand how residency status affects tuition costs and financial planning.
Table of Comparison
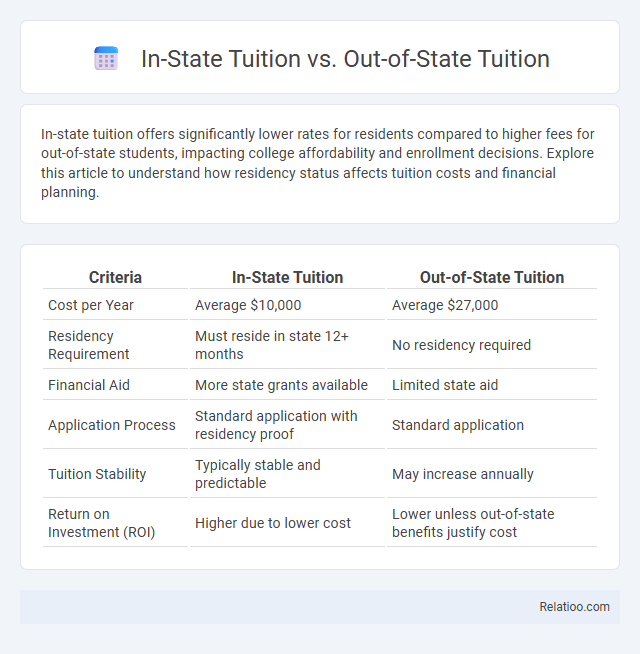
| Criteria | In-State Tuition | Out-of-State Tuition |
|---|---|---|
| Cost per Year | Average $10,000 | Average $27,000 |
| Residency Requirement | Must reside in state 12+ months | No residency required |
| Financial Aid | More state grants available | Limited state aid |
| Application Process | Standard application with residency proof | Standard application |
| Tuition Stability | Typically stable and predictable | May increase annually |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Higher due to lower cost | Lower unless out-of-state benefits justify cost |
Understanding In-State vs Out-of-State Tuition
Understanding in-state versus out-of-state tuition is crucial for optimizing your education expenses, as in-state tuition usually costs significantly less due to state subsidies for residents. Out-of-state tuition can be two to three times higher, impacting overall college affordability and financial planning strategies. Evaluating residency status and exploring education planning options can help you minimize costs and make informed decisions.
Key Differences in Tuition Costs
In-state tuition typically costs significantly less than out-of-state tuition due to subsidization by state taxpayers, often resulting in savings of 50% to 75% per credit hour. Out-of-state students face higher rates reflecting the absence of state residency benefits, which can increase total education expenses by thousands annually. Effective education planning involves understanding these cost distinctions to maximize financial aid opportunities and minimize educational debt.
Eligibility Criteria for In-State Tuition
Eligibility criteria for in-state tuition typically require students to demonstrate residency within the state for a minimum period, often 12 consecutive months, prior to enrollment, including proof of domicile, such as a state driver's license, voter registration, or tax filings. Unlike out-of-state tuition, which applies to non-residents and is significantly higher, in-state tuition rates offer substantial savings, making residency status critical for education planning and affordability. Understanding specific state regulations and maintaining or establishing legal residency are essential steps for students seeking to qualify for in-state tuition benefits.
Financial Impact on Students and Families
In-state tuition rates for public universities average around $10,000 annually, significantly lower than out-of-state tuition, which can exceed $25,000, creating a substantial financial burden on families. Strategic education planning, such as establishing residency prior to enrollment or utilizing state-specific scholarships and grants, can reduce the high cost differential and ease long-term financial stress. Understanding these cost variations and planning accordingly helps students and families optimize their higher education investment and minimize student debt.
Residency Requirements Explained
Understanding residency requirements is crucial when comparing in-state tuition versus out-of-state tuition costs, as meeting these criteria significantly lowers your educational expenses. States generally require proof of domicile for at least 12 consecutive months prior to enrollment, including evidence such as a state driver's license, voter registration, and tax filings. Properly navigating these requirements can be a key factor in effective education planning, ensuring you qualify for reduced tuition rates and optimize your college budget.
Pros and Cons of Each Tuition Type
In-state tuition offers significantly lower rates, making college more affordable for residents, but it limits your options to state universities, which may have fewer specialized programs. Out-of-state tuition provides access to a wider range of institutions and diverse academic opportunities, though the cost can be two to three times higher than in-state rates, increasing financial burden. Effective education planning requires balancing these tuition differences with scholarship availability, residency requirements, and long-term career goals to optimize both cost and educational outcomes.
Strategies for Qualifying for In-State Rates
Qualifying for in-state tuition rates often requires establishing residency by living in the state for at least 12 consecutive months and demonstrating intent to remain, such as obtaining a state driver's license or voter registration. Students can also benefit from education planning strategies like enrolling in community college first or seeking scholarships restricted to state residents. Understanding these requirements and proactively organizing documentation ensures access to significant tuition savings compared to higher out-of-state rates.
Effects on College Selection and Accessibility
In-state tuition typically offers significantly lower rates, making colleges more accessible and influencing students to select public universities within their state. Out-of-state tuition, often two to three times higher, limits affordability and narrows college options, particularly for families with constrained education budgets. Effective education planning, including early financial strategies and residency establishment, can bridge cost gaps and expand access to a broader range of institutions.
Scholarship and Financial Aid Considerations
In-state tuition offers significantly lower costs compared to out-of-state tuition, making scholarship opportunities and financial aid more accessible to residents through state-funded programs. Out-of-state students often face higher tuition fees but can offset expenses by targeting national scholarships, merit-based aid, and institution-specific grants designed for non-residents. Effective education planning includes researching eligibility criteria, applying early for scholarships, and leveraging financial aid calculators to maximize funding for both in-state and out-of-state tuition scenarios.
Future Trends in Tuition Policies
Future trends in tuition policies indicate a gradual shift towards more inclusive education planning, with states exploring hybrid tuition models that blend in-state and out-of-state rates to attract diverse student populations. Universities increasingly leverage data analytics to personalize tuition strategies, enhancing affordability and accessibility while addressing budget constraints. Policymakers are prioritizing investments in scholarship programs and digital learning platforms to mitigate the rising costs of both in-state and out-of-state tuition fees.
Infographic: In-State Tuition vs Out-of-State Tuition
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com