Power Distance highlights hierarchical relationships where authority is respected and accepted, while Egalitarianism promotes equal power distribution and collaborative interactions. Explore this article to understand how different cultures navigate these contrasting relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
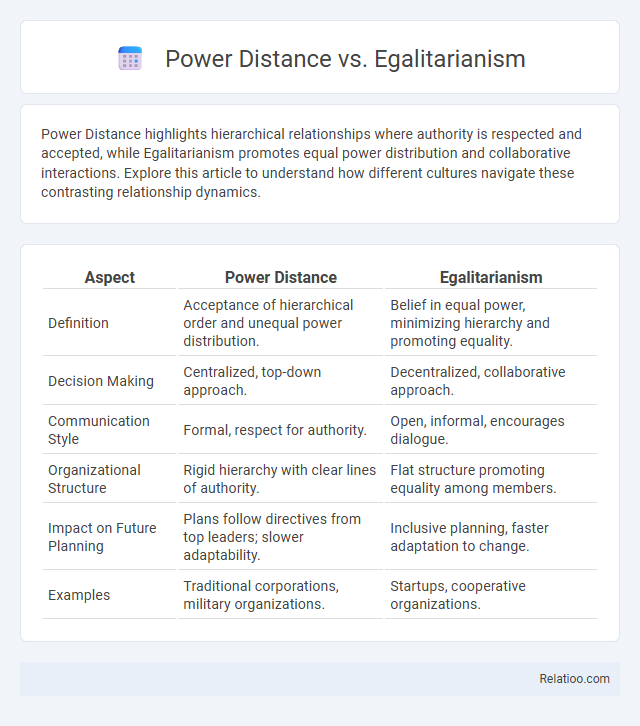
| Aspect | Power Distance | Egalitarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acceptance of hierarchical order and unequal power distribution. | Belief in equal power, minimizing hierarchy and promoting equality. |
| Decision Making | Centralized, top-down approach. | Decentralized, collaborative approach. |
| Communication Style | Formal, respect for authority. | Open, informal, encourages dialogue. |
| Organizational Structure | Rigid hierarchy with clear lines of authority. | Flat structure promoting equality among members. |
| Impact on Future Planning | Plans follow directives from top leaders; slower adaptability. | Inclusive planning, faster adaptation to change. |
| Examples | Traditional corporations, military organizations. | Startups, cooperative organizations. |
Understanding Power Distance and Egalitarianism
Power distance measures the acceptance of unequal power distribution within organizations or societies, influencing hierarchical structures and decision-making processes. Egalitarianism emphasizes equal rights and balanced power distribution, promoting inclusive participation and reducing status-based distinctions. Understanding these concepts aids in managing cultural differences, as high power distance cultures often value authority and obedience, while egalitarian cultures encourage autonomy and collaboration.
Historical Roots of Power Distance
Power Distance, a concept introduced by Geert Hofstede, measures the acceptance of unequal power distribution in societies, rooted in historical hierarchies and institutionalized authority. This dimension contrasts sharply with Egalitarianism, which emphasizes equal power distribution and challenges traditional social stratifications. Cultural differences in Power Distance reflect varying historical experiences with authority, governance, and social stratification, influencing organizational structures and interpersonal relationships worldwide.
Key Principles of Egalitarianism
Egalitarianism emphasizes equality, shared decision-making, and minimizing hierarchical distinctions within societies or organizations, contrasting sharply with high power distance cultures that accept unequal power distribution. Key principles of egalitarianism include promoting equal rights, inclusive participation, and fair treatment regardless of status or rank, fostering collaboration and mutual respect. Understanding these cultural differences helps you navigate social interactions and organizational dynamics effectively in diverse environments.
Cultural Dimensions: High vs Low Power Distance
High power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical structures where authority and inequality are accepted as a norm, reflecting clear distinctions between leaders and subordinates. In contrast, low power distance cultures prioritize egalitarianism, promoting equal relationships and minimizing inequalities in power distribution. Understanding these cultural dimensions reveals significant variations in communication styles, decision-making processes, and organizational behavior across different societies.
Impact on Leadership and Management Styles
Power distance significantly shapes leadership and management styles, with high power distance cultures favoring hierarchical, top-down decision-making and low power distance or egalitarian cultures promoting participative, collaborative approaches. In high power distance societies such as many Asian or Latin American countries, leaders are expected to maintain clear authority and control, while in egalitarian contexts like Scandinavian countries, leadership tends to be more democratic and inclusive. Understanding these cultural differences is essential for multinational organizations to adapt leadership strategies that effectively address diverse employee expectations and improve organizational performance.
Communication Patterns in Power Distance vs Egalitarian Cultures
Communication patterns in high power distance cultures often involve formal language, indirect expressions, and hierarchical protocols that emphasize respect and authority. In contrast, egalitarian cultures promote open, direct communication and encourage equal participation regardless of rank or status. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective cross-cultural interaction and mitigating misunderstandings in global business environments.
Social Structures and Hierarchies
Power distance measures the acceptance of unequal power distribution within social structures, where high power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical authority and centralized control. Egalitarianism promotes equal power distribution and minimizes hierarchy, encouraging participative decision-making and social mobility. Cultural differences shape how societies organize social hierarchies, with some valuing rigid status distinctions while others prioritize inclusivity and flatten organizational layers.
Workplace Dynamics and Team Collaboration
Power Distance significantly influences workplace dynamics by determining hierarchical structures and decision-making processes, where high power distance cultures expect clear authority and obedience. Egalitarianism fosters open communication and equal participation, enhancing team collaboration through mutual respect and shared responsibility regardless of rank. Cultural differences in power perception require adaptive leadership styles to balance authority with inclusiveness, optimizing team synergy and productivity across diverse work environments.
Implications for Global Business Practices
Power distance levels, which measure acceptance of unequal power distribution, significantly influence leadership styles, decision-making, and communication in global business contexts. Egalitarian cultures promote collaboration and flat organizational structures, whereas high power distance cultures emphasize hierarchy and authority, impacting negotiation tactics and employee relations. Understanding these cultural differences enables multinational companies to tailor management approaches, enhance cross-cultural teamwork, and improve international market performance.
Moving Toward Greater Egalitarianism
Moving toward greater egalitarianism involves reducing power distance, which refers to the extent to which less powerful members of a society accept unequal power distribution. Cultures high in power distance often emphasize hierarchical structures and centralized authority, while egalitarian societies promote equal rights, participative decision-making, and reduced status disparities. Embracing cultural differences requires recognizing these varying attitudes toward power and fostering inclusive environments that balance respect for tradition with the pursuit of social equity.
Infographic: Power Distance vs Egalitarianism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com