Early retirement offers financial independence and more leisure time by retiring before the conventional age of 65, while traditional retirement typically involves a structured pension and benefits tied to longer workforce participation. Explore the advantages and challenges of both paths in this article.
Table of Comparison
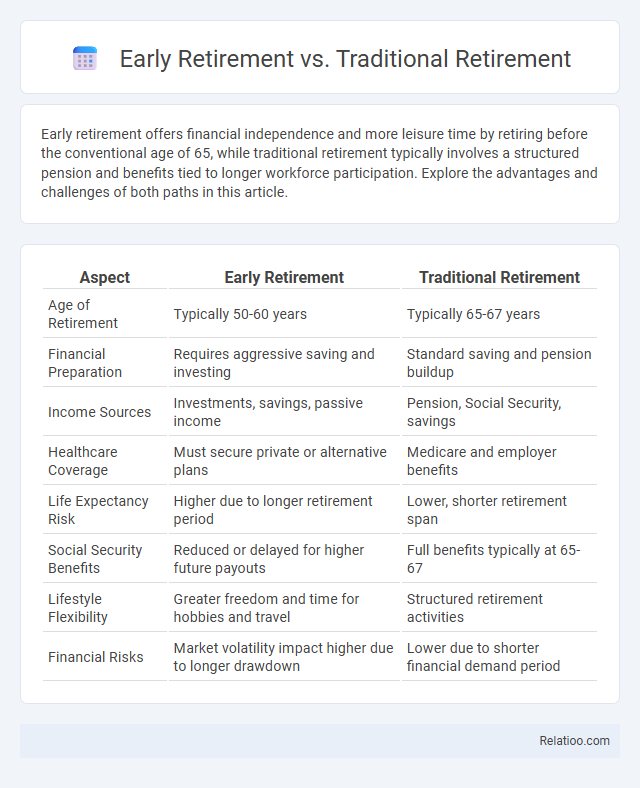
| Aspect | Early Retirement | Traditional Retirement |
|---|---|---|
| Age of Retirement | Typically 50-60 years | Typically 65-67 years |
| Financial Preparation | Requires aggressive saving and investing | Standard saving and pension buildup |
| Income Sources | Investments, savings, passive income | Pension, Social Security, savings |
| Healthcare Coverage | Must secure private or alternative plans | Medicare and employer benefits |
| Life Expectancy Risk | Higher due to longer retirement period | Lower, shorter retirement span |
| Social Security Benefits | Reduced or delayed for higher future payouts | Full benefits typically at 65-67 |
| Lifestyle Flexibility | Greater freedom and time for hobbies and travel | Structured retirement activities |
| Financial Risks | Market volatility impact higher due to longer drawdown | Lower due to shorter financial demand period |
Introduction to Early and Traditional Retirement
Early retirement allows you to exit the workforce years before the standard age, often by accumulating enough savings or passive income to sustain your lifestyle. Traditional retirement typically begins at 65, supported by Social Security, pensions, and savings designed to cover living expenses during your later years. Understanding these options helps you tailor your financial planning and lifestyle goals for a secure and fulfilling future.
Defining Early Retirement: Key Concepts
Early retirement entails ceasing full-time work significantly before the standard retirement age, often supported by strategic financial planning such as aggressive savings, investments, and passive income streams. Traditional retirement usually occurs around the age of 65, with a reliance on pensions, Social Security benefits, and accumulated retirement savings. Lifestyle change, by contrast, emphasizes modifying daily habits and priorities to balance work and personal fulfillment without completely exiting the workforce.
Traditional Retirement: Age and Expectations
Traditional retirement typically occurs around the age of 65, aligning with social security eligibility and pension plans. Expectations often include ceasing full-time work, maintaining financial stability through savings and benefits, and engaging in leisure or family activities. This approach assumes a linear career path culminating in a defined retirement phase, contrasting with more flexible lifestyle changes or early retirement options.
Financial Requirements for Early Retirement
Early retirement demands a robust financial strategy, including substantial savings, diversified investments, and a clear understanding of withdrawal rates to ensure sustainable income without employment. Traditional retirement often relies on consistent pension plans, Social Security benefits, and accumulated savings geared toward a conventional retirement age, typically 65 or older. Your financial requirements for lifestyle change prioritize flexibility and may involve adjusting spending habits and income sources to support varied experiences while maintaining financial stability.
Income Sources in Traditional Retirement
Traditional retirement typically relies on a combination of Social Security benefits, employer-sponsored pension plans, and personal retirement savings such as 401(k) or IRA accounts. Income stability depends largely on consistent contributions made during one's working years and the availability of employer pensions, which have become less common in recent decades. Many retirees supplement fixed income with part-time work, annuities, or withdrawals from investment portfolios to maintain financial security throughout retirement.
Lifestyle Differences: Early vs Traditional Retirement
Early retirement allows you to prioritize personal passions and flexible schedules, enhancing daily well-being and reducing work-related stress, while traditional retirement often follows decades of structured routines and delayed leisure activities. The lifestyle shift in early retirement typically includes more travel, hobbies, and family time, contrasting with traditional retirement's more gradual transition from work to leisure. These differences significantly impact how retirees allocate their time, maintain social connections, and manage health and financial resources.
Health and Well-being Considerations
Early retirement offers extended time for physical activity and stress reduction, which can lead to improved cardiovascular health and mental well-being. Traditional retirement may pose challenges such as social isolation and loss of daily structure, impacting cognitive function and emotional stability. Lifestyle changes focused on balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and mindfulness practices contribute significantly to sustaining health and enhancing quality of life regardless of retirement age.
Challenges of Early Retirement
Early retirement poses significant financial challenges due to the need for larger savings portfolios and sustained income streams over a longer period, increasing the risk of outliving assets. Unlike traditional retirement, where Social Security benefits and pensions typically commence at a standard age, early retirees must navigate complex investment strategies and healthcare costs without assured employer support. Lifestyle changes require ongoing planning to maintain social engagement and purpose, with early retirees often facing psychological challenges such as loss of identity and structure outside the conventional work environment.
Pros and Cons Comparison
Early retirement offers financial freedom and more personal time but requires substantial savings and may risk loss of purpose or social connections. Traditional retirement provides a gradual transition with steady income and benefits, yet it often limits time for new pursuits and can involve reduced energy. Lifestyle change enables flexibility and immediate quality of life improvements without strict financial targets but may lack the full security of retirement funds or structured planning.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right retirement path depends on financial readiness, personal goals, and lifestyle preferences. Early retirement requires substantial savings and disciplined investing to ensure long-term security, whereas traditional retirement often relies on steady income and Social Security benefits. Lifestyle change focuses on aligning daily activities and values with well-being, emphasizing flexibility and fulfillment beyond financial considerations.
Infographic: Early Retirement vs Traditional Retirement
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com