Private schools often offer smaller class sizes and specialized programs, enhancing personalized learning experiences compared to public schools. Explore this article to understand how these differences impact student relationships and academic outcomes.
Table of Comparison
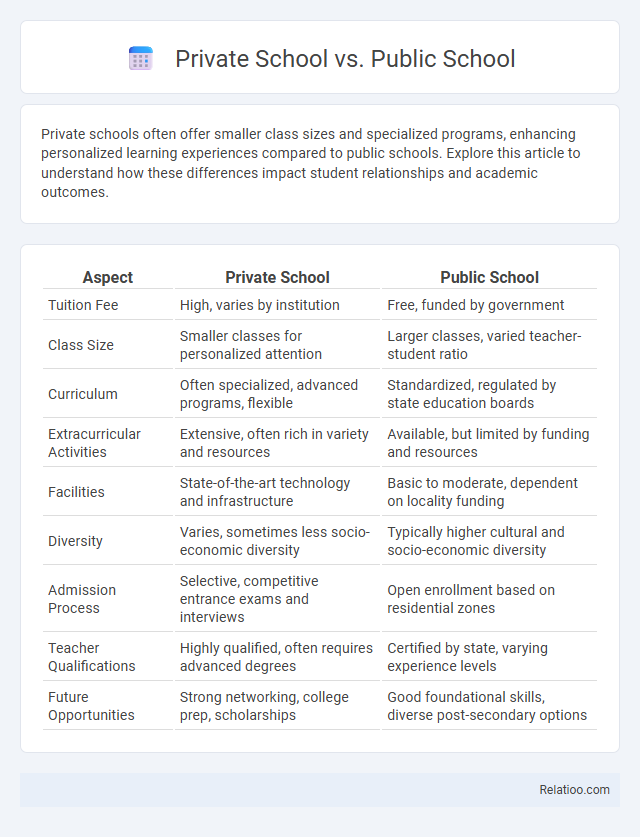
| Aspect | Private School | Public School |
|---|---|---|
| Tuition Fee | High, varies by institution | Free, funded by government |
| Class Size | Smaller classes for personalized attention | Larger classes, varied teacher-student ratio |
| Curriculum | Often specialized, advanced programs, flexible | Standardized, regulated by state education boards |
| Extracurricular Activities | Extensive, often rich in variety and resources | Available, but limited by funding and resources |
| Facilities | State-of-the-art technology and infrastructure | Basic to moderate, dependent on locality funding |
| Diversity | Varies, sometimes less socio-economic diversity | Typically higher cultural and socio-economic diversity |
| Admission Process | Selective, competitive entrance exams and interviews | Open enrollment based on residential zones |
| Teacher Qualifications | Highly qualified, often requires advanced degrees | Certified by state, varying experience levels |
| Future Opportunities | Strong networking, college prep, scholarships | Good foundational skills, diverse post-secondary options |
Introduction to Private and Public Schools
Private schools typically operate independently from government funding and offer specialized curricula, smaller class sizes, and more extracurricular options, often resulting in higher tuition fees. Public schools are funded and regulated by government entities, providing free education to all students with standardized curricula designed to meet state guidelines. Parenting choices influence the decision between private and public education based on factors like budget, educational goals, and community values.
Curriculum Differences: Private vs Public
Private schools often offer specialized curricula with advanced coursework and a focus on individualized learning, while public schools adhere to state-mandated standards that emphasize standardized testing and core subjects. The flexibility in private school curricula allows for enrichment programs, classical education models, and integrated arts or languages, contrasting with public school constraints due to funding and policy regulations. Parenting decisions around schooling frequently consider these curriculum differences to align educational approaches with a child's learning needs and family values.
Cost and Tuition Comparison
Private schools often have higher tuition fees compared to public schools, which typically offer free education funded by the government. Your decision should factor in not only the immediate cost of private school tuition but also related expenses like uniforms, extracurricular activities, and transportation. Parenting choices play a crucial role in balancing education quality with affordability, as many families prioritize budget-friendly public schools while seeking supplemental educational support at home.
Class Size and Student-Teacher Ratios
Private schools often maintain smaller class sizes, averaging around 12 to 15 students per classroom, which enhances personalized attention and tailored instruction. Public schools typically have larger class sizes, with averages ranging from 20 to 30 students, impacting the student-teacher ratio and potentially limiting individualized support. Parenting choices influence the selection based on desired class size and student-teacher ratios, with many parents opting for private education to ensure more focused learning environments.
Extracurricular Activities and Facilities
Private schools often offer a wider range of extracurricular activities and superior facilities, including specialized sports arenas, music studios, and advanced technology labs, enhancing student development beyond academics. Public schools typically provide diverse extracurricular programs that reflect community interests but may face limitations in funding which affects facility quality and availability. Parenting plays a crucial role in encouraging participation in these activities, supporting skill-building, and supplementing resources when school offerings are limited.
Academic Performance and Outcomes
Academic performance often varies between private and public schools, with private schools typically offering smaller class sizes and more specialized resources that can enhance student learning outcomes. Parenting plays a crucial role in mediating these effects by providing support that fosters motivation, discipline, and effective study habits regardless of school type. You can optimize your child's academic success by actively engaging in their education and choosing an environment that aligns with their learning needs and your educational values.
Admission Processes and Requirements
Choosing between private and public schools often hinges on differing admission processes and requirements, where private schools typically demand entrance exams, interviews, and comprehensive applications, while public schools usually accept students based on geographic zoning with minimal paperwork. Your preparation should address private school criteria like testing and recommendations to enhance acceptance chances, whereas public school enrollment prioritizes proof of residency and age verification. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate and optimize the admission experience tailored to your child's educational path.
Diversity and Inclusivity in Schools
Private schools often have selective admission policies that can limit diversity, while public schools are mandated to serve diverse student populations, promoting inclusivity through varied cultural and socioeconomic backgrounds. Your child benefits most in environments where educators actively implement inclusive curricula and foster acceptance, regardless of school type. Emphasizing diversity in both private and public settings prepares students for global citizenship and enriches social learning experiences.
Parental Involvement and Community
Parental involvement significantly shapes the educational experience in both private and public schools, with private schools often encouraging closer parent-teacher collaboration and community engagement. Public schools typically rely on a broader community network, offering diverse opportunities for parental participation through school boards and local programs. Understanding your role in fostering communication and support between home and school enhances your child's academic success and social development.
Making the Right Choice for Your Child
Choosing between private and public schools involves evaluating factors such as curriculum quality, class size, extracurricular opportunities, and school culture to align with your child's learning style and needs. Parenting plays a crucial role in this decision by assessing your family's values, financial resources, and long-term educational goals, ensuring the chosen environment supports your child's academic growth and emotional well-being. Research on student performance and parental involvement highlights that active engagement in your child's education often has a greater impact than the type of school alone.
Infographic: Private School vs Public School
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com