Anticipatory grief occurs when individuals experience sorrow before an expected loss, often during a loved one's terminal illness, while traditional grief arises after the actual loss has occurred. To explore the differences, effects, and coping strategies of these grief types, discover more in this article.
Table of Comparison
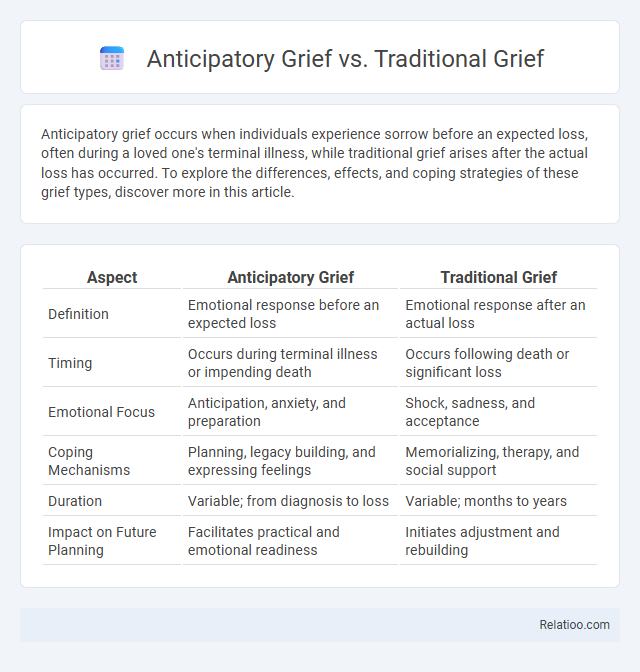
| Aspect | Anticipatory Grief | Traditional Grief |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional response before an expected loss | Emotional response after an actual loss |
| Timing | Occurs during terminal illness or impending death | Occurs following death or significant loss |
| Emotional Focus | Anticipation, anxiety, and preparation | Shock, sadness, and acceptance |
| Coping Mechanisms | Planning, legacy building, and expressing feelings | Memorializing, therapy, and social support |
| Duration | Variable; from diagnosis to loss | Variable; months to years |
| Impact on Future Planning | Facilitates practical and emotional readiness | Initiates adjustment and rebuilding |
Understanding Grief: Anticipatory vs. Traditional
Understanding grief involves differentiating anticipatory grief, which occurs before an impending loss such as terminal illness, from traditional grief experienced after a loss. Anticipatory grief allows individuals to emotionally prepare for the death, often involving a complex mix of hope and sorrow, while traditional grief centers on coping with the finality of loss and the ensuing emotional adjustment. Recognizing these variations helps in tailoring support strategies and interventions for those facing bereavement at different stages.
Defining Anticipatory Grief
Anticipatory grief occurs before an impending loss, often experienced by caregivers or loved ones facing terminal illness, allowing emotional processing in advance. Traditional grief emerges after the actual loss, marked by stages of mourning and adjustment to life without the deceased. Understanding anticipatory grief helps differentiate it from traditional grief by recognizing its proactive emotional responses to an expected death.
What Constitutes Traditional Grief?
Traditional grief constitutes the emotional, physical, and psychological response experienced after the loss of a loved one, typically unfolding through stages such as denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance. It often involves a period of mourning marked by memories, rituals, and social support, helping individuals process the reality of death. Your understanding of traditional grief is essential for distinguishing it from anticipatory grief, which occurs before an impending loss.
Key Differences Between Anticipatory and Traditional Grief
Anticipatory grief occurs before a loss, often triggered by a terminal illness diagnosis, allowing individuals to begin processing emotions in advance, while traditional grief happens after the actual death or loss. Key differences include the timing and emotional experience; anticipatory grief may involve hope, anxiety, and preparation, whereas traditional grief typically centers on shock, disbelief, and intense sorrow. Coping mechanisms vary, with anticipatory grief sometimes facilitating adjustment by fostering emotional acceptance and expected closure, contrasting with the suddenness and often more overwhelming nature of traditional grief.
Emotional Responses in Anticipatory Grief
Anticipatory grief involves emotional responses such as anxiety, sadness, and helplessness that occur before an actual loss, often triggered by the impending death of a loved one. Traditional grief typically manifests through intense sorrow, yearning, and depression after the loss has occurred. Emotional responses in anticipatory grief can help individuals prepare mentally and emotionally for the loss, potentially leading to a different grieving process compared to traditional grief.
Coping Mechanisms for Traditional Grief
Traditional grief involves emotional responses after the loss of a loved one, characterized by sadness, anger, and longing. Coping mechanisms for traditional grief include seeking support from friends, engaging in counseling or therapy, and practicing self-care activities to manage emotional pain. Your ability to process these feelings through rituals, journaling, or mindfulness can facilitate healing and adjustment during the grieving period.
The Role of Time: Before vs. After the Loss
Anticipatory grief occurs before the actual loss, allowing individuals to process emotions in advance, often during a prolonged illness or expected death. Traditional grief happens after the loss, involving a period of adjustment as individuals cope with absence and change. The key distinction lies in the timeline--anticipatory grief provides a preparatory phase, while traditional grief demands emotional adaptation solely post-loss.
Impact on Relationships and Support Systems
Anticipatory grief often alters relationships by creating emotional distance as individuals brace for a loss, leading to strained support systems due to unresolved feelings. Traditional grief, occurring after a loss, can either strengthen bonds through shared mourning or cause isolation if support is lacking. General grief impacts relationships variably, with strong networks fostering healing, while inadequate support can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and hinder recovery.
Navigating Both Types of Grief
Navigating anticipatory grief involves recognizing the emotional impact of impending loss, enabling individuals to process feelings before actual bereavement occurs, while traditional grief centers on coping with loss after it has happened. Strategies such as open communication, seeking counseling, and building support networks help manage both anticipatory and traditional grief effectively. Understanding the nuances between these types of grief allows for tailored emotional responses and healthier psychological adjustment throughout the grieving process.
Seeking Help: Resources for Grief Support
Seeking help for anticipatory grief involves accessing specialized counseling services that address the unique emotional challenges of expecting a loss, often available through hospice programs and mental health professionals. Traditional grief support frequently includes grief support groups, therapy, and community resources that aid individuals coping with loss after it occurs. Various organizations, such as the National Alliance for Grieving Children and GriefShare, provide tailored resources and educational materials to assist individuals navigating different stages and types of grief.
Infographic: Anticipatory Grief vs Traditional Grief
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com