A 529 Plan offers higher contribution limits and state tax benefits, making it ideal for long-term college savings, while a Coverdell ESA provides more investment flexibility and covers K-12 expenses with lower contribution limits. Learn more about how these education savings plans compare and which best suits your financial goals in this article.
Table of Comparison
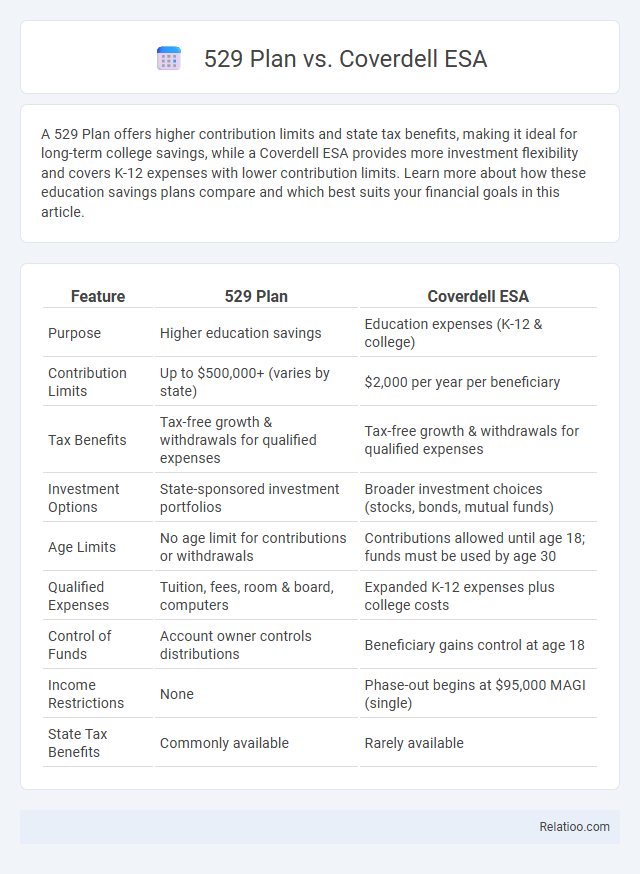
| Feature | 529 Plan | Coverdell ESA |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Higher education savings | Education expenses (K-12 & college) |
| Contribution Limits | Up to $500,000+ (varies by state) | $2,000 per year per beneficiary |
| Tax Benefits | Tax-free growth & withdrawals for qualified expenses | Tax-free growth & withdrawals for qualified expenses |
| Investment Options | State-sponsored investment portfolios | Broader investment choices (stocks, bonds, mutual funds) |
| Age Limits | No age limit for contributions or withdrawals | Contributions allowed until age 18; funds must be used by age 30 |
| Qualified Expenses | Tuition, fees, room & board, computers | Expanded K-12 expenses plus college costs |
| Control of Funds | Account owner controls distributions | Beneficiary gains control at age 18 |
| Income Restrictions | None | Phase-out begins at $95,000 MAGI (single) |
| State Tax Benefits | Commonly available | Rarely available |
Understanding 529 Plans and Coverdell ESAs
529 Plans offer tax-advantaged savings specifically for qualified education expenses, allowing contributions up to $500,000 per beneficiary with tax-free growth and withdrawals. Coverdell ESAs provide up to $2,000 annually per beneficiary, covering a broader range of educational expenses including K-12, but have lower contribution limits and phase out at higher incomes. Both plans support education planning by leveraging tax benefits to build funds for tuition, books, and supplies, with 529 Plans favored for college savings and Coverdell ESAs offering more flexibility for earlier education stages.
Key Features and Eligibility Requirements
529 Plans offer high contribution limits, tax-free growth, and withdrawals for qualified education expenses with no income restrictions, making them ideal for K-12 and college savings. Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) have lower contribution limits of $2,000 per beneficiary annually and stricter income eligibility, focusing on K-12 and college expenses with tax-free growth. Education planning involves evaluating these accounts' features, including tax benefits, contribution limits, and eligibility, to maximize funds for future education costs.
Contribution Limits and Rules
529 Plans offer high contribution limits, often exceeding $300,000 per beneficiary, making them ideal for long-term education savings with tax-free growth for qualified expenses. Coverdell ESAs have stricter rules, with an annual contribution limit of $2,000 per beneficiary and income restrictions for contributors, focusing on K-12 and college expenses. Your choice should consider contribution flexibility, beneficiary age limits, and the scope of qualified expenses to optimize education planning outcomes.
Qualified Expenses and Flexibility
529 Plans allow you to use funds for qualified expenses including tuition, room and board, and certain K-12 expenses with high contribution limits and state tax benefits. Coverdell ESAs cover a broader range of qualified education expenses such as tutoring and uniforms but have lower contribution limits and income restrictions. Your education planning should balance the 529 Plan's flexibility for higher education costs with the Coverdell ESA's advantages for elementary and secondary education expenses.
Investment Options and Growth Potential
529 Plans offer a broad range of investment options, including age-based portfolios and individual funds, with tax-deferred growth and no income limits, making them highly attractive for maximizing long-term education savings. Coverdell ESAs provide a wider variety of investment choices, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, but feature lower contribution limits and phase-outs for higher-income earners that may limit growth potential. Effective education planning involves balancing the flexibility and growth potential of 529 Plans against the investment diversity of Coverdell ESAs to optimize savings based on individual financial goals and risk tolerance.
Tax Benefits and Implications
A 529 Plan offers tax-free growth and tax-free withdrawals for qualified education expenses, making it highly advantageous for college savings with high contribution limits and state tax deductions. The Coverdell ESA provides tax-free growth and withdrawals but has lower contribution limits and income restrictions, allowing more flexibility for K-12 expenses. Your choice in education planning should consider these tax benefits alongside income limits, qualified expense definitions, and potential impact on financial aid to maximize savings efficiency.
State-Specific Advantages and Rules
State-specific advantages of a 529 Plan often include tax deductions or credits for contributions, which vary widely by state and can significantly impact Your savings growth potential. Coverdell ESAs offer more flexible investment options and can be used for K-12 expenses, but have lower contribution limits and state tax benefits are less common. Understanding differences in state tax treatment, contribution limits, and qualified expenses for both plans is crucial to optimize Your education planning strategy effectively.
Impact on Financial Aid and FAFSA
Maximizing financial aid eligibility requires understanding how 529 Plans and Coverdell ESAs impact your FAFSA results differently; 529 Plans are reported as parental assets and typically reduce aid eligibility by up to 5.64%, while Coverdell ESAs are student assets and may reduce aid by up to 20%. Your financial aid strategy should consider that 529 Plan withdrawals are not counted as income on FAFSA, whereas Coverdell ESA distributions can affect reported student income, potentially reducing aid in subsequent years. Strategic education planning leverages these differences to minimize your Expected Family Contribution (EFC) and maximize financial aid opportunities.
Withdrawal Penalties and Restrictions
529 Plans allow tax-free withdrawals for qualified education expenses with penalties and income tax on earnings if used for non-qualified expenses, while Coverdell ESAs impose similar penalties but have lower contribution limits and broader expense eligibility, including K-12 costs. Withdrawals from 529 Plans are generally more flexible for higher education expenses, whereas Coverdell ESA withdrawals must occur by age 30 to avoid penalties. Education planning must consider these withdrawal restrictions to maximize tax benefits and avoid penalties, balancing contribution limits, eligible expenses, and age-related constraints.
Choosing the Best Education Savings Account
Choosing the best education savings account depends on your specific financial goals, income limits, and the intended use of funds. 529 Plans offer higher contribution limits and tax-free growth for qualified education expenses, making them ideal for college savings, while Coverdell ESAs provide more investment options and flexibility with K-12 expenses but have lower contribution limits and income restrictions. Evaluating your education planning needs helps you select the account that maximizes tax benefits and suits your child's educational timeline.
Infographic: 529 Plan vs Coverdell ESA
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com