Egg freezing preserves a woman's unfertilized eggs for future use, while embryo freezing involves freezing fertilized eggs created through IVF, offering higher success rates for pregnancy. Learn more about the benefits and differences between egg freezing and embryo freezing in this article.
Table of Comparison
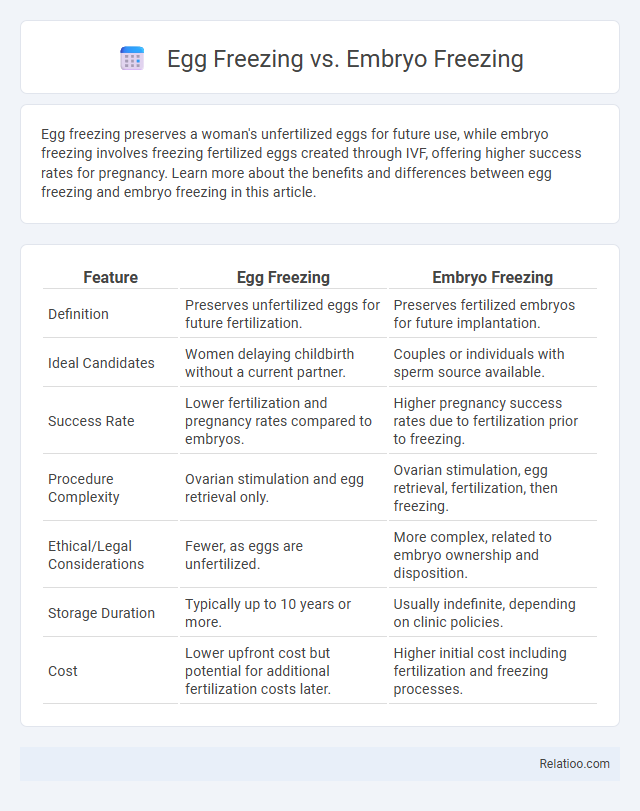
| Feature | Egg Freezing | Embryo Freezing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preserves unfertilized eggs for future fertilization. | Preserves fertilized embryos for future implantation. |
| Ideal Candidates | Women delaying childbirth without a current partner. | Couples or individuals with sperm source available. |
| Success Rate | Lower fertilization and pregnancy rates compared to embryos. | Higher pregnancy success rates due to fertilization prior to freezing. |
| Procedure Complexity | Ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval only. | Ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization, then freezing. |
| Ethical/Legal Considerations | Fewer, as eggs are unfertilized. | More complex, related to embryo ownership and disposition. |
| Storage Duration | Typically up to 10 years or more. | Usually indefinite, depending on clinic policies. |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost but potential for additional fertilization costs later. | Higher initial cost including fertilization and freezing processes. |
Introduction to Fertility Preservation
Fertility preservation encompasses techniques such as egg freezing and embryo freezing to safeguard reproductive potential for individuals facing medical treatments or delayed childbearing. Egg freezing involves retrieving and cryopreserving oocytes before fertilization, while embryo freezing requires fertilizing eggs with sperm prior to storage. Selecting between these methods depends on factors like age, relationship status, and medical conditions, with each offering distinct success rates and future family planning flexibility.
Understanding Egg Freezing
Egg freezing preserves your fertility by storing unfertilized eggs at low temperatures for future use, offering flexibility without the need for immediate sperm fertilization. Unlike embryo freezing, which involves fertilizing eggs before preservation and is often preferred by couples, egg freezing allows single individuals to maintain reproductive options independently. Understanding the benefits and limitations of egg freezing empowers you to make informed decisions about extending your fertility timeline.
Understanding Embryo Freezing
Embryo freezing is a fertility preservation method where fertilized eggs are frozen at the embryo stage, offering higher success rates compared to egg freezing due to the viability of embryos already fertilized with sperm. This procedure allows couples or individuals to store embryos for future use, increasing the chances of pregnancy while avoiding the variability of egg quality. Understanding embryo freezing involves recognizing its role in assisted reproductive technology, especially for those undergoing medical treatments that could impact fertility or for planned delayed parenthood.
Key Differences: Egg vs Embryo Freezing
Egg freezing preserves your unfertilized oocytes, allowing future fertilization options, whereas embryo freezing involves fertilized eggs at the blastocyst stage, ready for implantation. Egg freezing offers more flexibility for single women without a partner, while embryo freezing generally has higher success rates due to the embryos being pre-formed. Understanding these key differences is crucial for making informed decisions about your fertility preservation options.
Success Rates and Outcomes
Egg freezing and embryo freezing offer different success rates and outcomes depending on factors like age and fertility health. Embryo freezing generally shows higher success rates because embryos are fertilized before freezing, increasing implantation potential. Your choice depends on whether you have a partner or donor sperm available, with embryo freezing often recommended for higher pregnancy success compared to egg freezing.
Ideal Candidates for Each Method
Egg freezing is ideal for women under 35 who wish to preserve fertility before medical treatments or delayed childbirth, benefiting from better egg quality at a younger age. Embryo freezing suits couples undergoing IVF with a partner's sperm or donor sperm, offering higher success rates due to embryos being fertilized prior to freezing. Fertility preservation strategies, including both methods, are recommended based on age, medical history, and reproductive goals, ensuring personalized approaches to maximize future pregnancy outcomes.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Egg freezing, embryo freezing, and fertility treatments involve complex legal and ethical considerations that vary significantly by jurisdiction and impact your reproductive rights and options. Regulations often address consent, storage duration, and disposition of unused eggs or embryos, while ethical debates focus on the moral status of embryos and the implications of creating life in vitro. Understanding these factors is essential for informed decision-making and safeguarding your reproductive autonomy.
Cost Comparison and Financial Planning
Egg freezing typically costs between $6,000 and $15,000 per cycle, while embryo freezing expenses range from $7,000 to $20,000, with additional storage fees averaging $500 annually, impacting your overall financial planning. Fertility treatments often require multiple cycles, increasing cumulative costs and emphasizing the importance of budgeting for associated procedures like hormone injections and monitoring. Understanding these price differences helps you make informed decisions about your reproductive options and effectively manage long-term expenses.
Emotional and Psychological Impacts
Egg freezing and embryo freezing present distinct emotional and psychological challenges, where egg freezing may induce anxiety linked to uncertain future fertility outcomes, while embryo freezing often involves complex feelings around genetic parenthood and relationship dynamics. Fertility preservation decisions can trigger stress, depression, and feelings of loss or control, emphasizing the need for psychological support throughout the process. Understanding these nuances helps individuals navigate reproductive choices with better mental health outcomes and emotional resilience.
Making an Informed Decision: Which Is Right for You?
Egg freezing preserves a woman's unfertilized eggs for future use, ideal for those wanting to delay pregnancy without a partner or sperm source, while embryo freezing involves fertilizing eggs with sperm before freezing, offering higher success rates but requiring a partner or donor sperm at the time of preservation. Fertility considerations include age, ovarian reserve, medical conditions, and personal reproductive goals, all crucial for determining the most suitable method. Consulting a fertility specialist helps assess ovarian health, success probabilities, and ethical preferences, empowering an informed decision tailored to individual circumstances.
Infographic: Egg Freezing vs Embryo Freezing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com