Authoritarian relationships are characterized by strict control and lack of personal freedom, while democratic relationships emphasize mutual respect, communication, and shared decision-making. Discover more about the dynamics and impacts of these relationship styles in this article.
Table of Comparison
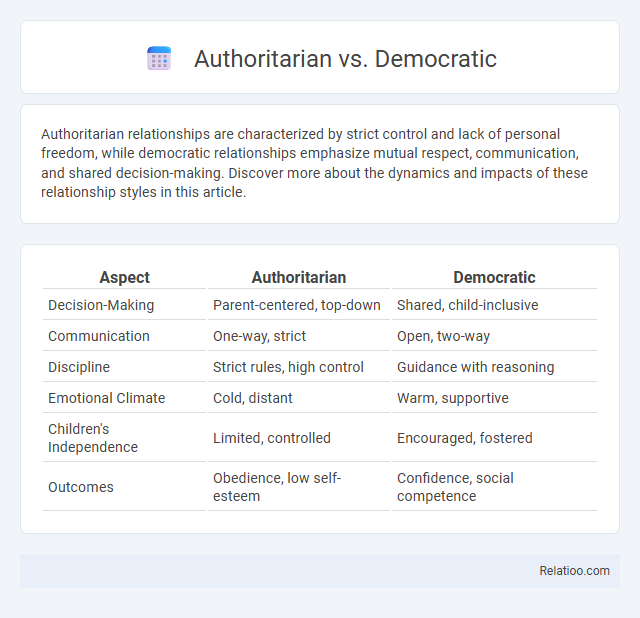
| Aspect | Authoritarian | Democratic |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Parent-centered, top-down | Shared, child-inclusive |
| Communication | One-way, strict | Open, two-way |
| Discipline | Strict rules, high control | Guidance with reasoning |
| Emotional Climate | Cold, distant | Warm, supportive |
| Children's Independence | Limited, controlled | Encouraged, fostered |
| Outcomes | Obedience, low self-esteem | Confidence, social competence |
Understanding Authoritarian and Democratic Systems
Authoritarian systems centralize power, limiting political freedoms and opposing dissent, often relying on strict control mechanisms and centralized decision-making. Democratic systems emphasize political pluralism, free elections, rule of law, and citizen participation, fostering an environment where power is dispersed and accountability is enforced. Understanding these fundamental differences highlights the impact on governance, civil liberties, and societal development within each system.
Historical Evolution of Political Regimes
The historical evolution of political regimes highlights a shift from authoritarian systems, characterized by centralized control and limited individual freedoms, to democratic structures that emphasize citizen participation and rule of law. Authoritarian regimes often arose from periods of instability or conflict, consolidating power through repression and limited political competition, while democratic regimes evolved through revolutions, social movements, and institutional reforms promoting representation and accountability. Your understanding of these transitions helps contextualize the dynamic interplay between governance models and societal development over time.
Key Characteristics of Authoritarian Governments
Authoritarian governments centralize power in a single authority or a small group, limit political pluralism, and restrict individual freedoms and dissent to maintain control. Unlike democratic systems that emphasize participation and accountability, authoritarian regimes often rely on censorship, surveillance, and coercion to suppress opposition. Understanding these characteristics helps you identify the constraints on political rights and civil liberties inherent to authoritarian rule.
Defining Features of Democratic Societies
Democratic societies prioritize individual freedoms, rule of law, and participatory governance where citizens actively engage in decision-making processes through free and fair elections. Your voice is protected by constitutional guarantees such as freedom of speech, press, and assembly, ensuring transparency and accountability of leaders. Unlike authoritarian regimes, democracies maintain checks and balances across branches of government to prevent concentration of power and enable pluralism.
Leadership and Power Distribution
Authoritarian leadership centralizes power in a single ruler or a small group, enforcing strict control with limited political freedoms and decision-making concentrated at the top. Democratic leadership distributes power among elected representatives or the populace, promoting participatory governance, accountability, and collective decision-making processes. Hybrid systems blend authoritarian control with democratic elements, often maintaining centralized power while allowing some degree of political pluralism or electoral competition.
Citizen Participation and Civil Liberties
Authoritarian regimes typically limit citizen participation and heavily restrict civil liberties, concentrating power in the hands of a single leader or ruling party. Democratic systems encourage widespread citizen participation through free elections and protect civil liberties like freedom of speech, assembly, and privacy. Your engagement in civic activities flourishes in democratic societies where civil rights are safeguarded, contrasting sharply with the controlled environments of authoritarian states.
Decision-Making Processes
Authoritarian decision-making centralizes power, allowing leaders to make swift choices without seeking input, which can streamline processes but limit diverse perspectives. Democratic decision-making encourages collective participation, where Your input influences outcomes through voting or open discussions, promoting transparency and inclusivity. Balancing these approaches involves weighing efficiency against collaboration to achieve effective leadership tailored to the organization's needs.
Economic Impacts of Governance Styles
Authoritarian governance often enables swift decision-making that can accelerate infrastructure projects and economic reforms but may stifle innovation due to limited political freedoms. Democratic regimes typically foster sustainable economic growth by encouraging transparency, accountability, and inclusive policies that stimulate entrepreneurship and foreign investment. Hybrid systems, blending elements of both, may experience economic volatility as conflicting governance practices impact investor confidence and policy consistency.
Social Stability and Human Rights
Authoritarian regimes often prioritize social stability through centralized control and strict enforcement, sometimes at the expense of human rights such as freedom of expression and assembly. Democratic systems promote social stability by fostering inclusive governance and protecting human rights, allowing for dissent and citizen participation in decision-making. Hybrid or semi-authoritarian governments may exhibit a mix of both approaches, maintaining control to ensure order while selectively permitting certain rights, resulting in varied impacts on social stability and human rights protection.
Global Trends and Future Prospects
Global trends reveal a complex balance between authoritarian and democratic governance, with an increasing number of countries experiencing hybrid regimes that blend elements of both systems. Emerging technologies and shifting geopolitical power are reshaping how authoritarian and democratic governments maintain control and influence, impacting your understanding of global stability and human rights. Future prospects suggest continued contestation between these models, driven by societal demands for transparency, economic development, and security challenges worldwide.
Infographic: Authoritarian vs Democratic
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com