Estrangement refers to a mutual distancing between individuals, often due to unresolved conflicts, while alienation describes one party feeling isolated or excluded within a relationship. Discover the key differences and impacts of estrangement and alienation in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
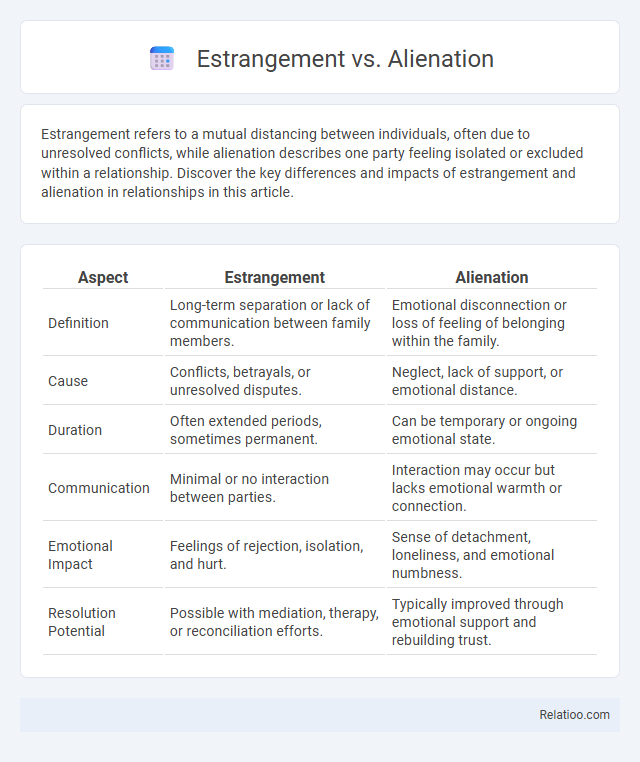
| Aspect | Estrangement | Alienation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long-term separation or lack of communication between family members. | Emotional disconnection or loss of feeling of belonging within the family. |
| Cause | Conflicts, betrayals, or unresolved disputes. | Neglect, lack of support, or emotional distance. |
| Duration | Often extended periods, sometimes permanent. | Can be temporary or ongoing emotional state. |
| Communication | Minimal or no interaction between parties. | Interaction may occur but lacks emotional warmth or connection. |
| Emotional Impact | Feelings of rejection, isolation, and hurt. | Sense of detachment, loneliness, and emotional numbness. |
| Resolution Potential | Possible with mediation, therapy, or reconciliation efforts. | Typically improved through emotional support and rebuilding trust. |
Understanding Estrangement: Definition and Context
Estrangement refers to the state of being emotionally or physically separated from someone or something, often involving a breakdown in relationships due to conflict or misunderstanding. It differs from alienation, which is a broader sense of disconnection or isolation from society, oneself, or loved ones. Understanding estrangement in your context involves recognizing its roots in personal experiences and the specific dynamics that lead to this relational distance.
What is Alienation? Core Concepts Explained
Alienation refers to a psychological state where individuals feel isolated or disconnected from their environment, society, or themselves, often leading to a sense of powerlessness or meaninglessness. Core concepts of alienation include loss of control, social isolation, and self-estrangement, primarily explored in Marxist and existentialist theories. Unlike estrangement, which emphasizes separation or distancing, alienation specifically highlights emotional and cognitive disconnection affecting identity and agency.
Key Differences Between Estrangement and Alienation
Estrangement refers to the loss of affection or connection between individuals, often within family or close relationships, characterized by emotional distance and withdrawal. Alienation describes a broader psychological state where individuals feel isolated or disconnected from their environment, society, or self, often resulting in feelings of powerlessness or estrangement from social norms. The key difference lies in estrangement's focus on interpersonal relationships, while alienation encompasses a wider sense of isolation affecting social and self-identity domains.
Causes of Estrangement in Relationships
Causes of estrangement in relationships often include unresolved conflicts, lack of communication, and betrayals that erode trust between parties. Alienation differs as it tends to involve emotional distancing and feelings of isolation without complete severance, while estrangement denotes a more definitive breakdown or absence of relationship. Understanding these distinctions aids in addressing underlying issues such as neglect, differing values, or traumatic events that contribute to estrangement's development.
Factors Leading to Alienation
Factors leading to alienation often include prolonged social isolation, unresolved conflicts, and lack of emotional support, which create feelings of powerlessness and disconnection from others. Unlike estrangement, which typically involves a mutual withdrawal between family members or close relations, alienation is characterized by a deeper psychological separation affecting your sense of belonging and identity. Understanding these factors helps in identifying the root causes of alienation to address emotional distance effectively.
Psychological Impacts of Estrangement
Estrangement involves a profound disconnection from loved ones, leading to feelings of isolation, decreased self-esteem, and increased risk of depression and anxiety. Unlike alienation, which is often a broader societal or existential detachment, estrangement specifically impacts interpersonal relationships and emotional well-being. Psychological effects of estrangement frequently include chronic stress and a weakened sense of identity, contributing to long-term mental health challenges.
The Emotional Effects of Alienation
Alienation often leads to intense emotional distress characterized by feelings of isolation, helplessness, and diminished self-worth, which differentiates it from estrangement where physical or relational separation may not involve such profound psychological impact. The emotional toll of alienation can manifest as anxiety, depression, and a pervasive sense of disconnection from others and oneself, disrupting mental well-being. In contrast, estrangement may primarily involve a breakdown in communication or attachment without necessarily fostering the deep emotional alienation that undermines identity and belonging.
Estrangement vs Alienation: Signs and Symptoms
Estrangement and alienation both involve emotional distance but differ in origin and intensity; estrangement typically arises from broken relationships often marked by silence and avoidance, while alienation is a broader sense of isolation and disconnection from self, others, or society. Signs of estrangement include feelings of bitterness, unresolved conflicts, and lack of communication, whereas alienation manifests as emotional numbness, withdrawal, and a sense of meaninglessness. Recognizing these symptoms can help you address the underlying issues and seek appropriate support.
Overcoming Estrangement: Strategies and Solutions
Overcoming estrangement involves rebuilding trust through open communication, empathy, and setting healthy boundaries to restore familial or social connections. You can implement strategies such as seeking professional counseling, practicing active listening, and fostering forgiveness to address the emotional distance causing estrangement. Consistent efforts to understand underlying issues and prioritize relationship healing are crucial for resolving both estrangement and alienation effectively.
Healing from Alienation: Steps Towards Reconnection
Healing from alienation involves recognizing the emotional barriers that cause isolation and taking intentional steps to rebuild trust and communication with those who are estranged. You can begin by fostering empathy, actively listening, and expressing vulnerability to bridge the gap created by alienation. Consistent efforts to reconnect, such as seeking professional support or family therapy, play a crucial role in transforming alienation into renewed relationships.
Infographic: Estrangement vs Alienation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com