Functional families provide emotional support, stability, and effective communication regardless of size or structure, while nuclear families consist of two parents and their children living together, often emphasizing traditional roles. Discover the key differences and benefits of each family type in this article.
Table of Comparison
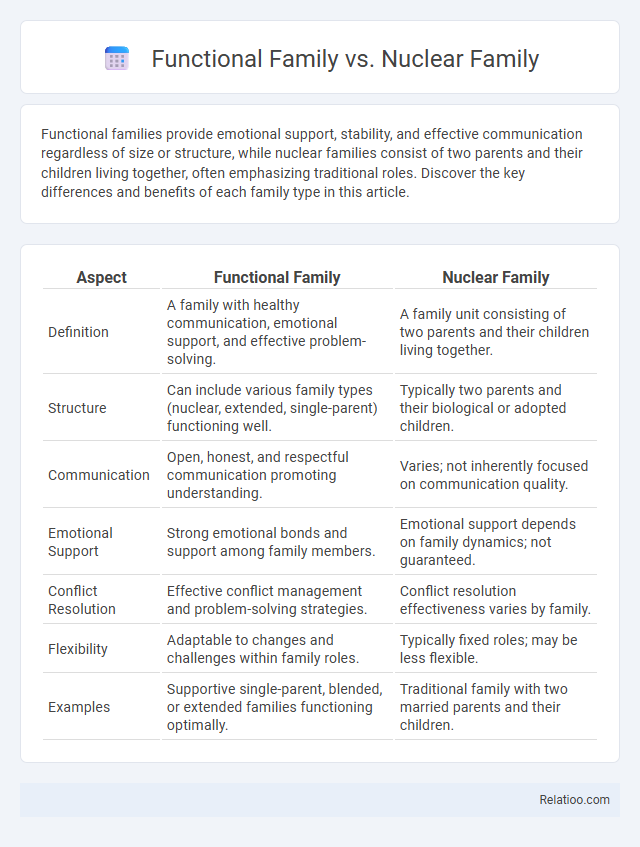
| Aspect | Functional Family | Nuclear Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A family with healthy communication, emotional support, and effective problem-solving. | A family unit consisting of two parents and their children living together. |
| Structure | Can include various family types (nuclear, extended, single-parent) functioning well. | Typically two parents and their biological or adopted children. |
| Communication | Open, honest, and respectful communication promoting understanding. | Varies; not inherently focused on communication quality. |
| Emotional Support | Strong emotional bonds and support among family members. | Emotional support depends on family dynamics; not guaranteed. |
| Conflict Resolution | Effective conflict management and problem-solving strategies. | Conflict resolution effectiveness varies by family. |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to changes and challenges within family roles. | Typically fixed roles; may be less flexible. |
| Examples | Supportive single-parent, blended, or extended families functioning optimally. | Traditional family with two married parents and their children. |
Defining Functional and Nuclear Families
A functional family is characterized by healthy communication, emotional support, and well-defined roles that promote individual growth and stability, whereas a nuclear family consists of two parents and their children living together as a basic social unit. Functional families emphasize effective interaction and adaptability, ensuring members' needs are met, while nuclear families are defined by their structural composition rather than the quality of relationships. Understanding the distinction highlights that a nuclear family can be functional or dysfunctional depending on the dynamics among its members.
Historical Evolution of Family Structures
Historical evolution of family structures reveals a transition from extended, functional family systems to more compact nuclear families that focus on emotional bonds and individual roles. Functional families emphasize adaptive roles and interdependence, crucial during agrarian and early industrial societies, while nuclear families emerged prominently in urbanized, industrialized societies demanding mobility and economic efficiency. Understanding these shifts helps you appreciate how cultural, economic, and social changes shape family dynamics and support mechanisms over time.
Core Characteristics of a Functional Family
A functional family is defined by strong communication, emotional support, and healthy boundaries among its members, fostering trust and resilience. Unlike nuclear families, which are typically composed of two parents and their children, functional families prioritize effective problem-solving and mutual respect regardless of structure. Your family's ability to provide stability, nurture positive relationships, and adapt to challenges reflects the core characteristics that distinguish a functional family unit.
Key Features of a Nuclear Family
A nuclear family typically consists of two parents and their children living together as a single unit, emphasizing close, direct relationships and shared responsibilities. Key features include economic cooperation, clear parental roles, and emotional support within a household, fostering stability and effective communication. Understanding these attributes helps you appreciate how a nuclear family distinctly differs from extended or functional family structures.
Emotional and Social Dynamics
The emotional and social dynamics in a functional family prioritize healthy communication, mutual support, and effective conflict resolution, fostering emotional security and strong interpersonal bonds. In contrast, a nuclear family typically consists of two parents and their children, with dynamics varying widely based on emotional expressiveness and social interactions, which can range from supportive to strained. Understanding these differences helps you recognize the impact of family structure on emotional well-being and social development, emphasizing the importance of functionality over mere composition.
Roles and Responsibilities within Each Family Type
In a Nuclear Family, roles are traditionally divided with parents responsible for income and caregiving, while children focus on education and development. Functional Families emphasize clear communication and adaptability, with members sharing responsibilities like emotional support, household tasks, and decision-making based on individual strengths. Both family types prioritize stability and healthy role distribution, but Functional Families may exhibit more flexibility in roles to meet changing needs.
Impact on Child Development and Well-being
The impact on child development and well-being differs significantly among functional family, nuclear family, and extended family structures, with functional families prioritizing emotional support and stability regardless of size. Your child benefits most from consistent nurturing environments that promote secure attachment, social skills, and resilience. Research shows that nuclear families often provide focused attention, while extended families can offer diverse role models and broader social networks, all contributing uniquely to a child's emotional and psychological growth.
Adaptability to Modern Societal Changes
Functional families prioritize effective communication and emotional support, allowing them to adapt seamlessly to modern societal changes by evolving roles and responsibilities within the household. Nuclear families, consisting of two parents and their children, may face challenges in adaptability due to limited extended support systems but can strengthen resilience through clear structure and role flexibility. Your ability to foster open communication and shared responsibilities enhances adaptability regardless of family type, ensuring stronger coping mechanisms in the face of societal shifts.
Challenges Faced by Functional and Nuclear Families
Functional families maintain stability through effective communication and role flexibility, but they face challenges such as balancing work-life demands and managing emotional stress. Nuclear families often struggle with limited support systems, leading to isolation and increased pressure on parents to fulfill multiple roles. Your ability to adapt and seek external support can mitigate these challenges and foster family resilience.
Choosing the Optimal Family Structure for Today’s World
Choosing the optimal family structure for today's world involves understanding the key differences between functional, nuclear, and extended families. Functional families prioritize healthy communication, emotional support, and adaptability, making them resilient across various social and economic challenges. Your best choice depends on personal values and lifestyle, as nuclear families emphasize privacy and simplicity, while extended families offer broader support networks essential in certain cultural contexts.
Infographic: Functional Family vs Nuclear Family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com