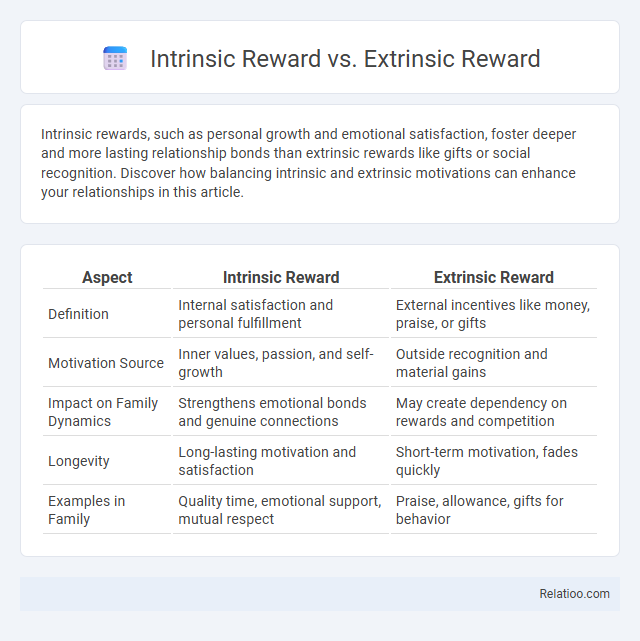
Intrinsic rewards, such as personal growth and emotional satisfaction, foster deeper and more lasting relationship bonds than extrinsic rewards like gifts or social recognition. Discover how balancing intrinsic and extrinsic motivations can enhance your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Intrinsic Reward | Extrinsic Reward |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal satisfaction and personal fulfillment | External incentives like money, praise, or gifts |
| Motivation Source | Inner values, passion, and self-growth | Outside recognition and material gains |
| Impact on Family Dynamics | Strengthens emotional bonds and genuine connections | May create dependency on rewards and competition |
| Longevity | Long-lasting motivation and satisfaction | Short-term motivation, fades quickly |
| Examples in Family | Quality time, emotional support, mutual respect | Praise, allowance, gifts for behavior |
Understanding Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Rewards
Intrinsic rewards stem from internal satisfaction and personal fulfillment, motivating individuals through enjoyment, interest, and a sense of accomplishment. Extrinsic rewards originate from external sources such as money, praise, or recognition, driving behavior by offering tangible incentives or avoiding punishment. Understanding the distinction between intrinsic and extrinsic rewards is crucial for designing effective motivational strategies that align with long-term engagement and performance outcomes.
Key Differences between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic reward stems from internal satisfaction, such as personal growth or enjoyment, while extrinsic reward involves external incentives like money, praise, or trophies. Key differences between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation include the source of motivation--internal feelings versus external rewards--and their impact on long-term engagement, where intrinsic motivation fosters sustained interest and extrinsic motivation may lead to temporary compliance. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize motivation strategies in educational, workplace, and behavioral contexts.
Psychological Foundations of Reward Systems
Intrinsic reward stems from innate satisfaction and personal fulfillment, engaging the brain's reward system through dopamine release during activities aligned with one's values or interests. Extrinsic reward involves external incentives such as money, praise, or prizes, which activate reward circuits but often depend on social context and tangible benefits. Understanding the psychological foundations of reward systems reveals that intrinsic motivation sustains long-term engagement, while extrinsic motivation can drive immediate behavior changes, highlighting the complementary roles of both in shaping human action.
Benefits of Intrinsic Rewards in Personal Growth
Intrinsic rewards foster personal growth by enhancing self-motivation, increasing engagement, and promoting long-term satisfaction. Unlike extrinsic rewards, which rely on external incentives such as money or recognition, intrinsic rewards stem from internal feelings of accomplishment and mastery. This internal drive encourages continuous learning, resilience, and a deeper sense of purpose in achieving personal goals.
Impact of Extrinsic Rewards on Performance
Extrinsic rewards, such as bonuses, promotions, and recognition, can significantly boost short-term performance by providing tangible incentives for achieving specific goals. However, overreliance on extrinsic rewards may undermine intrinsic motivation, reducing your long-term engagement and creativity in tasks. Balancing intrinsic and extrinsic rewards is crucial to sustain high performance and foster a deeper commitment to work.
Intrinsic Rewards in the Workplace
Intrinsic rewards in the workplace refer to the internal satisfaction and motivation employees experience from meaningful work, personal growth, and a sense of accomplishment. Unlike extrinsic rewards, such as bonuses or promotions, intrinsic rewards foster long-term engagement and creativity by aligning tasks with your values and passions. Prioritizing intrinsic rewards can enhance employee well-being, productivity, and retention by cultivating a fulfilling work environment.
Extrinsic Rewards and Employee Motivation
Extrinsic rewards, such as bonuses, promotions, and tangible incentives, play a crucial role in enhancing employee motivation by providing clear, measurable benefits tied to performance outcomes. These rewards can drive productivity and encourage goal-oriented behavior by linking effort directly to external recognition or compensation. Your organization can effectively motivate employees by strategically implementing extrinsic rewards that complement intrinsic motivations, fostering a balanced and engaging work environment.
Balancing Intrinsic and Extrinsic Rewards
Balancing intrinsic and extrinsic rewards is crucial for sustaining motivation and enhancing performance; intrinsic rewards, such as personal satisfaction and a sense of achievement, foster long-term engagement, while extrinsic rewards like bonuses and recognition provide immediate incentives. Research in behavioral psychology shows that overemphasis on extrinsic rewards can undermine intrinsic motivation, leading to decreased creativity and persistence. Effective reward systems integrate both types, tailoring extrinsic incentives to support rather than replace intrinsic drivers, thereby maximizing overall motivation and productivity.
Case Studies: Reward Systems in Action
Case studies reveal that intrinsic rewards, such as personal growth and mastery, consistently enhance long-term motivation and job satisfaction, as seen in companies like Google promoting autonomy and creativity. Extrinsic rewards, including bonuses and promotions, drive immediate performance improvements but may undermine intrinsic motivation if overused, demonstrated by sales teams relying heavily on commission-based pay. Balanced reward systems combining intrinsic and extrinsic elements yield the most sustainable outcomes, as highlighted in research on employee engagement in firms like SAS Institute.
Best Practices for Effective Reward Strategies
Intrinsic reward comes from internal satisfaction and personal growth, making it essential to align tasks with Your values and interests. Extrinsic reward involves tangible incentives like bonuses or recognition, effectively motivating performance when clearly tied to specific goals. Combining both intrinsic and extrinsic rewards in a balanced strategy maximizes employee engagement, productivity, and overall satisfaction.
Infographic: Intrinsic Reward vs Extrinsic Reward
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com