Matriarchal families prioritize maternal authority and emphasize strong female leadership, fostering collaborative decision-making and emotional connectedness. Patriarchal families center on paternal authority, often highlighting hierarchical structure and traditional gender roles. Discover deeper insights into these family dynamics in this article.
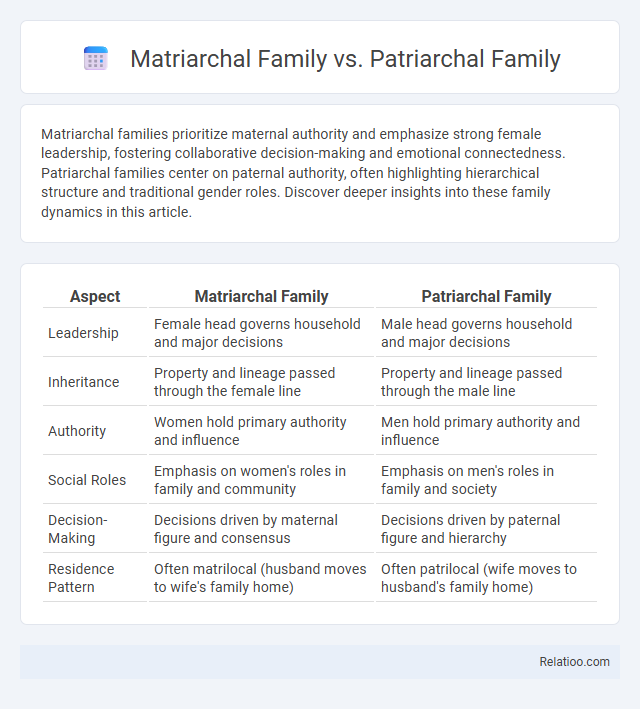
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Matriarchal Family | Patriarchal Family |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership | Female head governs household and major decisions | Male head governs household and major decisions |
| Inheritance | Property and lineage passed through the female line | Property and lineage passed through the male line |
| Authority | Women hold primary authority and influence | Men hold primary authority and influence |
| Social Roles | Emphasis on women's roles in family and community | Emphasis on men's roles in family and society |
| Decision-Making | Decisions driven by maternal figure and consensus | Decisions driven by paternal figure and hierarchy |
| Residence Pattern | Often matrilocal (husband moves to wife's family home) | Often patrilocal (wife moves to husband's family home) |
Defining Matriarchal and Patriarchal Family Structures
Matriarchal family structures center around female authority, where lineage, property, and decision-making predominantly follow the maternal line, emphasizing women's roles in leadership and social organization. Patriarchal family systems prioritize male dominance, with inheritance, authority, and family name typically passing through the male line, influencing societal norms and power dynamics. These contrasting family dynamics shape cultural traditions, gender roles, and social responsibilities within communities.
Historical Origins of Matriarchal and Patriarchal Systems
Matriarchal families, rooted in ancient societies where lineage and inheritance followed the mother's line, contrast sharply with patriarchal families, which emerged with the establishment of agricultural states emphasizing male dominance and property control. Historical origins reveal that matriarchal systems often centered on communal living and egalitarian roles, while patriarchal dynamics prioritized hierarchical structures and male authority in social, political, and economic spheres. Understanding your family's cultural background involves recognizing how these foundational systems influence contemporary gender roles and power distribution.
Key Characteristics of Matriarchal Families
Matriarchal families are characterized by female authority, with women holding central roles in decision-making, inheritance, and social organization, contrasting with patriarchal families where males dominate these functions. These families often emphasize communal support, matrilineal descent, and nurturing roles that foster strong kinship bonds and cooperative child-rearing. Power dynamics in matriarchal families prioritize female leadership and egalitarian social structures, influencing cultural norms and family cohesion significantly.
Key Characteristics of Patriarchal Families
Patriarchal families are characterized by male leadership, where the father or eldest male holds authority over household decisions and property. These families often emphasize traditional gender roles, with men as primary breadwinners and women managing domestic duties. Your understanding of family dynamics deepens by recognizing how power distribution influences communication and role expectations within patriarchal structures.
Social Roles and Gender Dynamics
Matriarchal families center social roles around female authority, emphasizing women's leadership in decision-making, property inheritance, and family governance, often fostering gender equity and cooperative responsibilities. Patriarchal families allocate social roles predominantly to men, establishing male dominance in power structures, control of resources, and lineage continuity, which typically reinforces traditional gender hierarchies and disparities. Dynamics in these family systems influence gender socialization, impacting behavioral expectations, interpersonal relationships, and societal status assigned to each gender in broader cultural contexts.
Cultural Examples Around the World
Matriarchal family structures, such as the Mosuo in China, emphasize female leadership and lineage, contrasting sharply with patriarchal families like those in traditional Saudi Arabian societies where male authority and inheritance dominate. Dynamics within these cultural models affect social roles, inheritance patterns, and decision-making processes, with matriarchal families often prioritizing communal support and patriarchal systems reinforcing hierarchical male control. These contrasting familial frameworks reveal how deeply cultural heritage shapes gender roles and power distribution across global societies.
Effects on Child Rearing and Education
Matriarchal families often promote collaborative decision-making and emotional openness, which can foster secure attachment and creativity in your child's education. Patriarchal families might emphasize discipline and hierarchical authority, potentially leading to structured learning environments but limiting emotional expression. Understanding these dynamics helps tailor child-rearing techniques that balance authority with nurturing, optimizing developmental and educational outcomes.
Economic Impacts within Family Systems
Matriarchal families often centralize economic decision-making around women, leading to diversified income strategies and enhanced resource allocation that prioritize collective well-being. Patriarchal families typically concentrate financial control with male heads, which can limit economic mobility and affect investment in education or health for other members. Understanding your family's structural dynamics helps optimize financial planning and fosters equitable economic contributions within household systems.
Power Dynamics and Decision-Making Processes
Matriarchal families centralize power and decision-making authority primarily with female members, often emphasizing collaborative and nurturing leadership styles. Patriarchal families concentrate control in the hands of male figures, reinforcing hierarchical structures and traditional authority in major decisions. The power dynamics in these family systems significantly influence communication patterns, resource distribution, and conflict resolution strategies within the household.
Modern Shifts and Future Trends
Modern shifts in family dynamics reflect a move away from traditional structures like matriarchal and patriarchal families toward more egalitarian models emphasizing shared decision-making and emotional support. Research highlights increasing recognition of diverse family roles regardless of gender, impacting how authority and responsibilities are distributed within households. Your understanding of these evolving trends can help navigate and adapt to the future landscape where flexible family dynamics foster inclusivity and resilience.
Infographic: Matriarchal Family vs Patriarchal Family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com