Authoritarian relationships are characterized by strict control and limited emotional exchange, while traditional relationships emphasize defined roles and mutual respect within cultural norms. Discover the key differences and impacts of Authoritarian versus Traditional relationships in this article.
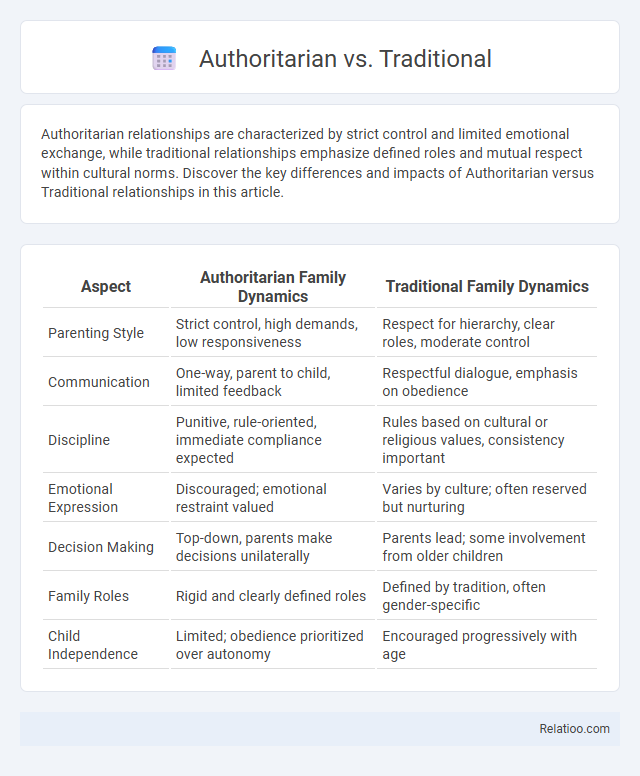
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Authoritarian Family Dynamics | Traditional Family Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Parenting Style | Strict control, high demands, low responsiveness | Respect for hierarchy, clear roles, moderate control |
| Communication | One-way, parent to child, limited feedback | Respectful dialogue, emphasis on obedience |
| Discipline | Punitive, rule-oriented, immediate compliance expected | Rules based on cultural or religious values, consistency important |
| Emotional Expression | Discouraged; emotional restraint valued | Varies by culture; often reserved but nurturing |
| Decision Making | Top-down, parents make decisions unilaterally | Parents lead; some involvement from older children |
| Family Roles | Rigid and clearly defined roles | Defined by tradition, often gender-specific |
| Child Independence | Limited; obedience prioritized over autonomy | Encouraged progressively with age |
Defining Authoritarian and Traditional Approaches
Authoritarian approaches emphasize centralized control, strict obedience, and limited personal freedom, often relying on top-down decision-making and enforcement of rules. Traditional approaches prioritize customs, cultural norms, and established practices, maintaining social order through inherited authority and long-standing conventions. Both approaches differ fundamentally in source of authority: authoritarianism hinges on power consolidation, whereas traditionalism rests on historical continuity.
Historical Background and Origins
Authoritarianism originated in early nineteenth-century Europe as a reaction against democratic revolutions and liberalism, emphasizing centralized power and limited political freedoms. Traditionalism traces its roots to pre-industrial societies, grounded in maintaining established customs, social hierarchies, and religious authorities dating back to medieval times. While authoritarianism seeks to control society through political institutions, traditionalism emphasizes cultural continuity and respect for inherited norms.
Key Characteristics of Authoritarian Systems
Authoritarian systems centralize political power in a single authority or ruling party, limiting political pluralism and suppressing dissent through legal or extralegal means. Key characteristics include restricted civil liberties, controlled media, and limited political competition, often maintained by coercive institutions like the military or secret police. Unlike traditional systems that rely on customs and hereditary rule, authoritarian regimes emphasize centralized control, modern bureaucratic structures, and often use propaganda to legitimize their authority.
Core Principles of Traditional Practices
Traditional practices emphasize preserving cultural heritage, social norms, and established rituals rooted in historical continuity. These core principles prioritize community cohesion, respect for authority derived from long-standing customs, and gradual change through consensus. Your understanding of traditional frameworks highlights stability and the transmission of values across generations.
Social Structures: Authority and Hierarchies
Authoritarian social structures feature centralized authority with strict hierarchies where power flows top-down, limiting individual autonomy. Traditional systems emphasize established customs and kinship, maintaining social order through inherited roles and community consensus rather than formal authority. Unlike authoritarian regimes, authoritarian traditional structures blend rigid control with deep-rooted cultural norms, reinforcing hierarchy through both power and tradition.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Authoritarian decision-making centralizes authority in a single leader or small group, enabling swift, unilateral choices often based on strict control and top-down directives. Traditional decision-making relies on established customs, cultural norms, and long-standing practices, typically involving consensus or the influence of elders and community leaders. Authoritative decision-making balances firm guidance with input from others, incorporating expert advice and clear goals while maintaining control over final decisions.
Impact on Individual Freedom and Expression
Authoritarian systems heavily restrict individual freedom and expression by enforcing strict obedience to centralized power, limiting personal autonomy and dissent. Traditional systems prioritize established customs and social norms, which may constrain expression but often allow some community-based freedoms within cultural boundaries. Your ability to express individuality is most suppressed under authoritarian regimes, whereas traditional frameworks provide a moderated balance between social order and personal liberty.
Cultural and Societal Implications
Authoritarian regimes impose strict control over societal behaviors and cultural expressions, often suppressing diversity and enforcing conformity to maintain power. Traditional societies emphasize cultural heritage and social norms passed down through generations, fostering community cohesion but sometimes resisting modernization. The blend of authoritarian and traditional elements can lead to the preservation of cultural identity while limiting individual freedoms and societal innovation.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies reveal that authoritarian regimes, such as North Korea, maintain strict centralized control with limited political freedoms, while traditional monarchies like Saudi Arabia blend cultural heritage with autocratic governance. In contrast, authoritarian populist governments, exemplified by Hungary under Viktor Orban, combine strongman tactics with nationalist rhetoric to consolidate power. These real-world examples illustrate how varying blends of authoritarian and traditional elements shape governance and societal structures.
Future Trends and Evolving Dynamics
Future trends in governance indicate a shifting balance between authoritarian, traditional, and authoritarian regimes, driven by technological advancements, changing socio-political dynamics, and global power realignments. The rise of digital surveillance and AI-powered control mechanisms strengthens authoritarian systems, while traditional governance faces pressures from modernization and demands for increased transparency. Evolving dynamics highlight hybrid models blending authoritarian control with selective traditional elements to maintain stability amidst growing calls for reform and citizen engagement.
Infographic: Authoritarian vs Traditional
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com