Extended family includes grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins, while immediate family consists of parents and siblings. Discover the unique dynamics and benefits of each family type in this article.
Table of Comparison
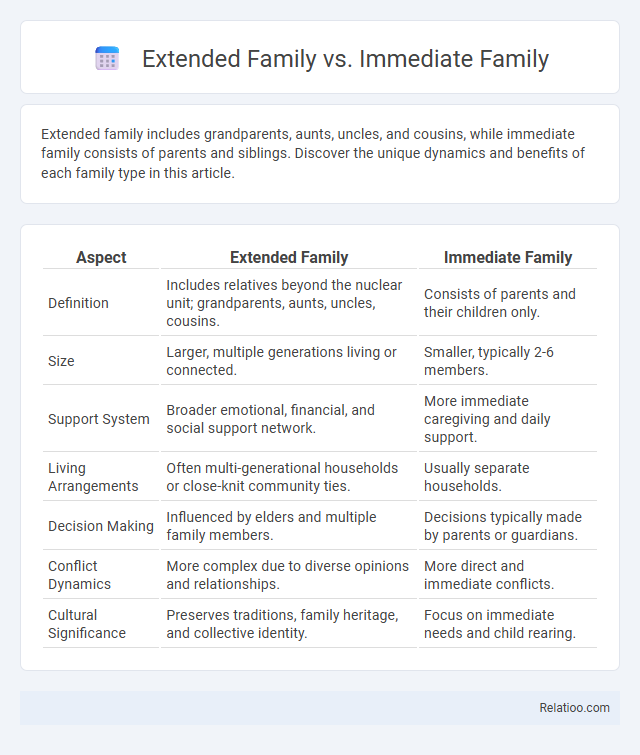
| Aspect | Extended Family | Immediate Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Includes relatives beyond the nuclear unit; grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins. | Consists of parents and their children only. |
| Size | Larger, multiple generations living or connected. | Smaller, typically 2-6 members. |
| Support System | Broader emotional, financial, and social support network. | More immediate caregiving and daily support. |
| Living Arrangements | Often multi-generational households or close-knit community ties. | Usually separate households. |
| Decision Making | Influenced by elders and multiple family members. | Decisions typically made by parents or guardians. |
| Conflict Dynamics | More complex due to diverse opinions and relationships. | More direct and immediate conflicts. |
| Cultural Significance | Preserves traditions, family heritage, and collective identity. | Focus on immediate needs and child rearing. |
Understanding Immediate Family
Immediate family consists of a person's closest relatives, typically including parents, siblings, and children, forming the core social unit for support and legal considerations. Unlike extended family, which includes grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins, immediate family plays a crucial role in daily life, emotional bonds, and decision-making processes. Understanding immediate family dynamics is essential for matters such as inheritance rights, healthcare decisions, and family law where legal definitions prioritize these direct relationships.
Defining Extended Family
Extended family includes relatives beyond your immediate family--such as grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins--who share a common ancestry or household ties. This broader kinship network differs from the immediate family, which typically consists of parents and their children living under one roof. Customary definitions of family vary across cultures, but recognizing your extended family often reflects deep-rooted social bonds and collective support systems.
Key Differences Between Immediate and Extended Family
Immediate family typically includes your closest relatives such as parents, siblings, and children, forming the core household unit. Extended family expands beyond this nucleus to include grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins, and other relatives, often linked by broader social and cultural ties. Understanding the key differences between immediate and extended family can help you navigate relationships and responsibilities more effectively within your family's structure.
Roles and Responsibilities in Immediate Families
Immediate families typically consist of parents and their children, where roles center on caregiving, financial support, and emotional nurturing to ensure individual growth and wellbeing. Parents hold primary responsibilities such as providing education, healthcare, and moral guidance, while children are generally expected to contribute by learning, helping with household tasks, and respecting family rules. Unlike extended families or custom family structures, immediate families emphasize direct and daily interactions that shape behavioral development and social stability.
Extended Family’s Influence on Cultural Traditions
Extended family plays a crucial role in preserving and transmitting cultural traditions through multi-generational interactions and shared rituals. This broader familial network strengthens cultural identity by incorporating diverse experiences, stories, and practices beyond the immediate family unit. The influence of the extended family fosters continuity of heritage, customs, and social values across communities.
Emotional Support Systems: Immediate vs Extended
Immediate family provides a core emotional support system through daily interactions and close-knit bonds, fostering a reliable environment for personal growth and well-being. Extended family offers a broader network of support, bringing diverse perspectives, traditions, and additional resources that enhance resilience during challenging times. Understanding your unique emotional needs helps balance the intimacy of immediate family ties with the expansive support of extended relatives to strengthen your overall support system.
Financial Dynamics in Different Family Structures
Understanding financial dynamics in extended family, immediate family, and custom family structures reveals distinct responsibilities and resource-sharing patterns. Extended families often pool income and expenses across multiple generations, providing a broader support network but requiring complex budgeting and financial negotiation. Your financial planning within immediate families prioritizes direct expenses like housing and education, while custom family setups may blend these approaches to suit unique cultural or personal financial arrangements.
Impact on Child Development and Socialization
Extended family provides a rich network of support and diverse role models that enhance a child's social skills and emotional security, fostering strong community ties and resilience. Immediate families often offer focused attention and consistent parenting styles, which contribute to stable attachment and clear behavioral expectations for Your child. Custom family arrangements influence development by blending diverse cultural practices and social norms, promoting adaptability and a broader understanding of social roles.
Modern Trends in Family Structures
Modern trends in family structures show a shift from traditional extended family units towards smaller immediate families and diverse custom arrangements tailored to individual needs. You may find that blended families, cohabitation without marriage, and chosen families reflect changing social values and economic factors influencing household composition. These evolving patterns highlight flexibility in defining family beyond biological ties, emphasizing support systems that fit contemporary lifestyles.
Choosing the Right Family Support System
Choosing the right family support system involves understanding the distinctions between extended family, immediate family, and custom family structures. Extended families include a wider network of relatives like grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins, providing diverse emotional and practical support. Your choice depends on where you find the most consistent, trustworthy, and culturally aligned support to meet your personal and social needs.
Infographic: Extended Family vs Immediate Family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com