Connected relationships foster emotional intimacy and mutual understanding, while separate relationships prioritize individual independence and personal space. Discover how balancing connection and separation impacts relational satisfaction and growth in this article.
Table of Comparison
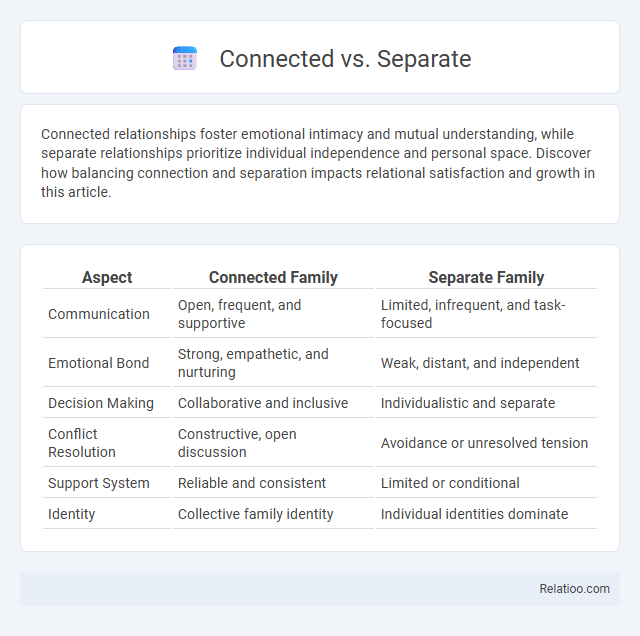
| Aspect | Connected Family | Separate Family |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Open, frequent, and supportive | Limited, infrequent, and task-focused |
| Emotional Bond | Strong, empathetic, and nurturing | Weak, distant, and independent |
| Decision Making | Collaborative and inclusive | Individualistic and separate |
| Conflict Resolution | Constructive, open discussion | Avoidance or unresolved tension |
| Support System | Reliable and consistent | Limited or conditional |
| Identity | Collective family identity | Individual identities dominate |
Understanding Connected and Separate Thinking
Connected thinking integrates ideas by recognizing relationships and patterns, enhancing comprehension and creativity, while separate thinking isolates concepts for detailed analysis and clarity. Your ability to balance connected and separate thinking improves problem-solving by combining holistic insight with focused evaluation. Mastering the distinction between these cognitive approaches strengthens critical thinking and decision-making skills.
Key Differences Between Connected and Separate Approaches
Connected approaches integrate components or systems to work seamlessly together, enhancing data flow and user experience, while separate approaches maintain distinct, independent units that minimize interdependence and increase modularity. You benefit from connected systems through improved efficiency and real-time coordination, whereas separate systems provide greater control and easier troubleshooting due to isolated functionalities. Understanding the distinction helps optimize your design strategy based on scalability, maintenance, and collaboration needs.
Psychological Foundations of Connected vs Separate Thinking
Connected thinking involves perceiving relationships and patterns within information, fostering holistic understanding. Separate thinking emphasizes analyzing components independently, promoting detail-focused and analytical cognition. Psychological foundations suggest connected thinking aligns with holistic cognitive styles prevalent in collectivist cultures, whereas separate thinking corresponds to analytic cognitive styles common in individualist societies, influencing problem-solving and reasoning approaches.
Real-World Examples: Connected and Separate in Action
Connected systems in smart homes integrate devices like thermostats, lighting, and security cameras, enabling seamless automation and centralized control, enhancing user convenience and energy efficiency. Separate systems, such as standalone kitchen appliances or individual entertainment gadgets, operate independently without data sharing or coordinated functionality. Cohesion in connected systems ensures components work harmoniously towards a common goal, exemplified by smart irrigation systems using weather data and soil sensors to optimize watering schedules.
Advantages of Connected Thinking
Connected thinking enhances problem-solving by integrating diverse ideas and knowledge, fostering innovative solutions tailored to your unique challenges. It strengthens decision-making through recognizing patterns and relationships that separate thinking often overlooks. This approach also improves collaboration by creating shared understanding and aligning team goals more effectively.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Separate Thinking
Separate thinking enhances focused problem-solving by isolating ideas, which reduces cognitive overload and encourages deep analysis. However, this approach can limit creativity and holistic understanding by overlooking connections between concepts, leading to fragmented solutions. Balancing separate thinking with connected and cohesive strategies fosters innovation while maintaining clarity and structure in decision-making processes.
When to Use Connected vs Separate Approaches
Use connected approaches when tasks share strong interdependencies or require continuous data flow between components, enhancing real-time collaboration and system integration. Separate approaches suit modular systems where components operate independently, allowing scalability and easier maintenance without tight coupling. Cohesion guides the choice by emphasizing high relatedness within modules, ensuring connected designs foster unified functionality while separated designs isolate distinct responsibilities.
Impact on Decision-Making and Problem Solving
Connected information enhances your decision-making by providing a holistic view, allowing patterns and relationships to emerge for more accurate problem solving. Separate data points limit understanding, causing fragmented analysis that can lead to oversights and inefficient solutions. High cohesion within data sets streamlines cognitive processing, improving the clarity and speed of your decisions by grouping related elements logically.
Fostering Both Connected and Separate Thinking Skills
Fostering both connected and separate thinking skills enhances cognitive flexibility and problem-solving abilities by encouraging integration of ideas alongside independent analysis. Connected thinking involves synthesizing information to form coherent patterns, while separate thinking emphasizes distinguishing details and critical evaluation. Balancing these approaches within educational or organizational contexts promotes deeper understanding and innovation through strengthened cognitive cohesion.
Choosing the Right Thinking Style for Success
Connected thinking integrates diverse ideas and disciplines, fostering innovation through synergy and holistic problem-solving. Separate thinking emphasizes independent analysis and specialization, enhancing deep expertise and precision in decision-making. Choosing the right thinking style depends on the context; cohesive thinking blends both by maintaining focus and consistency while leveraging connections and specialization to achieve balanced and effective outcomes.
Infographic: Connected vs Separate
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com