Formal caregivers provide professional care services with training and certification, while informal caregivers offer unpaid, often familial, support in daily activities. Discover detailed comparisons and insights on their roles and challenges in this article.
Table of Comparison
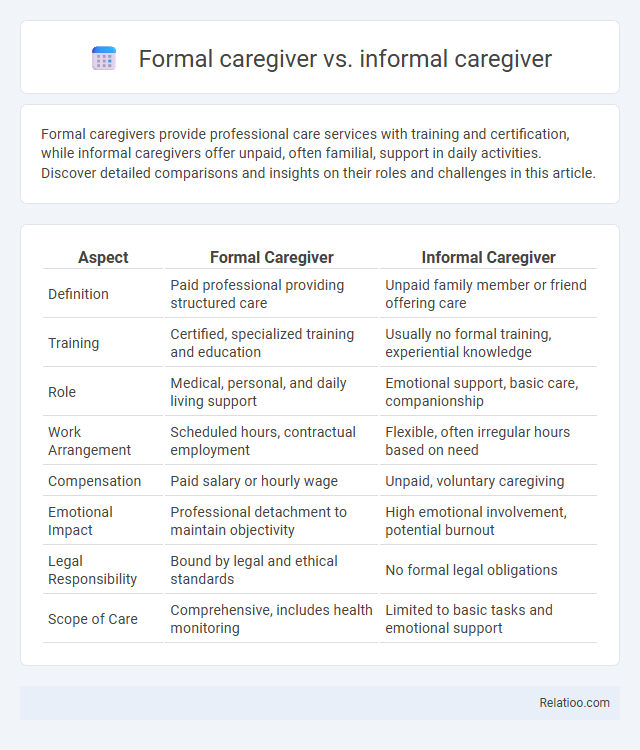
| Aspect | Formal Caregiver | Informal Caregiver |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Paid professional providing structured care | Unpaid family member or friend offering care |
| Training | Certified, specialized training and education | Usually no formal training, experiential knowledge |
| Role | Medical, personal, and daily living support | Emotional support, basic care, companionship |
| Work Arrangement | Scheduled hours, contractual employment | Flexible, often irregular hours based on need |
| Compensation | Paid salary or hourly wage | Unpaid, voluntary caregiving |
| Emotional Impact | Professional detachment to maintain objectivity | High emotional involvement, potential burnout |
| Legal Responsibility | Bound by legal and ethical standards | No formal legal obligations |
| Scope of Care | Comprehensive, includes health monitoring | Limited to basic tasks and emotional support |
Introduction to Formal and Informal Caregivers
Formal caregivers are trained professionals providing paid services such as nursing, therapy, or personal care in settings like hospitals or private homes. Informal caregivers, often family members or friends, offer unpaid, day-to-day assistance with activities like bathing, meal preparation, and medication management. Understanding the roles and differences between formal and informal caregivers helps you navigate the caregiving landscape and access appropriate support for your loved ones.
Defining Formal Caregivers
Formal caregivers are trained professionals who provide paid care services, including medical assistance, personal hygiene, and daily living support in settings like nursing homes or private residences. Informal caregivers, by contrast, are unpaid family members or friends offering emotional support and basic care without formal training. Caregiving encompasses both formal and informal roles, highlighting the spectrum of assistance essential for individuals requiring support.
Understanding Informal Caregivers
Informal caregivers, often family members or friends, provide unpaid, essential support to individuals with chronic illnesses or disabilities, acting as the backbone of home-based care. Unlike formal caregivers who receive professional training and compensation, informal caregivers rely on personal experience and emotional commitment, which can significantly impact their physical and mental well-being. Understanding informal caregivers helps you recognize their vital role in the caregiving ecosystem and the need for resources that support their unique challenges.
Key Differences Between Formal and Informal Caregiving
Formal caregiving involves professional caregivers who provide paid, structured support services such as medical care, therapy, and personal assistance, often under regulatory oversight. Informal caregiving is typically unpaid care given by family members or friends, focusing on emotional support and everyday tasks without formal training. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the appropriate type of care based on the level of expertise, cost, and personal involvement required.
Roles and Responsibilities in Care Provision
Formal caregivers are trained professionals, such as nurses or home health aides, responsible for providing medical care, administering medications, and monitoring health conditions in clinical or home settings. Informal caregivers, often family members or friends, assist with daily living activities, emotional support, and basic health management without formal training. Caregiving encompasses both formal and informal roles focused on maintaining the physical, emotional, and social well-being of individuals with chronic illnesses, disabilities, or age-related needs.
Benefits of Hiring Formal Caregivers
Hiring formal caregivers provides professional, trained assistance tailored to specific medical or personal care needs, ensuring reliable and consistent support. Formal caregivers often undergo background checks and certifications, offering peace of mind about Your loved one's safety and well-being. Their structured schedules and accountability contrast with informal caregivers, who may lack professional training and face challenges balancing caregiving with other responsibilities.
Advantages of Informal Caregiving
Informal caregiving offers the advantage of personalized and continuous support by family members or friends, fostering deep emotional bonds that enhance the care recipient's well-being. It often reduces financial strain since it typically involves unpaid care, making it accessible for long-term assistance in chronic illness or aging. This type of caregiving allows for flexible, culturally sensitive care that adapts quickly to the individual's evolving needs in a familiar environment.
Challenges Faced by Formal and Informal Caregivers
Formal caregivers face challenges such as managing complex medical tasks, navigating healthcare regulations, and balancing multiple client needs within institutional settings. Informal caregivers often struggle with emotional stress, lack of training, and limited access to resources while providing unpaid care to family members or friends. Understanding these distinct challenges can help you identify appropriate support systems and improve caregiving outcomes.
Support Systems for Caregivers
Formal caregivers provide professional support through structured healthcare services, offering consistent medical and personal care tailored to patients' needs. Informal caregivers, often family members or friends, deliver unpaid assistance, balancing emotional support with daily living tasks but may lack access to professional resources. Your caregiving journey benefits significantly from robust support systems that include community programs, respite care, and counseling services, ensuring both formal and informal caregivers maintain physical health and emotional well-being.
Choosing the Right Caregiver Type for Your Needs
Choosing the right caregiver type depends on your specific needs, budget, and the level of care required. Formal caregivers are trained professionals providing medical and personal support, ideal for complex health conditions, while informal caregivers, often family or friends, offer emotional support and basic assistance at no cost. Evaluating factors such as care complexity, reliability, and emotional connection helps ensure the most suitable caregiving arrangement for sustained well-being.
Infographic: Formal caregiver vs informal caregiver
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com