In-laws represent direct family connections through marriage, often requiring unique boundaries and communication styles, while extended family includes a broader network of relatives like cousins, aunts, and uncles with varying degrees of emotional closeness. Understanding the dynamics between in-laws and extended family can improve relationship harmony and social support; explore more insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
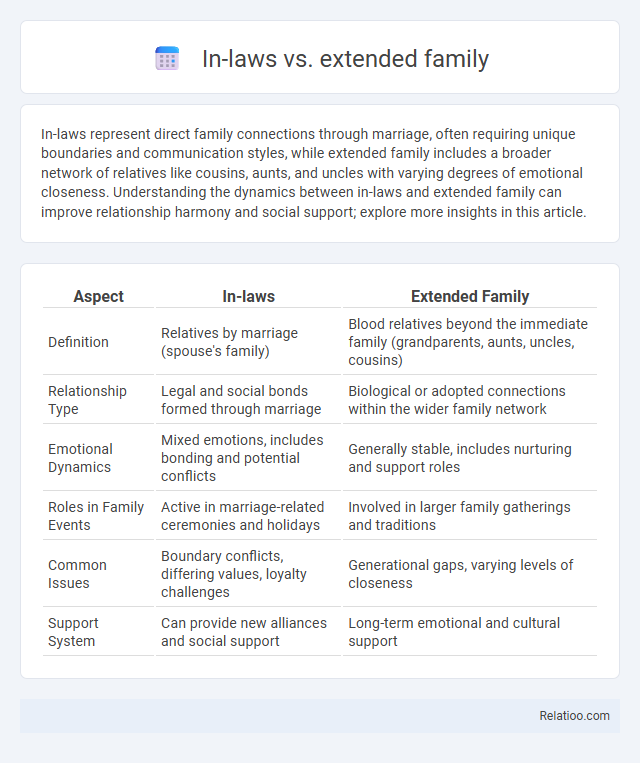
| Aspect | In-laws | Extended Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relatives by marriage (spouse's family) | Blood relatives beyond the immediate family (grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins) |
| Relationship Type | Legal and social bonds formed through marriage | Biological or adopted connections within the wider family network |
| Emotional Dynamics | Mixed emotions, includes bonding and potential conflicts | Generally stable, includes nurturing and support roles |
| Roles in Family Events | Active in marriage-related ceremonies and holidays | Involved in larger family gatherings and traditions |
| Common Issues | Boundary conflicts, differing values, loyalty challenges | Generational gaps, varying levels of closeness |
| Support System | Can provide new alliances and social support | Long-term emotional and cultural support |
Understanding In-Laws: Definition and Roles
In-laws refer specifically to the relatives acquired through marriage, such as your spouse's parents, siblings, and their families, distinct from the extended family which includes all relatives beyond the nuclear family. Understanding the roles of in-laws involves recognizing their influence on family dynamics, support systems, and cultural traditions within your married life. Your relationship with in-laws shapes communication patterns and contributes to building a cohesive family network beyond your immediate relatives.
Who Makes Up the Extended Family?
The extended family comprises relatives beyond your immediate family, including grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins, and in-laws. In-laws specifically refer to the family members related to you through marriage, such as your spouse's parents and siblings. Understanding who makes up your extended family helps clarify the distinctions between blood relatives and those connected by marriage, deepening your appreciation of family dynamics.
Key Differences: In-Laws vs Extended Family
In-laws refer specifically to relatives by marriage, such as a spouse's parents, siblings, and their direct family connections, whereas extended family includes a broader network of relatives like cousins, aunts, uncles, and grandparents beyond the immediate family. The key difference lies in the nature of relationship origins: in-laws are connected through marriage bonds, while extended family encompasses blood relations and can include several generations. Understanding this distinction is essential for clarifying social roles, inheritance rights, and familial responsibilities within diverse cultural contexts.
Evolution of Family Structures in Modern Society
The evolution of family structures in modern society reflects a shift from traditional in-laws and extended family networks to more fluid and diverse arrangements. Your relationships with in-laws often intertwine with broader extended family dynamics, shaped by cultural, social, and geographic factors. Understanding these changes highlights how individuals balance maintaining close family ties while adapting to contemporary lifestyles.
Cultural Perspectives on In-Laws and Extended Families
Cultural perspectives on in-laws and extended families vary significantly across societies, with many emphasizing the role of in-laws in maintaining family unity and social obligations. In collectivist cultures, extended family networks, including in-laws, are integral for emotional support, communal decision-making, and resource sharing, often living in multigenerational households. Contrastingly, individualistic cultures may prioritize nuclear family autonomy, viewing in-laws as peripheral, which influences interaction patterns and the degree of involvement in family matters.
Common Sources of Tension and Harmony
In-laws often experience tension with your immediate family due to differing traditions and expectations, while extended family may create challenges through varied communication styles and unresolved past conflicts. Harmony can arise from shared celebrations, mutual respect, and open dialogue that bridges generational or cultural gaps. Understanding these dynamics fosters stronger relationships and reduces friction in blended family environments.
In-Laws and Extended Family Dynamics in Marriage
In-laws and extended family dynamics significantly influence marriage stability and satisfaction, as spouses often navigate relationships with parents, siblings, and other relatives. Understanding boundaries and fostering mutual respect within in-law interactions enhances communication and reduces conflict between couples and their extended families. Effective management of these dynamics promotes emotional support networks critical for marital resilience and long-term harmony.
Setting Boundaries: Healthy Family Relationships
Setting boundaries with in-laws, extended family, and in-law members is crucial for maintaining healthy family relationships and your emotional well-being. Establish clear, respectful limits on communication, involvement in personal decisions, and physical space to prevent misunderstandings and conflicts. Respecting these boundaries encourages mutual respect, reduces tension, and fosters a balanced connection among family members.
Navigating Holidays and Family Gatherings
Navigating holidays and family gatherings can be challenging when balancing relationships with your in-laws, extended family, and in-law dynamics. Understanding the distinct roles and expectations within each group helps you create harmonious interactions and reduce potential conflicts during celebrations. Prioritizing open communication and respect for traditions strengthens bonds and ensures meaningful experiences with your loved ones.
Building Stronger Bonds: Tips for Positive Interactions
Building stronger bonds with your in-laws and extended family requires understanding each group's unique dynamics and showing genuine interest in their lives. Respecting boundaries and practicing open, empathetic communication fosters trust and warmth, which are key to positive interactions. Prioritizing quality time and shared experiences can transform relationships, making your extended family connections more meaningful and supportive.
Infographic: In-laws vs Extended Family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com